Human Neural System | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Introduction
The organs and organ systems in our body must work together in a coordinated manner to maintain homeostasis, which is the stable and balanced internal environment of the body. Coordination is essential because the functions of different organs are interdependent, and they need to complement each other to ensure the body operates effectively.
For instance, during physical exercise, the demand for energy and oxygen increases to support the heightened muscular activity. This increased demand triggers several coordinated responses in the body:
- Increased Rate of Respiration: To supply more oxygen to the body.
- Increased Heart Rate: To pump more blood, delivering oxygen and nutrients to the muscles.
- Increased Blood Flow: Through the blood vessels to facilitate the delivery of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide and other waste products.
When physical exercise stops, the activities of the nerves, lungs, heart, kidneys, and other organs gradually return to their normal levels. This example illustrates how the functions of various organs, including the muscles, lungs, heart, blood vessels, and kidneys, are coordinated during physical activity.
In the human body, the neural system and the endocrine system work together to coordinate and integrate the activities of different organs, ensuring they function in a synchronized manner.
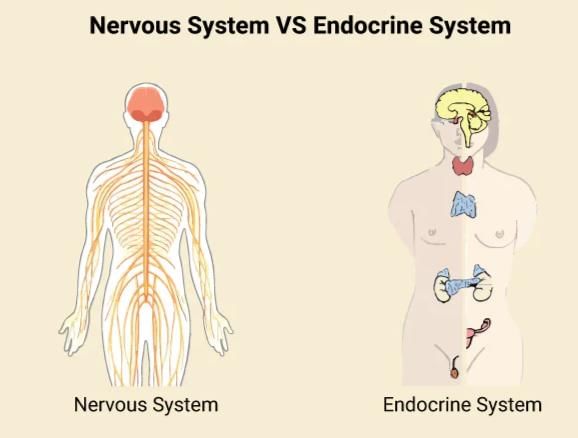
- Neural System: The neural system provides a quick and organized network of point-to-point connections for coordination. It uses electrical signals to transmit information rapidly between different parts of the body.
