Kirchhoff's Laws | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What are Kirchhoff's law? |

|
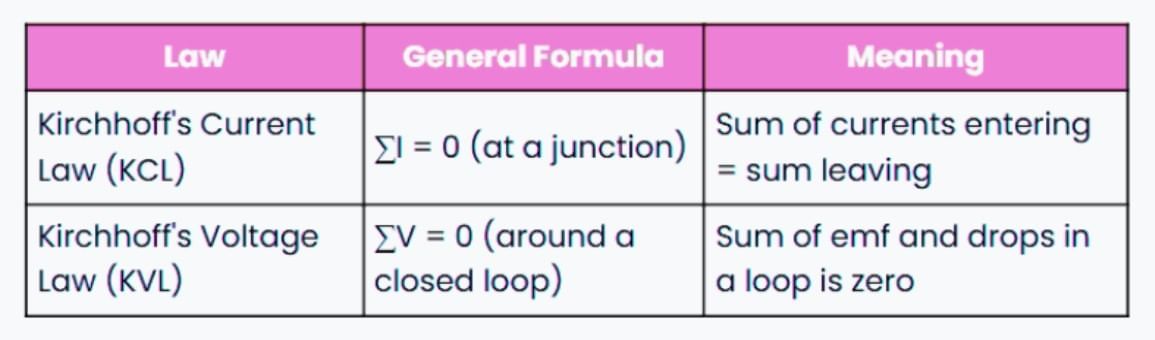
| Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) |

|
| Application of KCL in Circuits |

|
| Kirchhoff's Voltage Law OR Loop Law |

|
| Solved Examples |

|
In this document, we'll explore Kirchhoff's laws, which are two sets of rules about the flow of electricity in circuits. These laws talk about current (the flow of electricity) and potential difference (or voltage) in electrical circuits. They were first explained by a German physicist named Gustav Kirchhoff in 1845. Kirchhoff's laws build upon the ideas of Georg Ohm and came before the work of James Clerk Maxwell. These laws are widely used in electrical engineering and are sometimes simply called Kirchhoff's rules. They are crucial for analyzing networks of electrical components and can be applied to understand how circuits behave over time and at different frequencies.
What are Kirchhoff's law?
Kirchhoff's Laws are two fundamental principles used in the analysis of electrical circuits. These laws are crucial for understanding and solving complex circuits.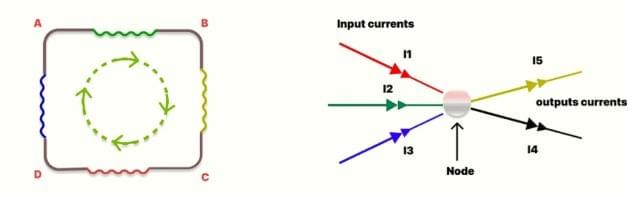 Kirchhoff's Law
Kirchhoff's Law
Two fundamental principles for analyzing electrical circuits:
Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL)
The total current entering a junction (or node) is equal to the total current leaving the junction.
In other words, the algebraic sum of the voltage drops and rises around a closed loop is always zero. This law is based on the conservation of charge, meaning that charge cannot be created or destroyed. In a junction, the sum of currents flowing into the node equals the sum of currents flowing out of the node. Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
I1 + I2 + I3 = I4 + I5
where I1, I2, and I3 are the currents entering the node, and I4 and I5 are the currents leaving the node.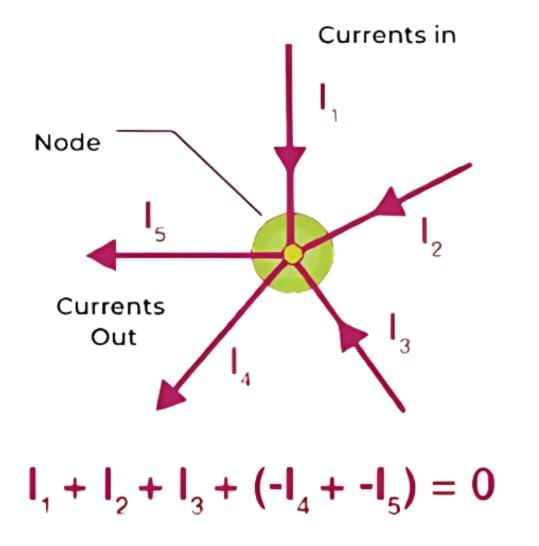
Application of KCL in Circuits
Writing an Equation for Junction/ Node in the Circuit:
Consider a point or junction O in an electrical circuit. Let I1, and I3 be the currents entering point O and I2, I4, and I5 be the current leaving point O.
