Atomic Masses and Composition of Nucleus | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
Nucleus
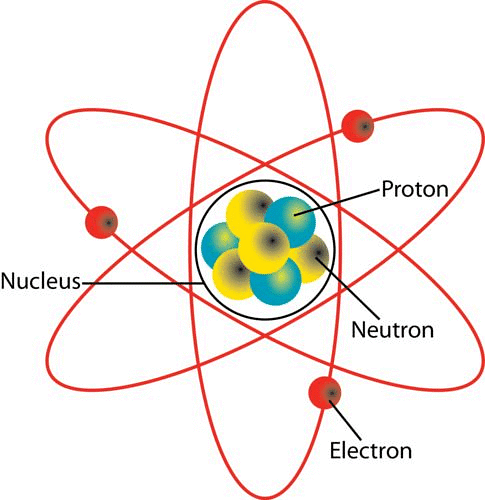
The entire positive charge and nearly the entire mass of atom is concentrated in a very small space called the nucleus of an atom.
 Atomic Nucleus
Atomic Nucleus
The nucleus consists of protons and neutrons. They are called nucleons.
Terms Related to Nucleus:
(i) Atomic Number: The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of the element is called atomic number (Z) of the element.
(ii) Mass Number: The total number of protons and neutrons present inside the nucleus of an atom of the element is called mass number (A) of the element.
(iii) Nuclear Size: The radius of the nucleus R ∝ A1/3
⇒ R = Ro A1/3
where, Ro = 1.1 * 10-15 m is an empirical constant.
(iv) Nuclear Density: Nuclear density is independent of mass number and therefore same for all nuclei.
ρ = mass of nucleus / volume of nucleus ⇒ ρ = 3m / 4π R3o
where, m = average mass of a nucleon.
(v) Atomic Mass Unit: It is defined as 1 / 12th the mass of carbon nucleus.
It is abbreviated as amu and often denoted by u. Thus
1 amu = 1.992678 * 10-26 / 12 kg
= 1.6 * 10-27 kg = 931 Me V
Isotopes:
The atoms of an element having same atomic number but different mass numbers are called isotopes.
e.g., 1H1, 1H2, 1H3 are isotopes of hydrogen.
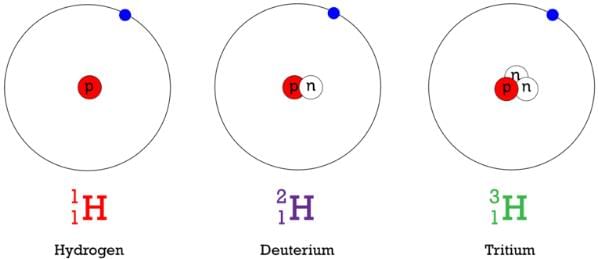 Fig: Isotopes of hydrogen
Fig: Isotopes of hydrogen
Isobars:
The atoms of different elements having same mass numbers but different atomic numbers, are called isobars.
e.g., 1H3, 2He3 and 10Na22, 10Ne22 are isobars.
Isotones:
The atoms of different elements having different atomic numbers and different mass numbers but having same number of neutrons, are called isotones.
e.g., 1H3, 2He4 and 6C14, 8O16 are isobars.
Isomers:
Atoms having the same mass number and the same atomic number but different radioactive properties are called isomers.
Nuclear Force:
The force acting inside the nucleus or acting between nucleons is called nuclear force.
Nuclear forces are the strongest forces in nature.
- It is a very short range attractive force.
- It is non-central. non-conservative force.
- It is neither gravitational nor electrostatic force.
- It is independent of charge.
- It is 100 times that of electrostatic force and 1038 times that of gravitational force.
According to the Yukawa, the nuclear force acts between the nucleon due to continuous exchange of meson particles.
Mass Defect:
The difference between the sum of masses of all nucleons (M) mass of the nucleus (m) is called mass defect.
Mass Defect (Δm) = M – m = [Zmp + (A – Z)mn – mn]
Nuclear Binding Energy:
The minimum energy required to separate the nucleons up to an infinite distance from the nucleus, is called nuclear binding energy.
Nuclear binding energy per nucleon = Nuclear binding energy / Total number of nucleons
Binding energy, Eb = [Zmp + (A – Z) mn – mN]c2
Packing Fraction (P):
p = (Exact nuclear mass) – (Mass number) / Mass number
= M – A / M
The larger the value of packing friction. greater is the stability of the nucleus.
[The nuclei containing even number of protons and even number of neutrons are most stable.
The nuclei containing odd number of protons and odd number of neutrons are most unstable.]
|
88 videos|421 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on Atomic Masses and Composition of Nucleus - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is the atomic mass of a nucleus? |  |
| 2. How is the composition of a nucleus determined? |  |
| 3. How do you calculate the atomic mass of an element using the composition of its nucleus? |  |
| 4. Why is the composition of a nucleus important in understanding the properties of an element? |  |
| 5. Can the composition of a nucleus change through nuclear reactions? |  |






















