Phylum: Hemichordata | Additional Study Material for NEET PDF Download
Introduction
– The term Hemichordata was given by Bateson.
– Animals of this phylum are all fossorial, and their tunnels are ‘U’ - shaped.
– Body worm-like, and soft.
This is a phylum that contains marine deuterostome animals. They are sometimes considered as the sister group of phylum Echinodermata. Phylum Hemichordata is a small phylum with only a 100 known species, with animals having a worm-like appearance. Some species may be solitary or some occur in colonies.
Parts of Body of Hemichordata
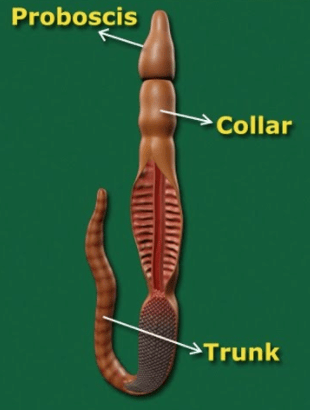
Body is divided into three parts:
A - proboscis
B - Collar
C - Trunk
 Phylum: Hemichordata
Phylum: Hemichordata
Characteristics of Hemichordata
Body wall has single layered epidermis. No dermis
– Body cavity is enterocoelus, that is divided into Protocoel, Mesocoel and Metacoel.
– Mostly ciliary feeders. Complete alimentary canal is present in digestive system. This is straight or ‘U’ - shaped.
– Circulatory system is open type. Blood is colourless with amoeboid corpuscles.
– Heart is dorsal.
– Skeletal tissue is absent.
– True notochord is absent.
– A notochord like structure is found in their buccal cavity, that is called ‘‘Buccal diverticulum’’ or ‘‘Stomochord’’ (a hollow out-growth arises from roof of buccal cavity).
– Post-anal tail is Absent.
– Dorsal heart, ventral nerve cord, no respiratory pigment.
– Respiration by gills.
– Excretion is done by a single glomerulus. This single glomerulus is situated in the proboscis known as Proboscis gland.
– Central nervous system is just like non-chordates. Brain is present in the form of nerve - ring.
– Most animals are unisexual and reproduction is sexual.
– Fertilization is external. Cleavage holoblastic.
– Development is direct or indirect because some animals have tornaria larva just like bipinnaria larva or Echinodermata in their developmental stages.
Classification of Hemichordata
Hemichordata is divided into two Classes
(1) Enteropneusta – *Balanoglossus. (Tongue worm or Acorn worm) – Rhabdopleura
2) Pterobranchia – *Saccoglossus
– Earliest included Hemichordata in Chordata phylum. Hyman (1959) kept in separate phylum Hemichordata in invertebrates.
– Hemichordata is connecting link between Non-Chordata & Chordata.
|
26 videos|312 docs|64 tests
|
FAQs on Phylum: Hemichordata - Additional Study Material for NEET
| 1. What are the main characteristics of Hemichordata? |  |
| 2. How are Hemichordata classified? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the stomochord in Hemichordata? |  |
| 4. How are Hemichordata adapted to their marine environment? |  |
| 5. What is the ecological importance of Hemichordata? |  |





















