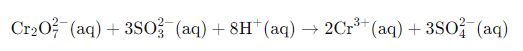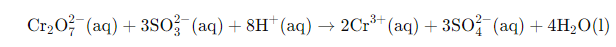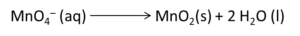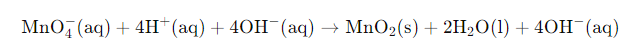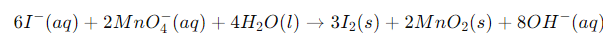Balancing Redox Equations | Chemistry Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Balancing of Redox Chemical Equations |

|
| Oxidation Number Method |

|
| Half Reaction Method |

|
| Solved Examples |

|
Balancing of Redox Chemical Equations
Every chemical equation must be balanced according to the law of conservation of mass. In a balanced chemical equation, the atoms of various species involved in the reactants and products must be equal in number.
Redox reaction can be balanced through
- Oxidation number method
- Half Reaction method
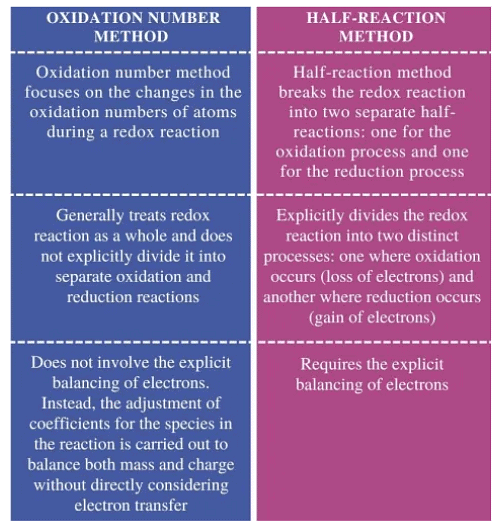 Difference between Oxidation Number Method & Half Reaction Method
Difference between Oxidation Number Method & Half Reaction Method
Oxidation Number Method
When writing equations for oxidation-reduction reactions, similar to other reactions, you need to know the compositions and formulas of the substances involved in the reaction and those that are produced.
Steps for balancing Redox Equations by Oxidation Number method
- Step 1: Begin by writing the unbalanced (skeletal) redox equation, including all known reactants and products.
- Step 2: Assign oxidation numbers to all atoms in the equation, placing them above each element's symbol.
- Step 3: Identify which elements have undergone a change in oxidation number. Generally, two elements are involved: one with an increase in oxidation number (reducing agent) and one with a decrease (oxidizing agent).
- Step 4: Determine the total increase or decrease in oxidation number for each element. If multiple atoms of the same element are involved, calculate the total oxidation change, then multiply this by the number of atoms that experienced the change.
- Step 5: To maintain balance, equate the total increase in oxidation numbers with the total decrease by adjusting the coefficients of the oxidizing and reducing agents on the reactant side.
- Step 6: Balance the remaining atoms in the equation, except for hydrogen and oxygen.
- Step 7: Balance hydrogen and oxygen:
Acidic Solution: If the reaction occurs in an acidic solution, add H⁺ ions to the side lacking hydrogen.
Basic solution: Add H₂O molecules to the side deficient in hydrogen and, at the same time, add an equal number of OH⁻ ions to the opposite side. - Step 8: Simplify the final equation by canceling out any identical species that appear on both sides of the equation.
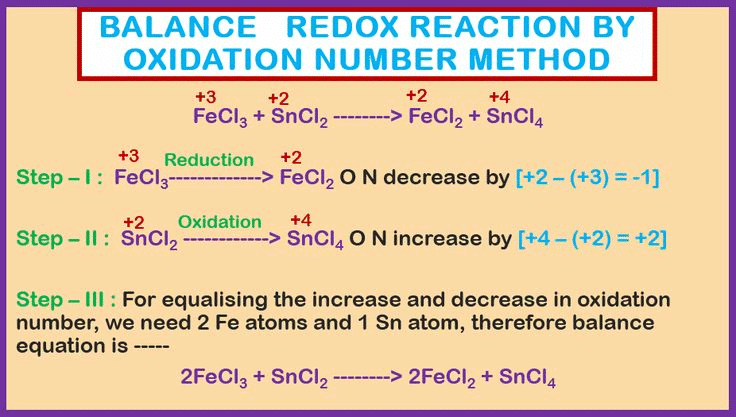
Let's understand it by the following example
Zn + HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
It involves the following steps.
Step I: Write the skeleton equation (if not given).
