Blood Vessels | Biology for JAMB PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What are Blood Vessels? |

|
| Types of Blood Vessels |

|
| Layers of Blood Vessels |

|
| Difference between Arteries, Veins & Capillaries |

|
| Functions of Blood Vessels |

|
| Concept Based Questions |

|
What are Blood Vessels?
Blood vessels are intricate networks of hollow tubes that transport blood throughout the entire body.
- The human circulatory system consists of the heart, blood cells, lymphatic system and network of blood vessels. These four main organs have specific roles and functions, which work together to keep us active and healthy.
- Blood Vessels vessels carry blood in both directions, i.e. one from the heart to all other parts and another from all body parts to the heart.
Types of Blood Vessels
In the closed type of blood vascular system blood vessels are of 3 major types:
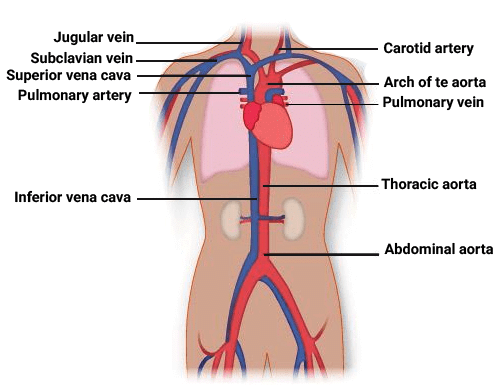 Blood Vessels in Body
Blood Vessels in Body
1. Arteries
1. Arteries
Arteries are the main blood vessels that carry and transport oxygenated blood or oxygen-rich blood from the heart to other parts of the body.
- They are the strongest blood vessels with thicker walls and are muscular in nature. It consists of three distinct layers, which are rigid, thicker and highly muscular.
- Arteries are located deep within the body and are red in colour.
- These blood vessels are with high pressure and move in a downward direction from the heart to the body tissues. Normally Artery carries pure blood from heart to the different organs of the body.
2. Veins
Veins are blood vessels that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins,
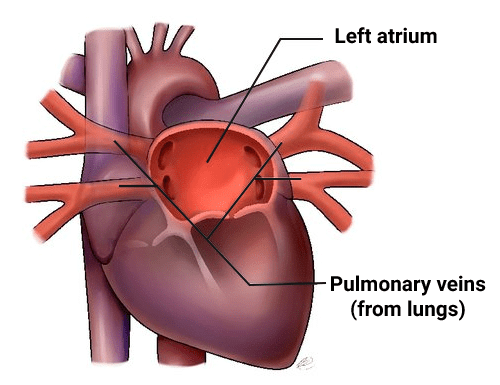 Veins carry deoxygenated blood except for the Pulmonary Vein
Veins carry deoxygenated blood except for the Pulmonary Vein
- Veins are thin, tube-like elastic blood vessels, present closer to the surface of the skin.
- These translucent blood vessels are blue in colour and carry impure or deoxygenated blood from all parts of the body to the heart.
- These blood vessels are with low pressure and move in an upward direction, i.e. from the cells, tissues and other organs to the heart.
- Compared to the arteries, veins are thin-walled. Veins carry impure blood from body organs to the heart and this blood is impure normally.Question for Blood VesselsTry yourself:Deoxygenated blood is carried by?View Solution