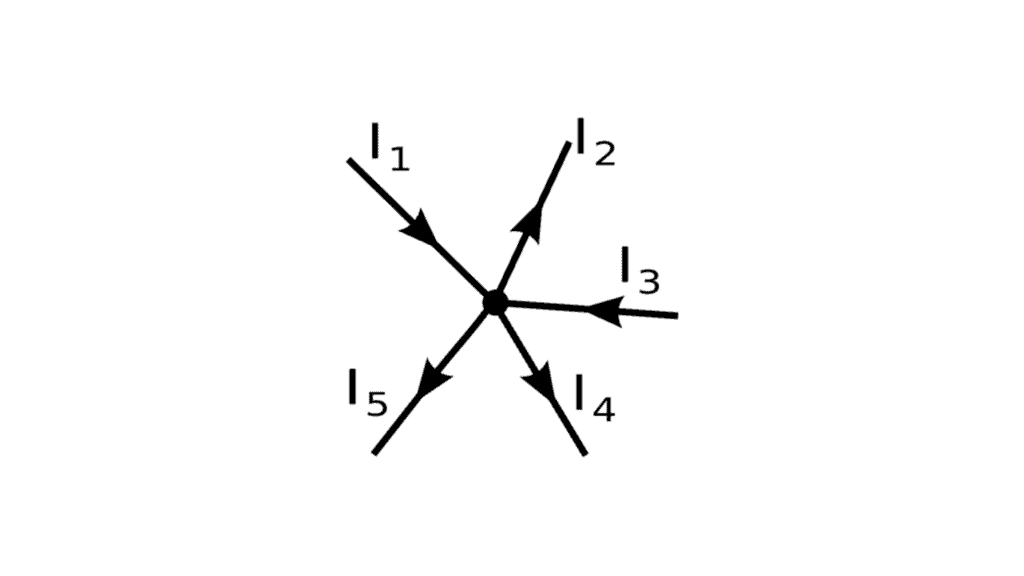
Then, according to KCL, the algebraic sum of the current entering and leaving the junction is zero. So apply KCL to junction O.
According to Kirchhoff’s first law,
I1 + I3 = I2 + I4 + I5
The above equation can also be written as,
I1 + I3 + (–I2 ) + (–I4 ) + (–I5 ) = 0; I1 + I3 – I2 – I4 – I5 = 0 (i.e. ∑Ik=0 )
Kirchhoff's Voltage Law OR Loop Law
The sum of the electrical potential differences (voltage) around any closed circuit loop is zero.
