Speciation & Genetic Drift | Biology for ACT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Speciation? |

|
| Types of Speciation |

|
| Genetic Drift |

|
| Types of Genetic Drift |

|
| Genetic Drift Example |

|
| Causes of Genetic Drift |

|
Evolution is a continuous process through which new species emerge over millions of years. This process, known as speciation, can occur naturally through evolution or artificially through methods like hybridization. Speciation involves the development of distinct new species with unique genetic features that are reproductively isolated from their ancestors.
What is Speciation?
The process by which a new species is created is known as Speciation. The process can be started by a natural process like Evolution. Or Speciation can be started by an artificial process like Hybridization. Creating a new species from the existing species in any form is known as the speciation process.
Characteristics
- The species which will develop by the Speciation process must be a new species. The species should have distinct new features from the ancestors.
- The new species should have some uniqueness in the genetic structure. The genetic structure should be different from the ancestors.
- The new species should not breed with their ancestors. This means the new species should be reproductively isolated from the ancestor species.
Types of Speciation
1. Allopatric Speciation
2. Parapatric Speciation
3. Peripatric Speciation
4. Sympatric Speciation
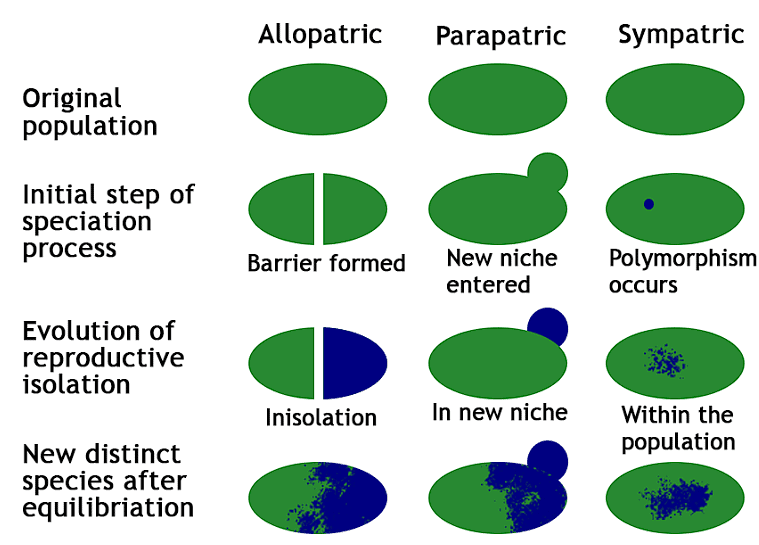
- Allopatric Speciation: This form of speciation occurs when a physical barrier separates existing species, preventing them from interacting and evolving together. Examples include predators or natural disasters creating barriers that force species apart.
- Parapatric Speciation: In this process, one group of organisms migrates to a new habitat and evolves separately from the original population. Meanwhile, the original population undergoes its own evolutionary changes in a different environment. This leads to the development of two distinct species from one.
- Peripatric Speciation: Similar to allopatric speciation, this type involves the development of new species without a physical barrier, but rather due to geographic isolation. Different populations inhabit separate locations and undergo independent evolutionary changes, leading to the emergence of new species.
- Sympatric Speciation: This fascinating type of speciation occurs when two species inhabit the same geographic location but do not interbreed. They develop distinct characteristics or behaviors, leading to the formation of separate species without the need for geographical barriers or habitat changes.
Genetic Drift
Genetic Drift is plays a very an important part in the evolutionary process of evolution. It refers to means the variation in allele frequencies from one generation to the next which happens because of the random sampling of gametes in finite a countable populations. This drift process happens in all types of populations whether small or large.
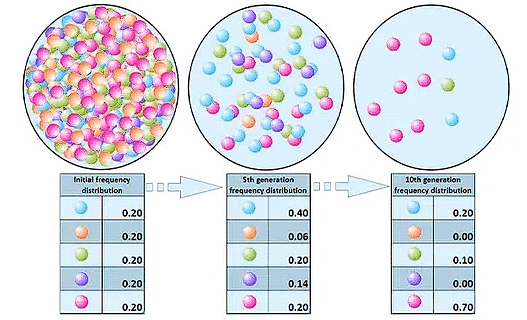
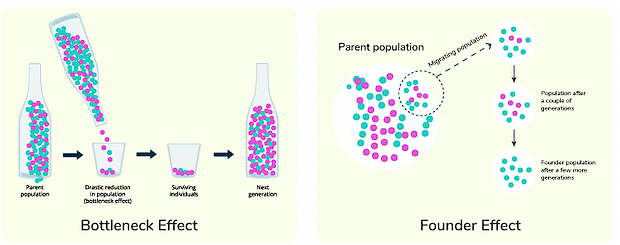
Types of Genetic Drift
There are two types of genetic drift namely the Bottleneck Effect and the Founders effect. These can be explained as follows.
1. Bottleneck Effect: In this effect, the size of the population decreases which is due to competition, predation, or diseases. The frequency of some alleles in a population changes because the organisms carrying them die. Thus, the frequency of other alleles increases because they are the only alleles left. This is observed many times during natural disasters like earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, drought, tsunamis, etc. These natural calamities result in the death of most of the population.
2. Founders Effect: In this effect, a new population is found in a new location which happens due to geographical or physical barriers. They grow completely separate from the original population. This newly formed population does not interact as well as mate with the original population which results in new allele frequencies that are different from the original population.
Genetic Drift Example
The examples of Genetic drift are as follows:
(a) Island Populations: Small islands have less population. This can be understood as the small-sized population is positively related to the area thus, as the area of the island is small the population there is more likely to get influenced by genetic drift. This leads to low genetic diversity in the island population.
(b) Cheetahs: There is a hypothesis about the population of cheetahs (scientific name Acinonyx jubatus), according to which their population faced a population bottleneck in the recent history. They have been described as a species with low levels of genetic variation.
Causes of Genetic Drift
Unlike natural selection, which operates based totally on the differential health of individuals, genetic drift is pushed with the aid of hazard events. The situations that causes this phenomenon are as follows:
(a) Population Size: Genetic drift is more suggested in smaller populations, the place hazard activities can have a larger have an impact on on allele frequencies due to the confined wide variety of reproducing individuals.
(b) Random Mating: When mating is no longer based totally on the individuals’ genetic characteristics or fitness, risk performs a large function in allele transmission, probably main to shifts in allele frequencies over generations.
(c) Migration: Movement of people into or out of a population can introduce new alleles or eliminate current ones, influencing genetic variety through the random nature of migration events.
|
226 videos|247 docs|150 tests
|
FAQs on Speciation & Genetic Drift - Biology for ACT
| 1. What is speciation? |  |
| 2. What are the types of speciation? |  |
| 3. What is genetic drift? |  |
| 4. What are the types of genetic drift? |  |
| 5. Can genetic drift lead to speciation? |  |





















