Taxonomical Categories | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Taxonomic Categories |

|
| 1. Species |

|
| 2. Genus |

|
| 3. Family |

|
| 4. Order |

|
| 5. Class |

|
| 6. Division/Phylum |

|
| 7. Kingdom |

|
Taxonomic Categories
Classification is the process of grouping organisms that are genetically similar. The groups that share characteristics are combined to form larger groups.The various grouping levels or ranks in classification are known as taxonomic categories.
Example: Insects represent a group of organisms sharing common features like three pairs of jointed legs.
There are seven main taxonomic categories:
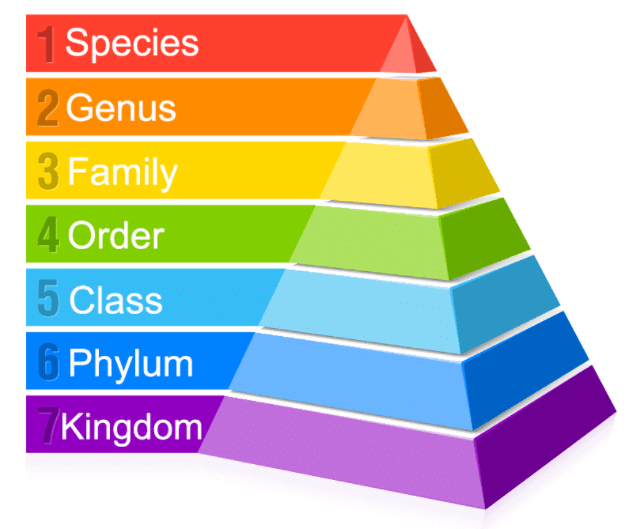
Taxonomic Hierarchy
Taxonomic hierarchy is the process of arranging various organisms into successive levels of the biological classification either in a decreasing or an increasing order from kingdom to species and vice versa.
Organisms are classified into similar categories namely kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species.
1. Species
Species (used both as singular and plural) is a natural population of individuals or groups of populations that resemble one another in all essential morphological and reproductive characteristics so that they are able to interbreed freely and produce fertile offspring. It has the lowest taxonomic characteristics. Individuals can be distinguished due to distinct morphological features.- For example, the scientific name of mango is Mangifera indica, where "Mangifera" is the genus and "indica" is the species. The scientific name of potato is Solanum tuberosum, where “Solanum” is the genus and “tuberosum” is the species.
2. Genus
It is a group or assemblage of related species that share certain associated characteristics. Correlated Characters are those similar or common features used to classify a taxon above the rank of species.- All the species of a genus are presumed to have evolved from a common ancestor.
- Among animals, for example, the species of horses and zebras from the genus Equus, lion, and tiger are placed under the genus Panthera.
3. Family
It is a taxonomic category that contains one or more related genera.- All the genera of a family have some common features or correlated characters.
- They are separable from the genera of a related family by important and characteristic differences in both vegetative and reproductive features.
- Example: The genera of cats (Felis) and leopards (Panthera) are included in the family Felidae.
4. Order
Order is a more specific rank than class. The category includes one or more related families.- Plant families such as Convolvulaceae and Solanaceae are classified in the order Polymoniales based on their floral characteristics.
- In the animal family, Felidae and Canidae are included in the same order Carnivora.
5. Class
A class is a group of one or more related orders.- Example: The class dicotyledonous (Dicotyledonae, dicotyledons) of flowering plants contains all dicots which are grouped into several orders.
- For example order Primata comprising monkeys, gorillas and gibbons are placed in Class Mammalia along with order Carnivora which includes animals like tiger, cat, and dog all having a common feature that is hair on skin and milk glands.
6. Division/Phylum
It is a category of related animals of classes.- The term phylum is used for animals, while division is commonly used for plants.
- A division of phylum is formed of one or more classes.
- For example, Chordata is a phylum that includes organisms that share characteristics such as a notochord and a dorsal hollow neural system, so based on these characteristics phylum chordate of animals contains not only class mammalian but also Aves (birds), reptilian (reptiles), amphibians (amphibians), Cyclostomata, Chondrichthyes, Osteichthyes (fishes), etc.
7. Kingdom
It is the highest taxonomic category of biological classification.- For example, all plants are included in the kingdom Plantae while all animals belong to the kingdom Animalia.
- There are some extra categories, like subdivision, suborder, subfamily, tribe, sub-tribe, etc. They are not regularly used. They are used only when they are needed.
Note:
As we go higher from species to kingdom, the number of common characters decreases. Lower the taxa more are the characteristics that the members within the taxon share. Higher the category, greater is the difficulty of determining the relationship to other taxa at the same level.
Note:
These taxonomic categories/groups are distinct biological entities and not merely morphological aggregates.
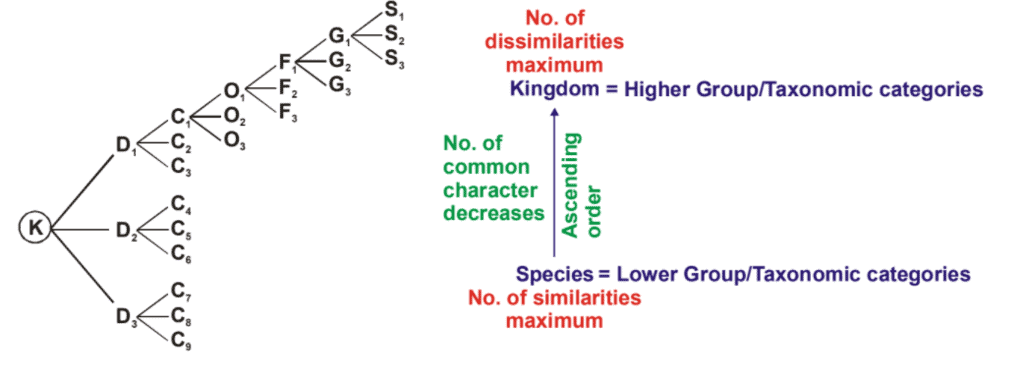
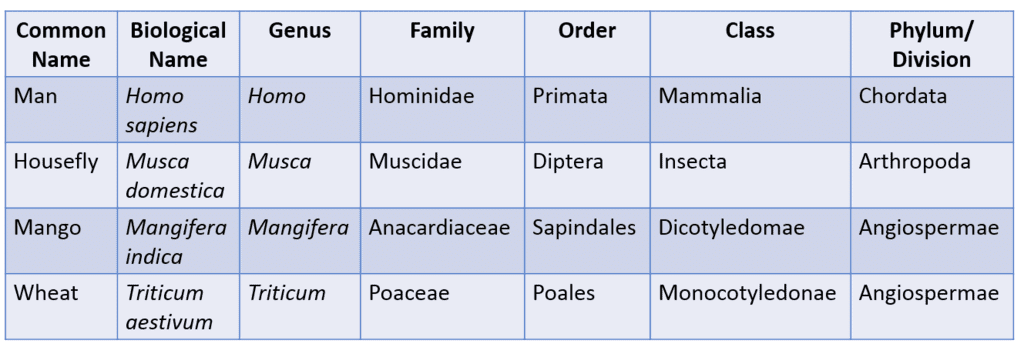 Examples of Taxonomic Categories
Examples of Taxonomic Categories
|
150 videos|399 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Taxonomical Categories - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the main taxonomic categories used in biological classification? |  |
| 2. How does the classification of organisms help in understanding biodiversity? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between a genus and a species? |  |
| 4. Why is the concept of 'kingdom' important in taxonomy? |  |
| 5. How do scientists determine the classification of a new species? |  |
