Zn + HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
Step II: Assign the oxidation number of each atom.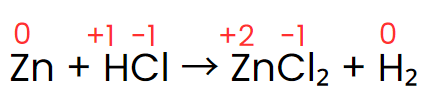
Step III: The oxidation number of zinc increases from 0 to +2, while hydrogen’s oxidation number decreases from +1 to 0. The oxidation number of chlorine, however, stays the same on both sides of the reaction. Thus, zinc acts as the reducing agent, and HCl serves as the oxidizing agent, as shown in the changes below.
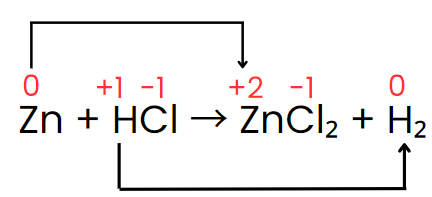 Step IV: The increase and decrease in oxidation number per atom can be indicated as:
Step IV: The increase and decrease in oxidation number per atom can be indicated as: 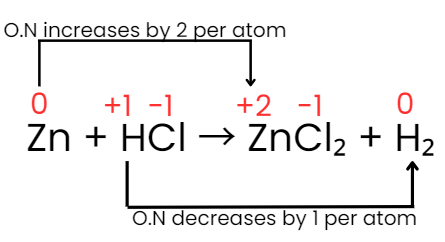
Step V: The increase in oxidation number of 2 per atom can be balanced with decrease in oxidation number of 1 per atom if Zn atoms are multiplied by 1 and HCl by 2. Consequently the equation will be:
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
Step VI: Balance all other atoms on both sides of the equation.
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
Half Reaction Method
In this approach, you balance each half of the equation separately and then combine them to create a balanced overall equation. This method of balancing was developed by Jette and Lamer in 1927.
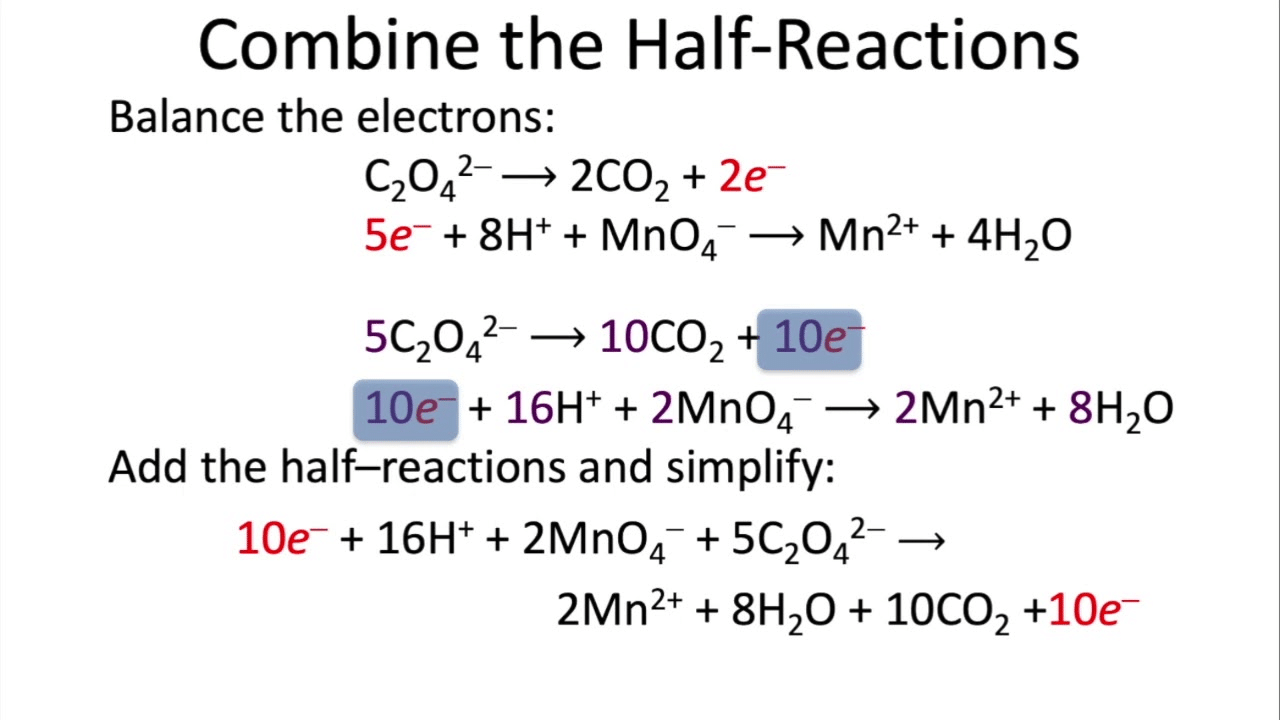
Steps for balancing a chemical equation using the ion-electron method (half-reaction method):
Step 1: Identify elements that have changed oxidation numbers, and select the oxidizing and reducing agents.
