Pharynx & Oesophagus: Alimentary Canal | Additional Study Material for NEET PDF Download
Pharynx
Pharynx is the common passage of the respiratory system and digestive system located in the throat. It connects the mouth to the oesophagus and nose to the larynx. Food and water from the oral cavity and air from both oral and nasal cavity comes to the pharynx. Pharynx is present in vertebrates and also in invertebrates such as annelids, arthropods, etc.
Pharynx
➢ Pharynx Location
- Pharynx is present behind the oral and nasal cavity. It is a part of the throat and a common passage for both the digestive and respiratory system.
- Pharynx opens into the oesophagus in the digestive tract and opens into the larynx in the respiratory tract.
- Pharynx is also present in some of the invertebrates. The shape and size vary in different organisms. It may be thick and muscular, rotated or turned outward.
➢ Pharynx Structure and Parts
The pharynx can be divided into three main regions according to its location. They are:
(i) Nasal pharynx – As the name suggests, it is the part of the pharynx that is present posterior to the nasal cavity.
(ii) Oral pharynx – It is the part behind the oral cavity and continues in the throat till hyoid bone.
(iii) Laryngeal pharynx – It is the lowermost part of the pharynx from epiglottis and continues to the oesophagus.
The main features of pharynx are:
- The wall of pharynx consists of both longitudinal and circular muscles. These muscles determine the shape of the lumen.
- Isthmus connects oropharynx to nasopharynx. It is useful for breathing through the mouth and inserting food into the oesophagus through the nasal tube if required.
- Pharyngeal adenoids or tonsils are located in the wall of nasopharynx.
- Nasopharynx is lined with pseudostratified, columnar and ciliated respiratory epithelium.
- Eustachian tubes connect middle ears to pharynx. It helps in equalizing air pressure on the eardrum.
- Palatine tonsils are present in the lateral wall of the oropharynx.
- The wall of oropharynx is made up of non-keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium.
- The opening of the pharynx to the larynx is controlled by a muscular flap known as epiglottis. It is present over the larynx opening and prevents food from entering the trachea.
- The wall of laryngopharynx consists of stratified squamous epithelium.
- Laryngopharynx regulates the movement of air to lungs and food to oesophagus.
- Pharyngeal, tubal, palatine and lingual tonsils present in different parts of the pharynx are called Waldeyer’s ring. These are lymphoid tissues present in the nasopharynx and oropharynx. It provides defence against invasion of microorganisms in the digestive and respiratory tract.
➢ Pharynx Function
Pharynx performs a dual function. It allows passage for both air and food.
The main functions of the pharynx are:
- It makes air warm and humidifies it before reaching the lungs.
- It helps in the movement of food to the oesophagus. Circular muscles help in pushing the food down and longitudinal muscles help in swallowing the food by lifting and widening the walls.
- Pharynx also helps in speech, it amplifies the sound produced by the larynx or soundbox.
- Lymphoid tissues present in the pharynx are the first line of defence against foreign pathogens.
➢ Pharynx Diseases
Some of the diseases associated with the pharynx are:
(i) Pharyngitis - inflammation of the pharynx
(ii) Tonsillitis - inflammation of tonsils
(iii) Pharyngeal cancer
Oesophagus
The food we swallow passes through a pipe which leads to the stomach. This pipe is known as the food pipe or the oesophagus. Food reaches the stomach from pharynx through peristaltic contractions.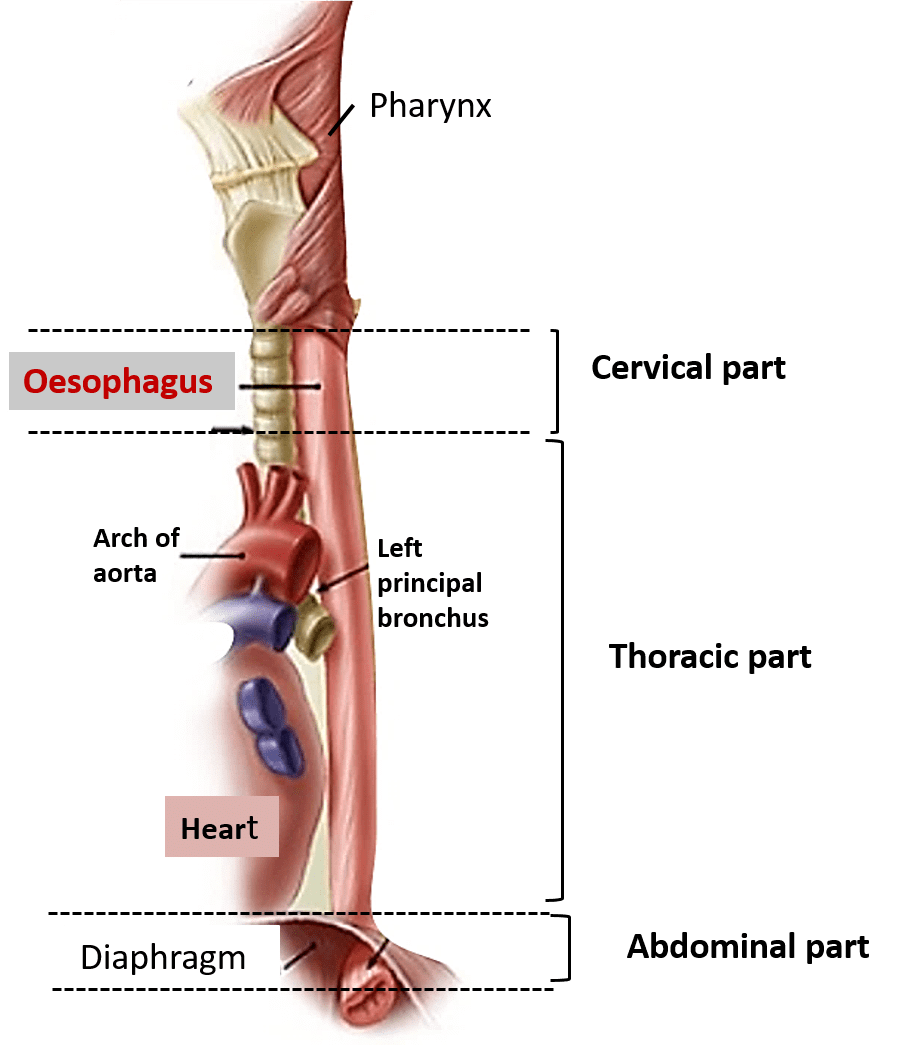 Oesophagus