This law is based on the conservation of energy. It means that the total amount of energy gained per unit charge is equal to the total amount of energy lost per unit charge around a loop. Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
V1 + V + V3 = 0
where V1, V2 , and V3 are the voltages around a closed loop.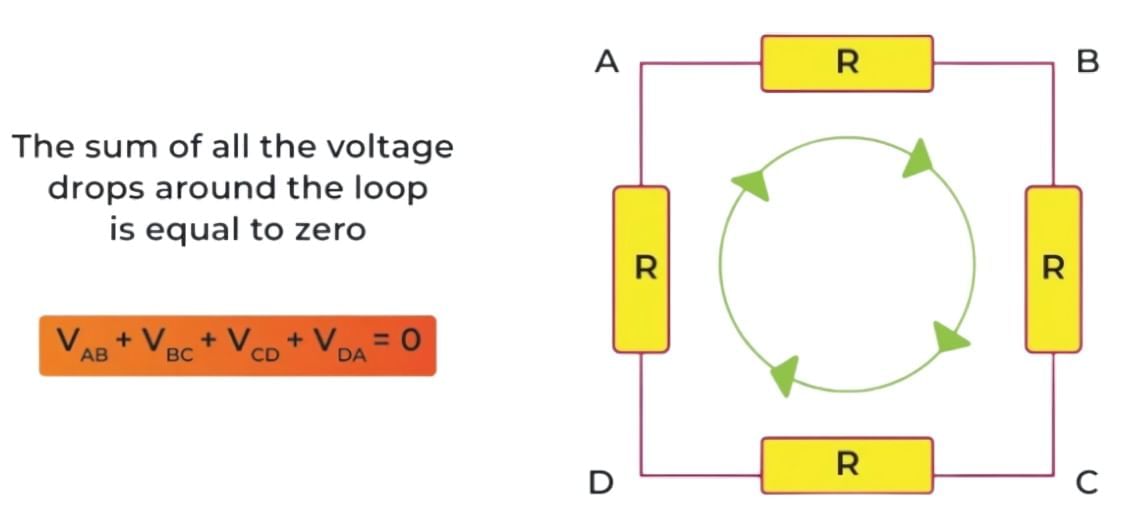
- The KVL reflects that electric force is conservative, the work done by a conservative force on a charge taken around a closed path is zero.
- We can move clockwise or anticlockwise, it will make no difference because the overall sum of the potential difference is zero.
- We can start from any point on the loop, we just have to finish at the same point.
- An ideal battery is modeled by an independent voltage source of emf E and an internal resistance r as shown in Figure. A real battery always absorbs power when there is a current through it, thereby offering resistance to the flow of current.
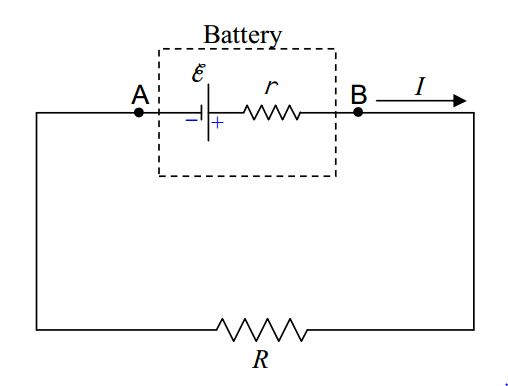
Sign Conventions for Circuit Analysis
Before moving on to the statement of Kirchhoff's law, there are state some sign conventions to be followed in circuit analysis :
(a) The direction of conventional current is from high potential to low potential terminal.
(b) If we traverse from point A to B, there is a drop of potential; similarly, from B to A, there is a gain of potential. If a source of emf is traversed from negative to positive terminal, the change in potential is +E.
(c) While discharging, current is drawn from the battery, and the current comes out from the positive terminal and enters the negative terminal, while charging the battery, the current is forced from the positive terminal of the battery to the negative terminal. Irrespective of the direction of current through a battery, the sign convention mentioned above holds.
(d) The positive plate of a capacitor is at high potential and the negative plate is at low potential. If we traverse a capacitor from a positive plate to a negative plate, the change in potential is -Q/C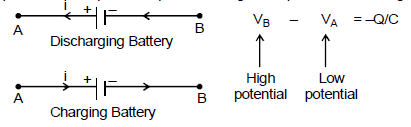
- If we traverse a resistor in the direction of current, the change in potential is -IR.
- If we traverse a resistor in the direction opposite to the direction of the current, the change in potential is +IR.
