Muscle and Neural Tissue (Only in NEET
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Connective Tissues |

|
| Muscle Tissue |

|
| Neural Tissue |

|
Introduction
Connective, muscle, and neural tissues are three of the primary types of tissues found in the bodies of animals, including humans, and each plays a crucial role in the body's function and structure.Connective Tissue: This type of tissue supports, binds together, and protects tissues and organs of the body. It's characterized by an abundance of extracellular matrix, which contains protein fibers, and the cells are spaced apart. Connective tissue includes bone, blood, adipose, cartilage, and lymphatic tissue. Its main functions are to provide structural support, nutrient transportation, insulation, and energy storage.
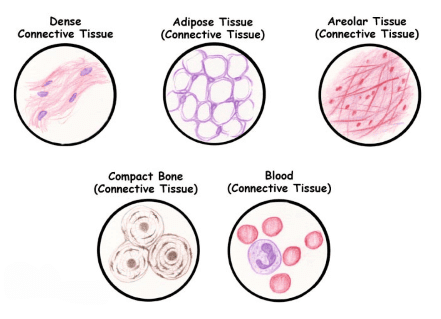 Connective Tissue
Connective Tissue
Muscle Tissue: Specialized for contraction, muscle tissue facilitates movement of the body and its parts, and it is crucial for maintaining posture and producing heat. There are three types of muscle tissue: skeletal, which is voluntary and attached to bones; cardiac, which is involuntary and makes up the heart; and smooth, which is also involuntary and found in the walls of internal organs, such as the intestines and blood vessels.
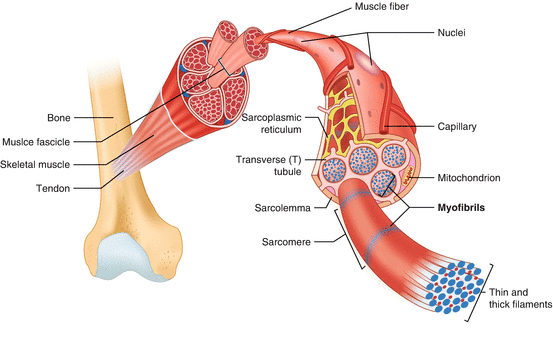 Muscle Tissue
Muscle Tissue
Neural Tissue: Also known as nervous tissue, this type forms the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system, which includes all the nerves that branch from the brain and spinal cord and extend to other parts of the body. Neural tissue is composed of neurons, which transmit electrical impulses, and glial cells, which provide support and nutrition to neurons. Its primary function is to generate and transmit nerve impulses to and from body organs via neurons.
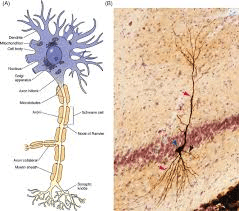 Neuron
Neuron
Connective Tissues
- Connective tissues are the most abundant and widely distributed tissues in the bodies of complex animals.
- They are called "connective" because their primary function is to link and support other tissues and organs.
- Connective tissues vary from soft types to specialized forms, including cartilage, bone, adipose tissue (fat), and blood.
- With the exception of blood, the cells in connective tissues secrete fibers made of structural proteins like collagen or elastin. These fibers provide strength, elasticity, and flexibility to the tissue.
- The cells also secrete modified polysaccharides that accumulate between the cells and fibers, forming a matrix or ground substance.
Connective tissues are classified into three main types:
(i) Loose connective tissue
(ii) Dense connective tissue
(iii) Specialized connective tissue
(i) Loose Connective Tissue
It features cells and fibers arranged loosely within a semi-fluid ground substance. Generally it is of 2 Types namely:
(a) Areolar tissue is found beneath the skin and often serves as a supportive framework for epithelium. This tissue contains fibroblasts(which produce and secrete fibres), macrophages, and mast cells.
(b) Adipose tissue, another type of loose connective tissue, is primarily located beneath the skin. The cells in this tissue are specialized for fat storage. Nutrients that are in excess and not used immediately are converted into fats and stored in this tissue.
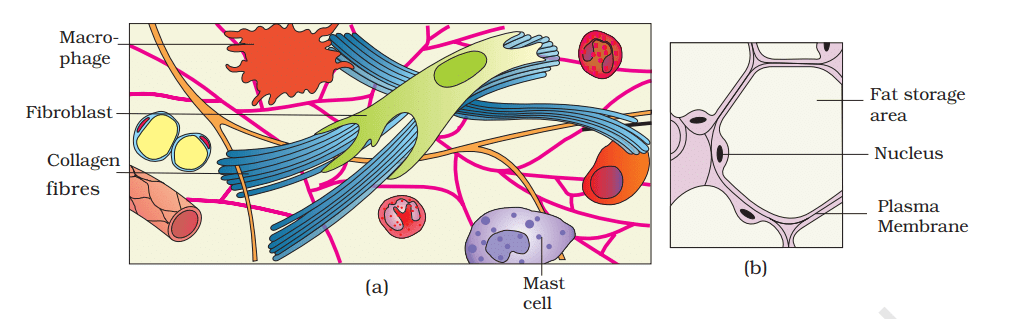 Loose connective tissue : (a) Areolar tissue (b) Adipose tissue
Loose connective tissue : (a) Areolar tissue (b) Adipose tissue
(ii) Dense Connective Tissue
Fibres and fibroblasts are tightly packed in dense connective tissues.The orientation of fibres can be regular or irregular, leading to the classification of dense regular and dense irregular tissues.