Step 2: Split the equation into two half-reactions: one for the oxidizing agent’s change and one for the reducing agent’s change.
Step 3: Balance each half-reaction by:
(i) Balancing all atoms except H and O.
(ii) Adjusting oxidation numbers by adding electrons to the necessary side.
(iii) Ensuring both sides have the same charge.
(iv) Adding water molecules to finalize the balance.
Step 4: Combine the two balanced half-reactions, multiplying as needed to equalize electrons between them.
Redox reactions can occur in acidic, basic, or neutral media. In acidic media, H⁺ ions appear in the equation; in basic media, OH⁻ ions are present; and in neutral media, neither H⁺ nor OH⁻ ions appear. Adjustments may be needed depending on the medium.
Let's understand this with an example:
Cu + HNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + NO + H2O
It involves the following steps:
Step I: Write the redox reaction in ionic form.
Cu + H+ + NO3– → Cu2+ + NO + H2O
Step II: Split the redox reaction into its oxidation half and reduction half-reaction.

Step III: Balance atoms of each half-reaction (except H and O) by using simple multiples.
Cu → Cu2+ and NO–3 → NO
(Except for H and O, all atoms are balanced)
Step IV: Balance H and O as
(i) For acidic and neutral solutions- Add the H2O molecule to the side deficient in oxygen and H+ to the side deficient in hydrogen.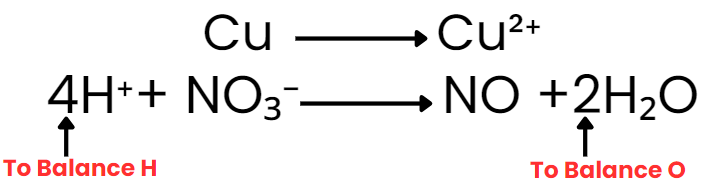 (ii) For alkaline solutions- For each excess of oxygen, add one water molecule to the same side and OH– ion to the other side to balance H.
(ii) For alkaline solutions- For each excess of oxygen, add one water molecule to the same side and OH– ion to the other side to balance H.
Step V: Add electrons to the side deficient in electrons.
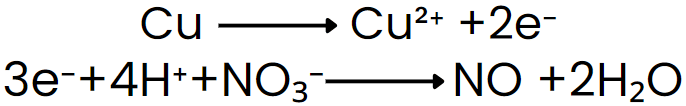 Step VI: Equalize the number of electrons in both reactions by multiplying a suitable number.
Step VI: Equalize the number of electrons in both reactions by multiplying a suitable number.
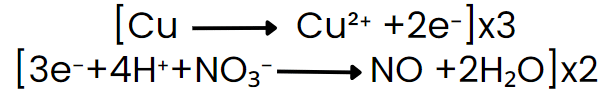 Step VII: Add the two balanced half-reactions and cancel common terms of opposite sides.
Step VII: Add the two balanced half-reactions and cancel common terms of opposite sides.
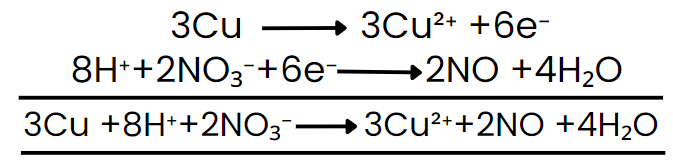 Step VIII: Convert the ionic reaction into molecular form by adding spectator ions.
Step VIII: Convert the ionic reaction into molecular form by adding spectator ions.
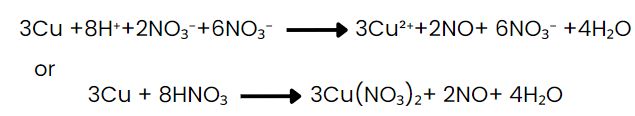
(Ions that are present in solution but do not take part in the redox reaction are omitted while writing the net ionic equation of a reaction and are known as spectator ions.)