3. Capillaries:
Capillaries are tiny blood-containing structures that connect arterioles to venules. They are the smallest and most abundant form of a blood vessel in the body.
- Short and tiny blood vessels, found within the tissues are called capillaries.
- Capillaries bring about the exchange of substances between blood and tissues.
- These blood vessels also function by connecting arterial systems to the venous system and help in the exchange of substances across cells.
- Capillaries are present in the organs, and these are the vessels through which exchange takes place.
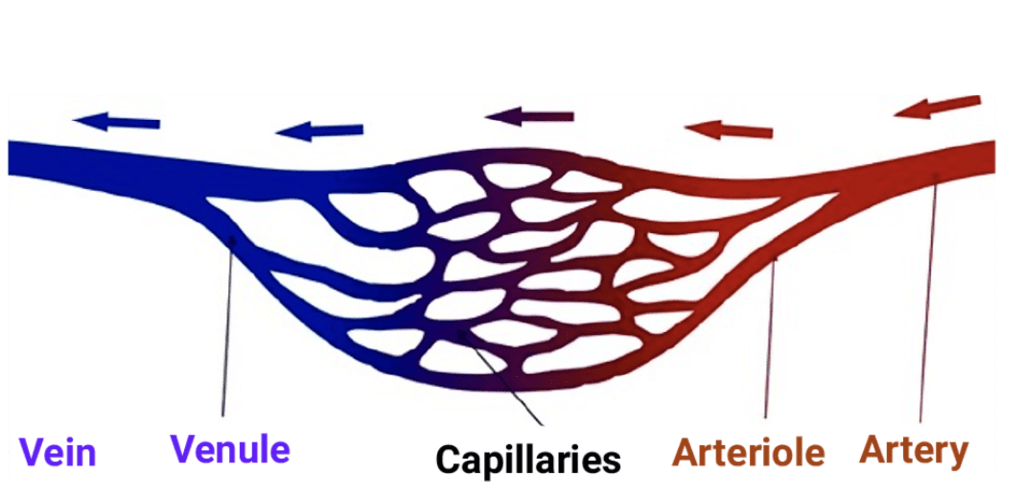
Capillaries are the finest blood vessels interconnecting arteries and veins.
Layers of Blood Vessels
Normally there are three layers are found in the walls of blood vessels:
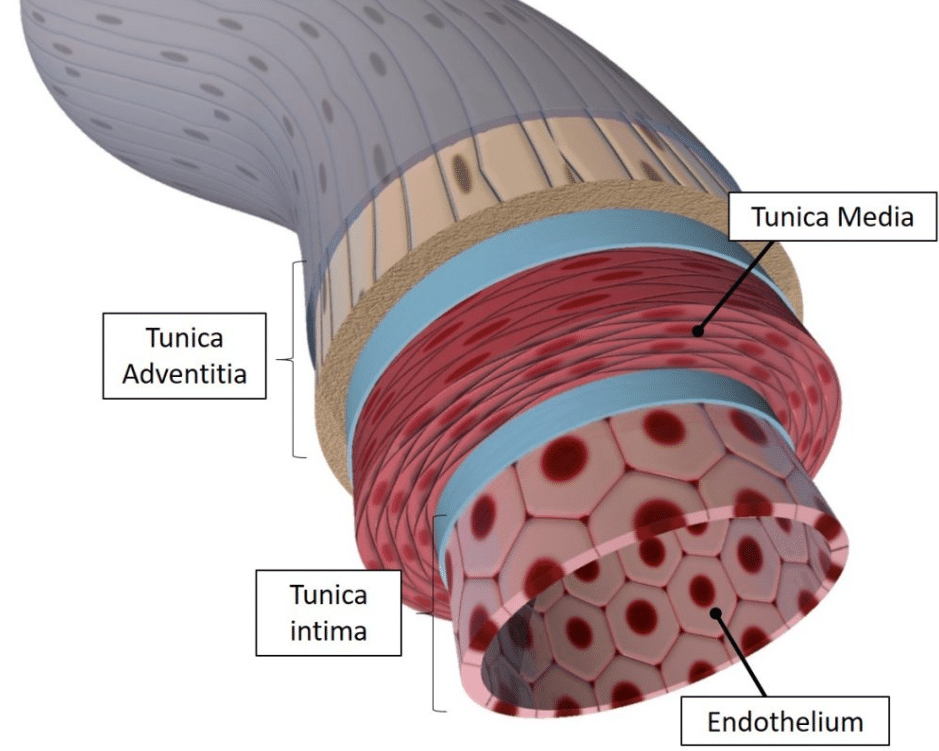
- Tunica Externa: It is the outermost layer. It is formed of loose connective tissue in which many collagen fibres, elastin fibres and longitudinal muscles are found.
- Tunica Media: It is a thick layer of circular non-striated muscles and a network of elastin fibres.
- Tunica Interna: This layer is made up of squamous epithelium, It is also known as Endothelium
One more layer is present in the wall bigger arteries, that is known as elastic membrane. This is found in between the tunica media and tunica interna layers.
These all layers are well developed in the walls of arteries as compared to the walls of veins.
Walls of arteries are thick and more muscular and these walls are elastic and non-collapsable.
The walls of veins are thin, less muscular non-elastic and collapsable.
In the walls of blood capillaries, only the endothelium layer is found. Its cells are flat and squamous,Their walls are perforated. These blood capillaries join the arteries with the veins.
Blood capillaries were discovered by a scientist named as Marcello Malpighi
A thin network of blood capillaries is present in the walls of blood vessels itself which supply blood and other necessary substances to the blood vessels. This blood supply is known as Vasa-vasorum.
Difference between Arteries, Veins & Capillaries
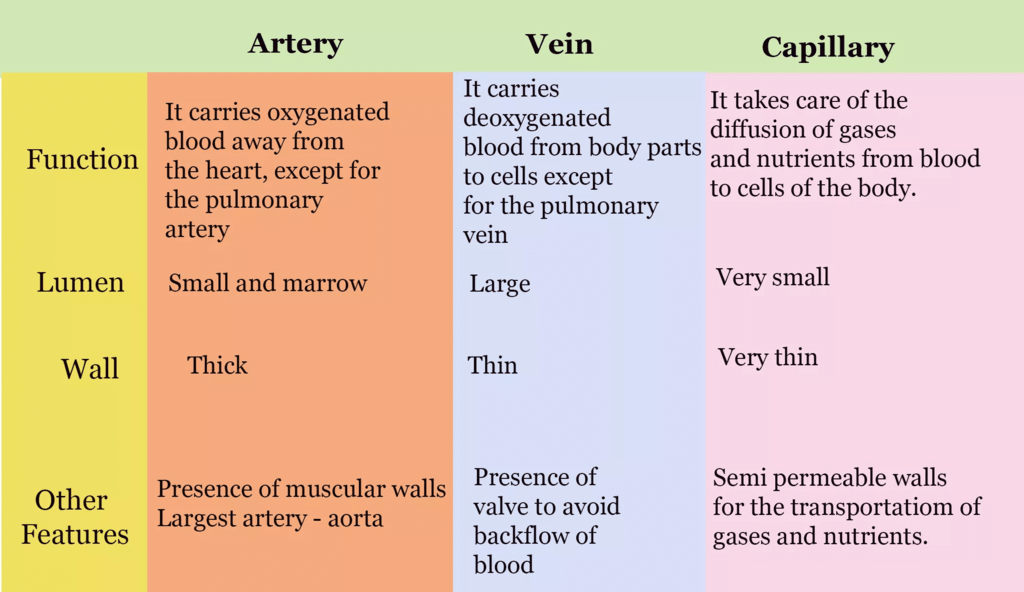
Functions of Blood Vessels
- Blood vessels play a vital role in the gaseous exchange.