(a) Dense Regular Connective Tissues
- In dense regular connective tissues, collagen fibres are arranged in rows between parallel bundles of fibres.
- Examples include tendons(which connect skeletal muscles to bones) and ligaments (which connect one bone to another).
(b) Dense Irregular Connective Tissues
- Dense irregular connective tissue contains fibroblasts and fibres (mostly collagen) oriented in different directions.
- This type of tissue is found in the skin.
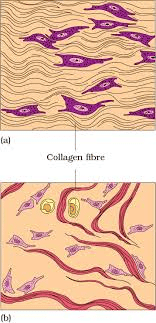 (a) Regular (b) Irregular
(a) Regular (b) Irregular
(iii) Specialized Connective Tissues
(a) Cartilage
- The intercellular material of cartilage is solid and pliable, allowing it to resist compression.
- Cells called chondrocytes are enclosed in small cavities within the matrix they secrete.
- Most cartilage in vertebrate embryos is replaced by bone in adults.
- Cartilage is found in the tip of the nose,outer ear, joints,vertebral column, and in the limbs and hands of adults.
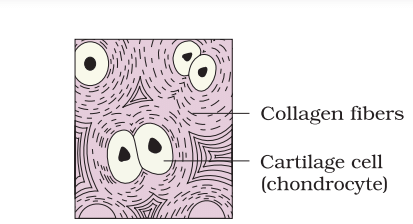 Special Connective Tissue: Cartilage
Special Connective Tissue: Cartilage
(b) Bones
- Bones have a hard, non-pliable ground substance rich in calcium salts and collagen fibres, which provide strength.
- Bones are the main tissue providing structural support and protection for softer tissues and organs.
- Bone cells, called osteocytes, are located in spaces called lacunae.
- Limb bones, such as the long bones of the legs, bear weight and facilitate movement by interacting with attached skeletal muscles.
- Some bones contain bone marrow, which is a site for blood cell production.
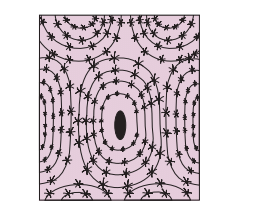 Bone
Bone
(c) Blood
- Blood is a fluid connective tissue composed of plasma,red blood cells(RBCs),white blood cells(WBCs), and platelets.
- It serves as the main circulating fluid for transporting various substances throughout the body.
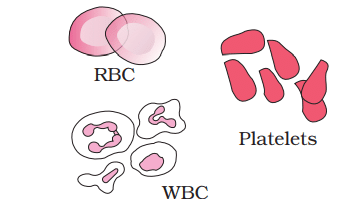 Blood cells
Blood cells
Muscle Tissue
Muscle Structure and Function
- Muscles are made up of long, cylindrical fibers that are arranged in parallel. These fibers are called muscle fibers and are responsible for the contraction and relaxation of the muscle.
- Within each muscle fiber, there are many tiny strands called myofibrils. These myofibrils are the basic units of muscle contraction.
- When a muscle fiber receives a signal to contract, it shortens, and when the signal stops, it relaxes and returns to its original length. This process is coordinated across many fibers to produce movement.
- Muscles are essential for adjusting the body to changes in the environment and for maintaining the position of different body parts. They are involved in all body movements.