Solved Examples
Example: Balance the following Reaction
VO2+ + MnO4¯ ---> V(OH)4+ + Mn2+
Solution:
1) Half reactions:
VO2+ ---> V(OH)4+
MnO4¯ ---> Mn2+2) Balance:
3H2O + VO2+ ---> V(OH)4+ + 2H+ + e¯
5e¯ + 8H+ + MnO4¯ ---> Mn2+ + 4H2O3) Equalize electrons:
15H2O + 5VO2+ ---> 5V(OH)4+ + 10H+ + 5e¯
5e¯ + 8H+ + MnO4¯ ---> Mn2+ + 4H2O4) Add:
11H2O + 5VO2+ + MnO4¯ ---> 5V(OH)4+ + Mn2+ + 2H+
Example: Balance the equation for the reaction of a stannous ion with pertechnetate in an acidic solution. Products are stannic ions, Sn4+, and technetium(IV), and Tc4+ ions.
Solution:
1) Net ionic:
TcO4¯ + Sn2+ ---> Tc4+ + Sn4+2) Half-reactions:
TcO4¯ ---> Tc4+
Sn2+ ---> Sn4+3) Balance:
3e¯ + 8H+ + TcO4¯ ---> Tc4+ + 4H2O
Sn2+ ---> Sn4++ 2e¯4) Equalize electrons:
6e¯ + 16H+ + 2TcO4¯ ---> 2Tc4+ + 8H2O
3Sn2+ ---> 3Sn4++ 6e¯5) Add:
16H+ + 2TcO4¯ + 3Sn2+ ---> 2Tc4+ + 3Sn4+ + 8H2O
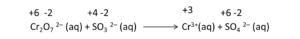
Example: Solve the net ionic equation where potassium dichromate(VI) (K2Cr2O7) reacts with sodium sulphite (Na2SO3) in an acidic medium to form sulphate ion and chromium(III) ion.
Solution:
Step 1-
The basic equation or the skeletal form of the reaction is
Step 2-
Correctly assign oxidation numbers to Cr and S
Therefore, from the reaction we can decipher that dichromate ion is the oxidant in the reaction and the sulphite ion is the reductant in the reaction
Step 3-
Calculation of the increase and the decrease in the oxidation number for making each side of the equation equal
Step 4-
We know from the equation, the reaction occurs in the acidic medium. Moreover, we can see that the ionic charges in both the sides of the equation are not same. Therefore, we will add 8H+ I order to make the ionic charges equal.
Step 5-
In the final step, we will calculate the required amount of water molecules and add it on the right side of the equation to make the equation a balanced redox reaction. In the given equation, we will need to add 4 water molecules on the right side to balance the equation.
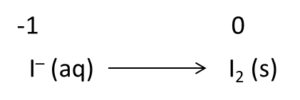
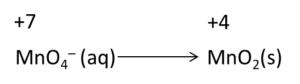
Example: Write the balanced redox equation by half-reaction method when Permanganate(VII) ion (MnO4) produces iodine molecule (I2) and manganese (IV) oxide (MnO2) in a basic medium.
Solution:
Step 1-
Firstly, we will write the base form of the equation
Step 2-
In this step, we will find the two half-reactions and write them
Oxidation Half
Reduction Half
Step 3-
We will balance the iodine atoms present in the oxidation half of the reaction. Therefore, the equation will become
Step 4-
We will balance the oxygen atoms in the reduction half of the reaction by the addition of two water molecules. Refer to the equation below
Now, we will balance the H atoms by the addition of four H+ ions on the left half of the reduction half-reaction.
We know that the reaction occurs in a basic medium. Thus, to balance four H+ ions, we need to add four OH– ions to each side of the equation.
Finally, we will interchange the H+ ions and OH– ions with the water molecule. The final equation of the fourth step will be
Step 5-
The charges on the two half-reactions are balanced
Finally, we have to equalize the electrons in the above reactions. Thus, we will multiply the oxidation half of the equation by 3 and the reduction half of the reaction by 2.
Step 6-
We have to determine the net reaction by the addition of two halves of the reaction and by the cancellation of electrons on each side.
Step 7-
Finally, we have to verify the equation in terms of the number of atoms and charges on both sides. Additionally, verification needs to be done about the equations written on both sides.
|
114 videos|263 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on Balancing Redox Equations - Chemistry Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the oxidation number method for balancing redox equations? |  |
| 2. How do you use the half-reaction method to balance redox equations? |  |
| 3. What are some common mistakes to avoid when balancing redox equations? |  |
| 4. Can you provide an example of a redox reaction and how to balance it using both methods? |  |
| 5. How are redox reactions relevant for NEET and other competitive exams? |  |