- Endocrine System: The endocrine system coordinates activities through chemical signals called hormones. Hormones are released into the bloodstream and act on specific target organs, regulating various functions such as metabolism, growth, and mood.
In this chapter, we will focus on the neural system in humans and explore how neural coordination occurs through the transmission of nerve impulses and the conduction of these impulses across a synapse, which is the junction between two nerve cells.
Neural System
The neural system in animals is made up of specialized cells called neurons. Neurons are responsible for detecting, receiving, and transmitting different kinds of stimuli. The organization of the neural system varies among different groups of animals.
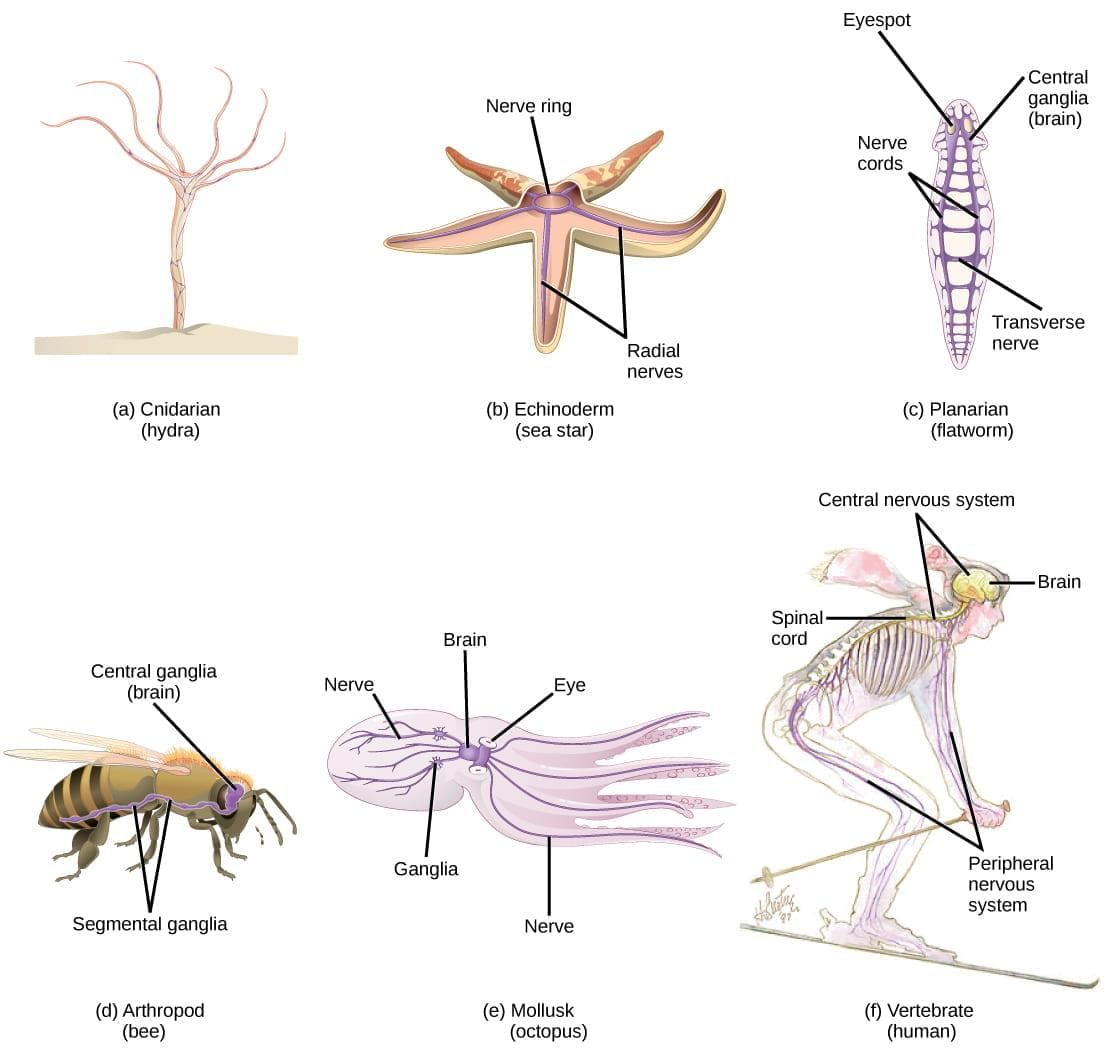
- Lower Invertebrates: In animals like Hydra, the neural system is very simple and consists of a basic network of neurons.
- Insects: Insects have a more organized neural system, which includes a brain, several ganglia, and neural tissues.
- Vertebrates: Vertebrates possess a highly developed neural system, which is more complex than that of insects.
Human Neural System
The nervous system is a complex network in our body responsible for coordinating various activities. It's divided into two main parts: the Central Nervous System (CNS) and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS).
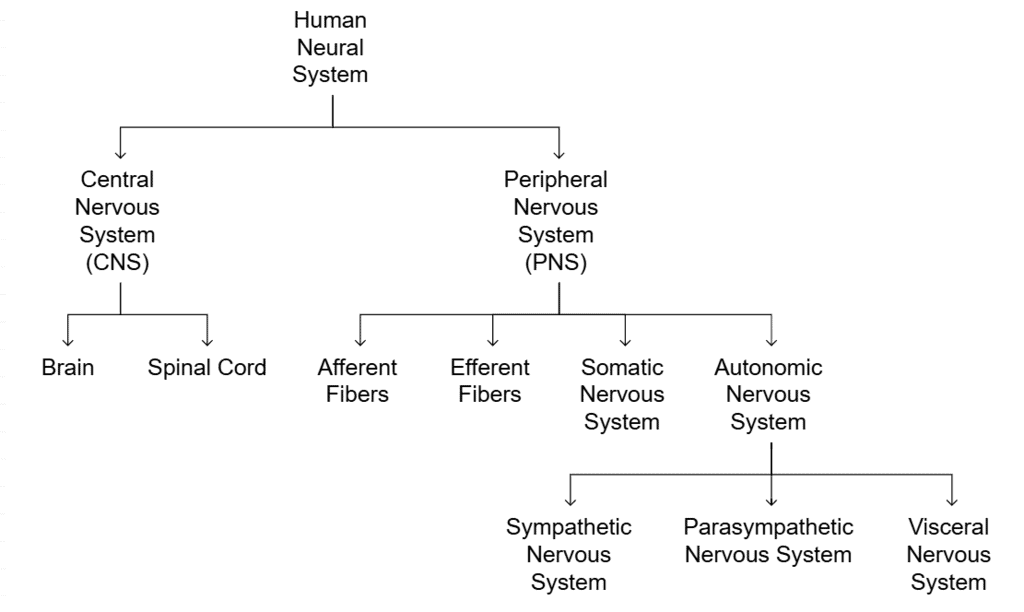
1. Central Nervous System (CNS):
- The CNS includes the brain and spinal cord.
- It acts as the control center, processing information and making decisions.
2. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS):
- The PNS consists of all the nerves outside the CNS.
- It connects the CNS to the rest of the body, transmitting signals back and forth.
The Nerve fibres of PNS is further divided into:
(i) Afferent Fibers: These fibers carry sensory information from organs and tissues to the CNS.
(ii) Efferent Fibers: Efferent fibers transmit signals from the CNS to peripheral organs and tissues, regulating their functions.
PNS is further divided into
(a) Somatic Nervous System: This system relays impulses from the CNS to skeletal muscles, controlling voluntary movements.
(b) Autonomic Nervous System:
- The autonomic system transmits impulses from the CNS to involuntary organs and smooth muscles.
- It regulates automatic functions like heart rate and digestion.
Autonomous Nervous System is further divided into
(i) Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nervous Systems
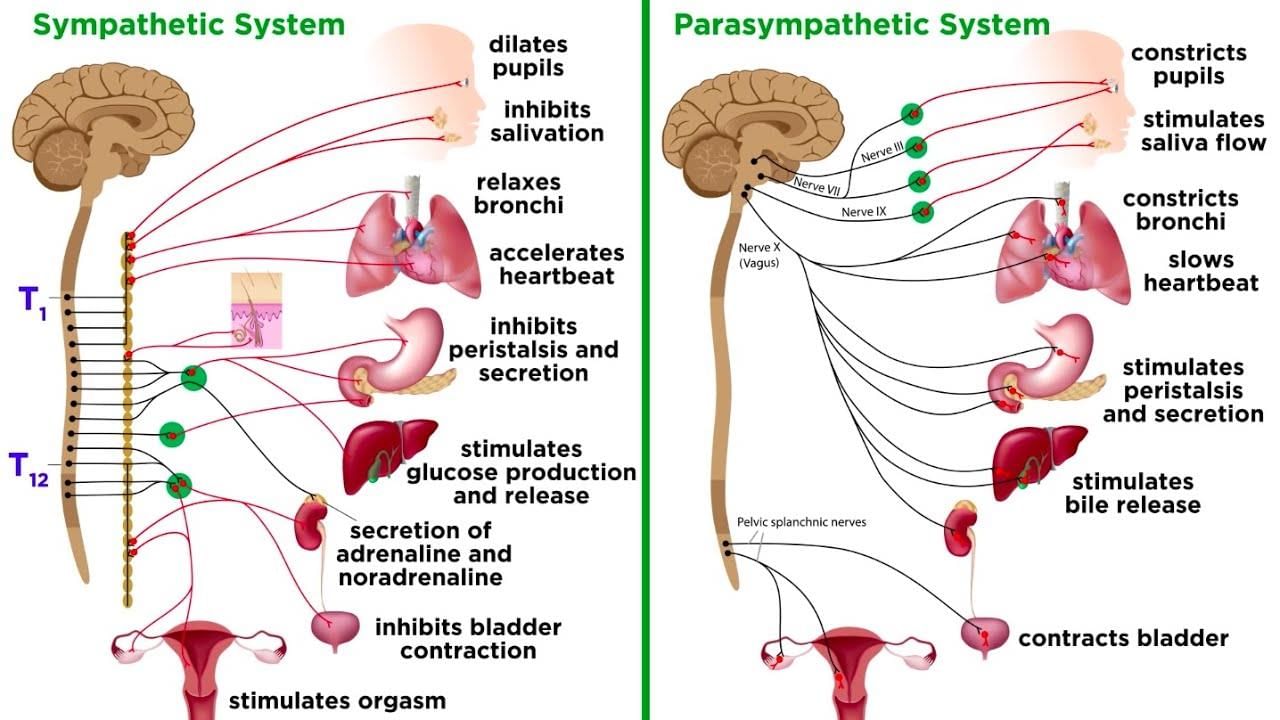
- The autonomic nervous system is further divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.
- The sympathetic system prepares the body for 'fight or flight' responses, while the parasympathetic system promotes 'rest and digest' activities.
(ii) Visceral Nervous System:
- This part of the PNS includes nerves, fibers, ganglia, and plexuses that transmit impulses between the CNS and the visceral organs.
- It plays a crucial role in regulating the functions of internal organs.
|
150 videos|399 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Human Neural System - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the main function of neurons in the human neural system? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of neurons found in the human body? |  |
| 3. How do neurons communicate with each other? |  |
| 4. What is the role of glial cells in the neural tissue? |  |
| 5. What is myelin, and why is it important for neurons? |  |






