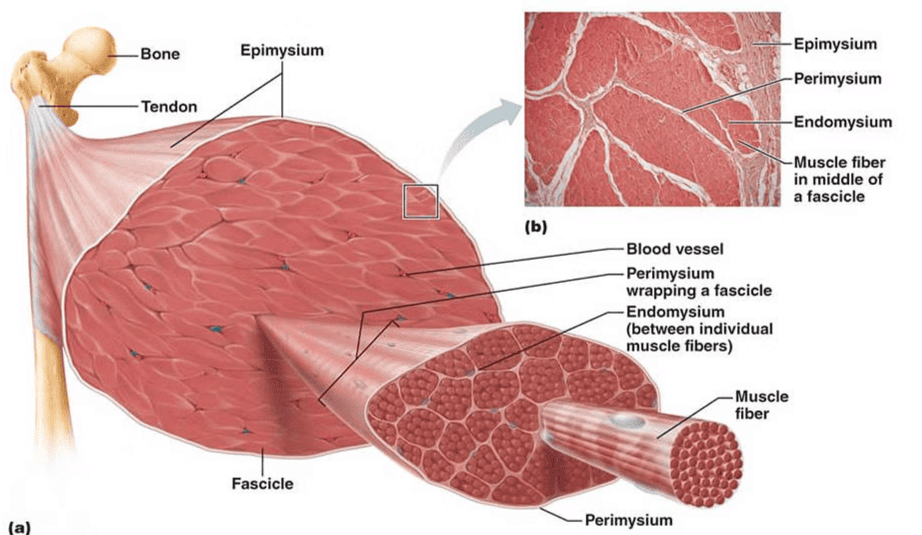 Muscle Tissue
Muscle Tissue
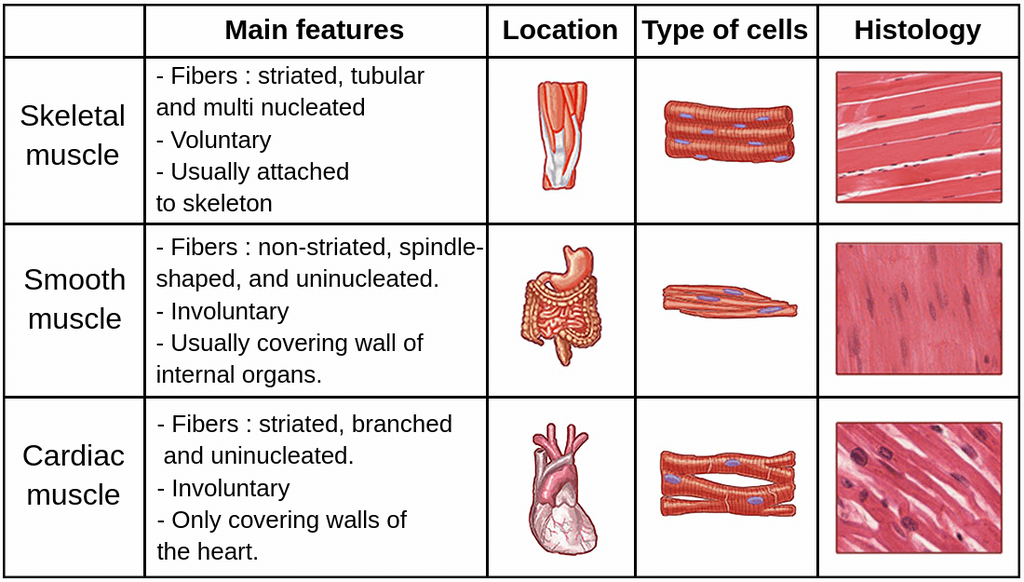
There are three types of muscles in the body:
(a) skeletal(voluntary muscles attached to bones),
(b) smooth(involuntary muscles found in organs)
(c) cardiac(the heart muscle, which is also involuntary).
 Types of Muscles
Types of Muscles
(a) Skeletal Muscle
- Skeletal muscle tissue is firmly attached to skeleton bones.
- In muscles like the biceps, the striated (striped) skeletal muscle fibers are grouped together in parallel bundles.
- A tough connective tissue sheath surrounds and protects these bundles of muscle fibers.
(b) Smooth Muscle
- Smooth muscle fibres are fusiform, meaning they taper at both ends, and they do not have visible striations, which differentiates them from skeletal muscle fibres.
- These fibres are held together by cell junctions and are bundled within a connective tissue sheath.
- Smooth muscle tissue is found in the walls of internal organs such as blood vessels, stomach, and intestine.
- Smooth muscles are classified as involuntary muscles because their contractions are not under direct voluntary control.
- Unlike skeletal muscles, which can be contracted at will, smooth muscles operate automatically without conscious thought.
(c) Cardiac Muscle
- Cardiac muscle tissue is found only in the heart.
- The plasma membranes of cardiac muscle cells are fused at cell junctions, which helps them stick together.
- Intercalated discs act as communication junctions, allowing the cells to contract together as a unit. When one cell gets the signal to contract, its neighbouring cells are also triggered to contract.
Neural Tissue
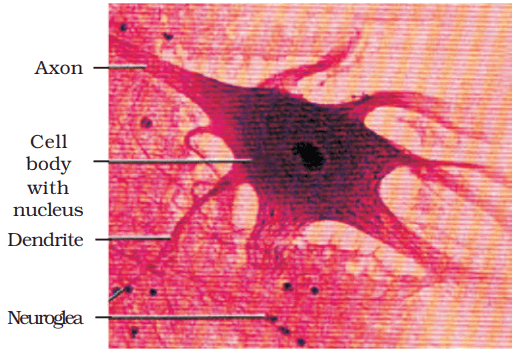
Neural tissue plays a crucial role in controlling the body's response to changing conditions. It is made up of neurons and neuroglial cells.
 Neural Tissue
Neural Tissue
- Neurons are the basic units of the neural system and are excitable cells. When a neuron is stimulated, it generates an electrical disturbance that travels along its plasma membrane.
- Neuroglial cells make up more than half the volume of neural tissue in the body. They protect and support neurons.
- When the electrical disturbance reaches the end of the neuron, it triggers events that can stimulate or inhibit adjacent neurons and other cells.
|
169 videos|524 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Muscle and Neural Tissue (Only in NEET
| 1. What are the main types of connective tissues in the body? |  |
| 2. How do muscle tissues differ from each other? |  |
| 3. What is the role of neural tissue in the body? |  |
| 4. What are the characteristics of connective tissues? |  |
| 5. How does muscle tissue contribute to movement in the body? |  |