Oesophagus
➢ Food Pipe Definition
- “Food pipe or oesophagus is the part of digestive system of vertebrates with a distinct path exclusively meant for passage of food.”
➢ What is Food Pipe?
- Food pipe is a muscular tube which is 25 centimetres long, passing just behind the heart region connecting the mouth to the stomach. It is made up of connective tissues and is the uppermost part of the digestive system.
- The veins and arteries that pass through the oesophagus or food pipe are called oesophageal veins and oesophageal arteries respectively. The upper part of the oesophagus is behind the windpipe. Oesophagus joins the stomach at a point called the gastro-oesophageal junction. When we swallow food, oesophagus contracts and squeezes the food which pushes the food down towards the stomach.
➢ Layers Of Food Pipe
The food pipe or oesophagus is divided into the following layers:
(i) Mucosa: The inner layer
(ii) Submucosa: The layer responsible for producing secretions
(iii) Muscularis: Food is pushed down through this layer made up of muscles
(iv) Adventitia: Oesophagus is attached to the other parts through this outer layer
➢ Functions Of Food Pipe
The food pipe or oesophagus performs the following important functions:
- The food we eat reaches the oesophagus after passing through the larynx.
- After the buccal cavity, the oesophagus is the next point of contact for food into the gastrointestinal tract.
- Responsible in preventing the entry of food into the windpipe by controlling the movement of the epiglottis.
- Radially symmetric contractions of oesophagus help push food downwards.
- Rhythmic contractions and relaxations of oesophageal muscles result in the swift movement of food towards the gastro-oesophageal junction.
Care needs to be taken about the health of oesophagus or food pipe as negligence can cause severe disorders in the food pipe. One such ailment of the food pipe is Oesophageal cancer.
➢ Disorder Of The Food Pipe – Oesophageal Cancer
It is a cancer of the food pipe where the cells multiply in an uncontrolled way. It is mostly diagnosed in people above 60 years of age. When the tumour is small, it does not show any symptoms. It is only when it enlarges, the symptoms become apparent and develop.
The commonly occurring symptoms are:
- Dysphagia – patient finds it difficult to swallow food
- Regurgitation – Food tends to come back up before even making it to the stomach
- Nausea
- While swallowing, the patient suffers from throat pain or pain in the middle of the chest
- Heartburn or indigestion
- Tends to develop a hoarse voice
- Cough
- Weight loss
- Uneasiness or dull pain between the shoulder blades
The initial treatment of the oesophageal cancer is dependant upon the stage as to how far it has grown. With an early diagnosis, endoscopic procedures can be carried out, however, if it has advanced to a higher stage, a part or most of the food pipe is surgically removed. Many other treatments are recommended such as chemotherapy, targeted therapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, etc.
|
26 videos|312 docs|64 tests
|
FAQs on Pharynx & Oesophagus: Alimentary Canal - Additional Study Material for NEET
| 1. What is the function of the pharynx in the alimentary canal? |  |
| 2. How does the pharynx function in swallowing? |  |
| 3. What is the role of the esophagus in the alimentary canal? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the process of peristalsis in the esophagus? |  |
| 5. What can cause disorders or diseases in the pharynx and esophagus? |  |

