- Blood vessels help in maintaining a constant internal temperature of an organism.
- The vital function of the blood vessels is to protect against the loss of blood during injuries.
- Blood vessels are also involved in circulating both oxygenated (poor) and deoxygenated (impure) blood from and to the heart.
- Blood vessels help in the transportation of nutrients, water, minerals, hormones and all other essential components required for the different body metabolism.
Concept Based Questions
Q1. What are the 3 types of blood vessels and their functions?
Ans: There are three kinds of blood vessels: arteries, veins, and capillaries. Each of these plays a very specific role in the circulation process. Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart. They're tough on the outside but they contain a smooth interior layer of epithelial cells that allows blood to flow easily.
Q2. What is the largest blood vessel?
Ans: The largest artery is the aorta, which receives blood directly from the heart. Veins are blood vessels that carry blood toward the heart.
Q3. What are the smallest blood vessels?
Ans: Arterioles carry blood and oxygen into the smallest blood vessels, the capillaries. Capillaries are so small they can only be seen under a microscope.
Q4. How do blood vessels work?
Ans: The heart, blood and blood vessels work together to service the cells of the body. Using the network of arteries, veins and capillaries, blood carries carbon dioxide to the lungs (for exhalation) and picks up oxygen. From the small intestine, the blood gathers food nutrients and delivers them to every cell.
Q5. Why the colour of human blood is red?
Ans: Human blood is red because hemoglobin, which is carried in the blood and functions to transport oxygen, is iron-rich and red in color. It's bright red when the arteries carry it in its oxygen-rich state throughout the body. And it's still red, but darker now, when it rushes home to the heart through the veins.
|
225 videos|175 docs|156 tests
|
FAQs on Blood Vessels - Biology for JAMB
| 1. What are Blood Vessels? |  |
| 2. What are the Types of Blood Vessels? |  |
| 3. What are the Layers of Blood Vessels? |  |
| 4. What is the Difference between Arteries, Veins & Capillaries? |  |
| 5. What are the Functions of Blood Vessels? |  |
