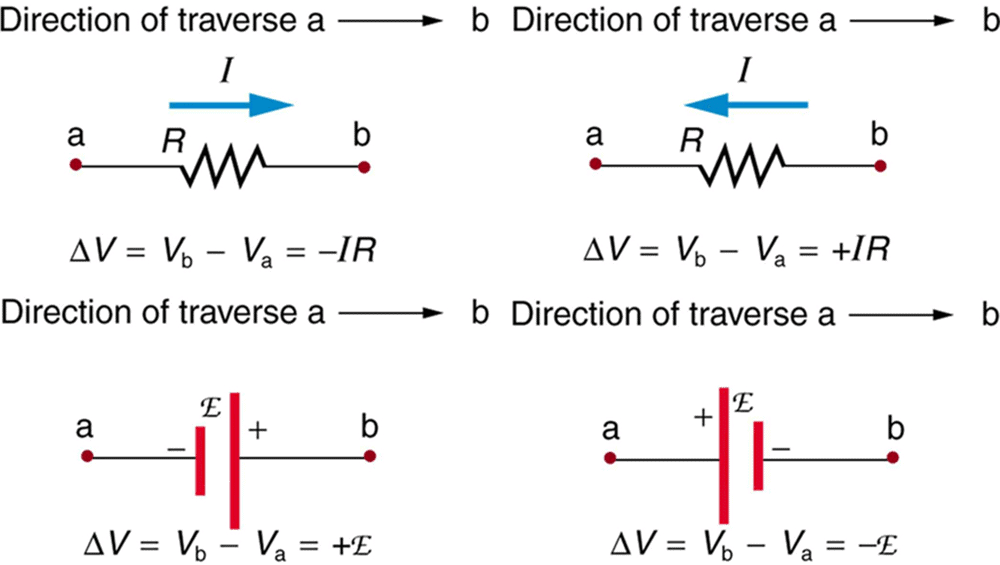
- The positive terminal of the source of emf is at high potential and the negative terminal is at low potential. If we traverse a source of emf from the positive terminal to the negative terminal, the change in potential is -E.
- If a capacitor is traversed from a negative plate to a positive plate, the change in potential is Q/C
To summarise:
Solved Examples
Q1: 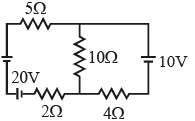
In the figure shown, the current in the 10 V battery is close to :
(a) 0.71 A from positive to negative terminal
(b) 0.42 A from positive to negative terminal
(c) 0.21 A from positive to negative terminal
(d) 0.36 A from negative to positive terminal
Ans: (c)
Sol: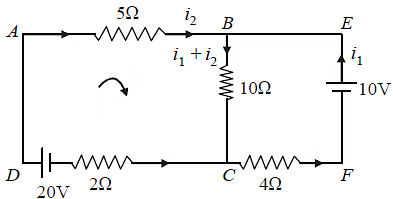
Using Kirchoff's loop law in loop ABCD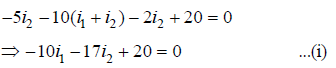
Using Kirchoff's loop law in loop BEFC
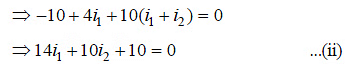
Multiplying equation (i) by 10, we have
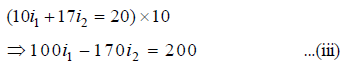
Multiplying equation (ii) by 17, we have
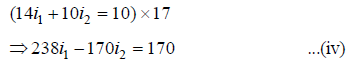
On solving equations (iii) and (iv), we get
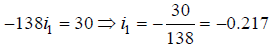
i1 is negative it means current flows from positive to negative terminal.
Q2: Four resistances 40 Ω, 60 Ω, 90 Ω and 110 Ω make the arms of a quadrilateral ABCD. Across AC is a battery of emf 40 V and internal resistance negligible. The potential difference across BD in V is __________.
