Classification of Organic Compounds | Chemistry Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
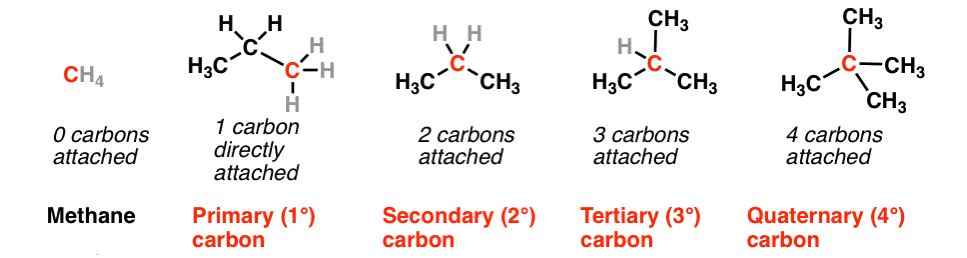
1. On the Basis of Number of Carbon atoms Attached
(i) Primary carbon atom When carbon atom is attached with one other carbon atom only, it is called primary or 1° carbon atom.
(ii) Secondary carbon atom When carbon atom is attached with two other carbon atoms, it is called secondary or 2°carbon atom.
(iii) Tertiary carbon atom When acarbon atom is attached with three other carbon atoms, it is called tertiary or 3° carbon atom.
(iv) Quaternary carbon atom When carbon atom is attached with four other carbon atoms, it is called quaternary or 4º carbon atom.
The reactivity order of carbon atoms is as follows 3° > 2° > 1°.
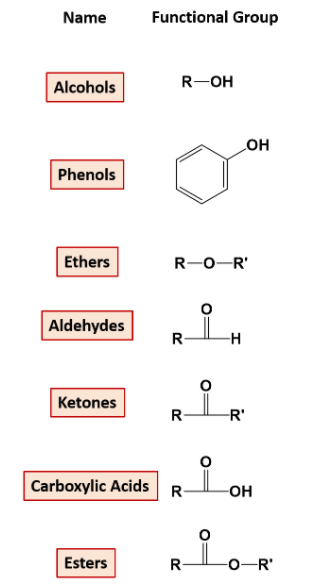
2. On the Basis of Functional Groups Attached:
Compounds with a particular functional group are given a particular name and are classified in one category. for example- functional group alcohol has an -OH attached to the carbon chain. The list of functional groups is below.
3. On the Basis of Position of Functional Group:
(i) α – carbon Carbon which is directly attached to the functional group.
(ii) β- carbon Carbon which is directly attached to the n-carbon.
Classification of Hydrogen Atoms:
- 1°-hydrogen (primary) attached to 10-carbon,
- 2°-hydrogen (secondary) attached to 2°-carbon.
- 3°-hydrogen (tertiary) attached to 3°·carbon.
- α- hydrogen(s) Hydrogens which are attached to n-carbon atom.
- β – hydrogen(s) Hydrogens which are attached to ~-carbon atom (-R-).
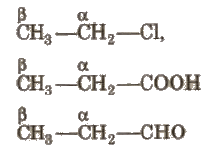
Homologous Series
The series in which the molecular formula of adjacent members differ by a – CH2 unit, is called homologous series and the individual members are called homologue. e.g., The homologous series of alkene group is:
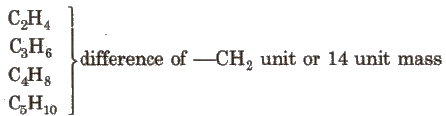
The general characteristics of this series are :
1. All the homologues contain the same functional group. That’s why their chemical properties are almost similar.
2. All the members of a series have a same general formula, e.g.,
Series | General formula |
Alkanes | CnH2n+ 2 |
Alkenes | CnH2n |
Alkynes | CnH2n-2 |
Alcohol and ether | CnH2n+ 2O |
Aldehyde and ketone | CnH2n O |
Acid and ester | CnH2n O2 |
3. All the members can be prepared by almost similar methods.
4. With the increase in the molecular weight of a series, the physical properties vary gradually.
4.
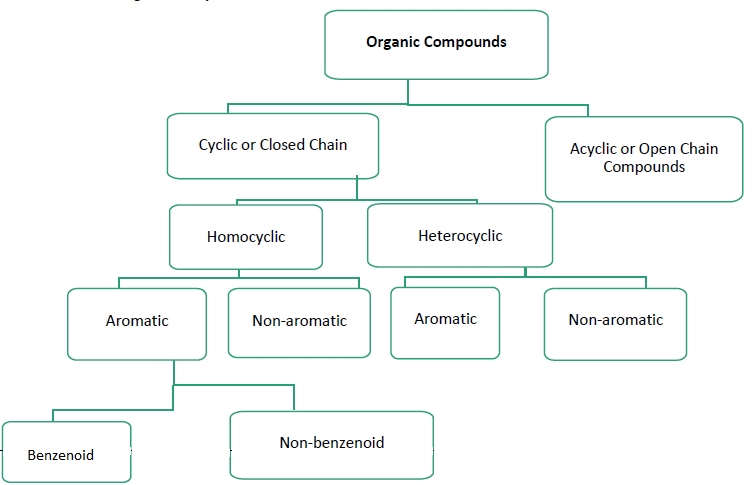
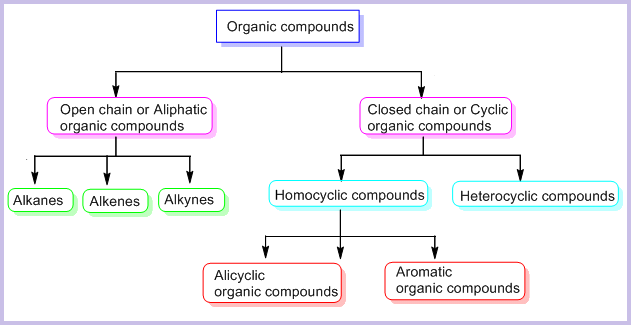
On the Basis of Structure:
The existing large number of organic compounds and their ever-increasing numbers has made it necessary to classify them on the basis of their structures. Organic compounds are broadly classified as follows:
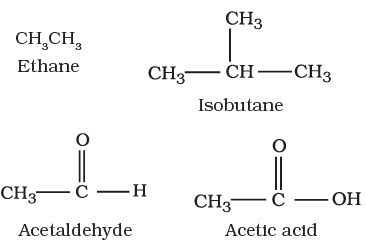
I. Acyclic or open chain compounds
These compounds are also called as aliphatic compounds and consist of straight or branched chain compounds, for example:
II Cyclic or closed chain or ring compounds
Alicyclic (aliphatic cyclic) compounds contain carbon atoms joined in the form of a ring (homocyclic). Sometimes atoms other than carbon are also present in the ring (heterocyclic). Some examples of this type of compounds are:
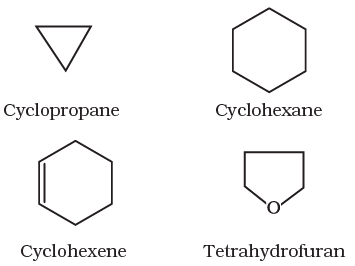 These exhibits some of the properties similar to those of aliphatic compounds.
These exhibits some of the properties similar to those of aliphatic compounds.
Aromatic Compounds
Aromatic compounds are special types of compounds. You will learn about these compounds in detail in Unit 13. These include benzene and other related ring compounds (benzenoid). Like alicyclic compounds, aromatic compounds may also have heteroatom in the ring. Such compounds are called heterocyclic aromatic compounds. Some of the examples of various types of aromatic compounds are:
Benzenoid aromatic compounds
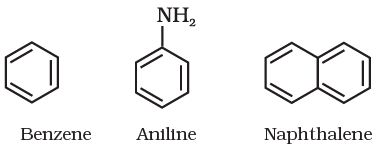
Heterocyclic aromatic compounds
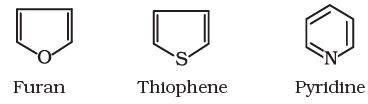



Organic compounds can also be classified on the basis of functional groups, into families of homologous series.
|
114 videos|263 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on Classification of Organic Compounds - Chemistry Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are aromatic compounds? |  |
| 2. How are aromatic compounds classified? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of aromatic compounds? |  |
| 4. How are aromatic compounds different from aliphatic compounds? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of aromatic compounds in organic chemistry? |  |