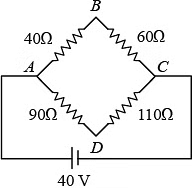
Sol:
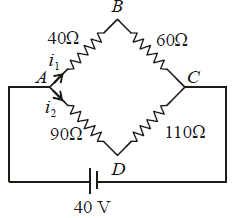
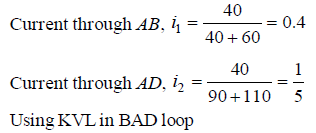
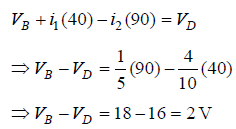
Q3: In the circuit shown, the current in the 1W resistor is: 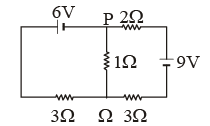
(a) 0.13 A, from Q to P
(b) 0.13 A, from P to Q
(c) 1.3 A from P to Q
(d) 0 A
Ans: (a)
Sol:
From KVL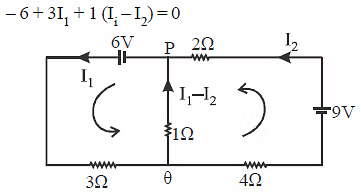
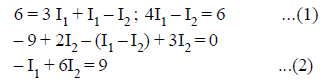
On solving (1) and (2)
I1 = 0.13A
Direction Q to P, since I1 > I2.
Q4: A 5V battery with an internal resistance of 2W and a 2V battery with an internal resistance of 1W are connected to a 10W resistor as shown in the figure. 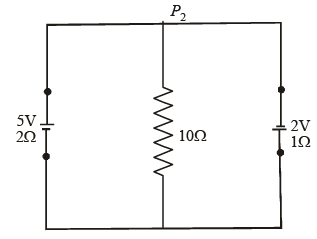
The current in the 10Ω resistor is
(a) 0.27 A P2 to P1
(b) 0.03 A P1 to P2
(c) 0.03 A P2 to P1
(d) 0.27 A P1 to P2
Ans: (c)
Sol: Applying Kirchoff’s second law in AB P2P1A, we get
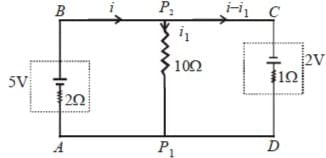
Again applying Kirchhoff's second law in P2 CDP1P2we get,
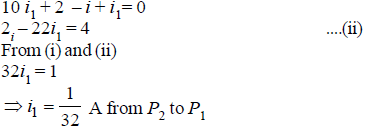
Q5: Calculate the current I3 in the circuit below:
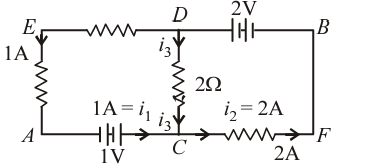
Sol:
At node or junction C, applying KCL:
Current entering at C=Current leaving from C
I1+I3=I2
1A+I3=2A
I3=2-1=1A
Q6: In the given circuit diagram, the currents, I1 = – 0.3 A, I4 = 0.8 A, and I5 = 0.4 A, are flowing as shown. The currents I2, I3 and I6, respectively, are:
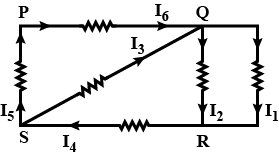
Sol: 
Q7: When the switch S, in the circuit shown, is closed then the value of current will be:
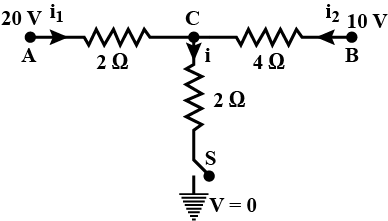
Sol:
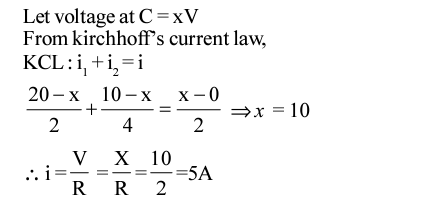
|
74 videos|314 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on Kirchhoff's Laws - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL)? |  |
| 2. How is Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) applied in circuits? |  |
| 3. What are some applications of KCL in circuits? |  |
| 4. Can you provide a solved example of Kirchhoff's Laws in a circuit? |  |
| 5. What are some frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to Kirchhoff's Laws in exams like JEE? |  |
















