NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Biology Class 12 > Fertilization and Implantation
Fertilization and Implantation | Biology Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Fertilisation Process |

|
| Sex Determination |

|
| Cleavage and Development of Zygote |

|
| Attachment and Implantation |

|
Introduction
During copulation (coitus), semen is released by the penis into the vagina (insemination). The motile sperm swim rapidly, passing through the cervix, entering the uterus, and finally reaching the ampullary region of the fallopian tube. The ovum released by the ovary is also transported to the ampullary region, where fertilisation occurs. Fertilisation can only take place if the ovum and sperm are transported simultaneously to the ampullary region. This is why not all instances of copulation result in fertilisation and pregnancy.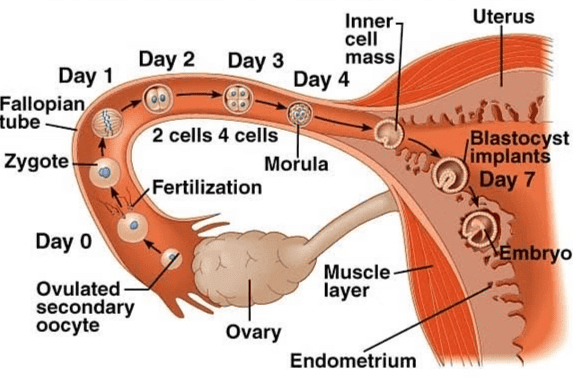 From Ovulation to Implantation
From Ovulation to Implantation
Fertilisation Process
- The process of fusion between a sperm and an ovum is known as fertilisation. When a sperm comes into contact with the zona pellucida layer of the ovum , it induces changes in the membrane that block the entry of additional sperms. This ensures that only one sperm can fertilise an ovum.
- The secretions of the acrosome help the sperm enter the cytoplasm of the ovum through the zona pellucida and the plasma membrane. This action triggers the completion of the meiotic division of the secondary oocyte.
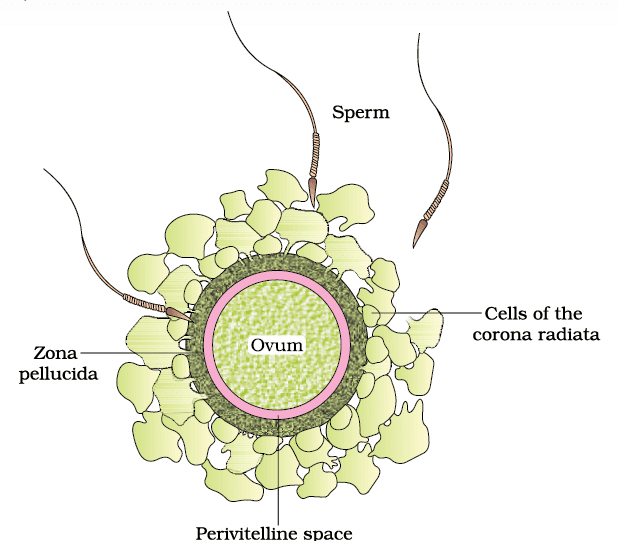
- The second meiotic division is also unequal, resulting in the formation of a second polar body and a haploid ovum (ootid). Shortly after, the haploid nuclei of the sperm and the ovum fuse together to form a diploid zygote.
Question for Fertilization and ImplantationTry yourself: Which process involves the fusion of a sperm and an ovum to form a zygote?View Solution
Sex Determination
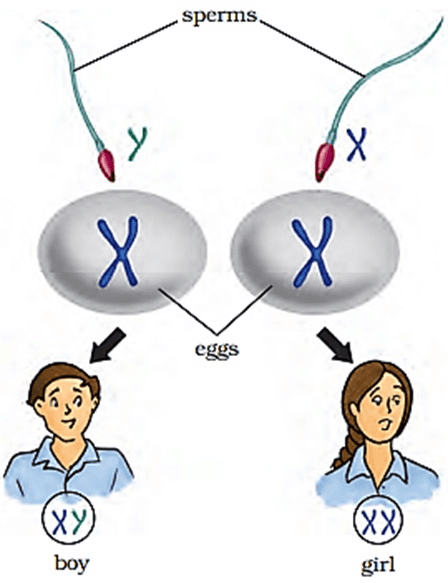
- The zygote inherits 46 chromosomes—23 from the sperm and 23 from the ovum. The sex of the baby is determined at this stage based on the sex chromosomes contributed by the parents.
- Human females have two X chromosomes (XX), while males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY). All female gametes (ova) carry an X chromosome, while male gametes (sperms) carry either an X or a Y chromosome. Thus, 50% of sperms carry X and 50% carry Y.
- If a sperm carrying an X chromosome fertilises the ovum, the zygote will be XX (female). If a sperm carrying a Y chromosome fertilises the ovum, the zygote will be XY (male).
- Therefore, the sex of the baby is determined by the father, not the mother.
Cleavage and Development of Zygote
- As the zygote travels through the isthmus of the oviduct towards the uterus, it undergoes mitotic divisions, creating 2, 4, 8, 16 daughter cells known as blastomeres.
- The embryo with 8 to 16 blastomeres is called a morula.
- The morula continues to divide and transforms into a blastocyst as it moves further into the uterus.
- In the blastocyst, the blastomeres are arranged into an outer layer called trophoblast and an inner group of cells called the inner cell mass.
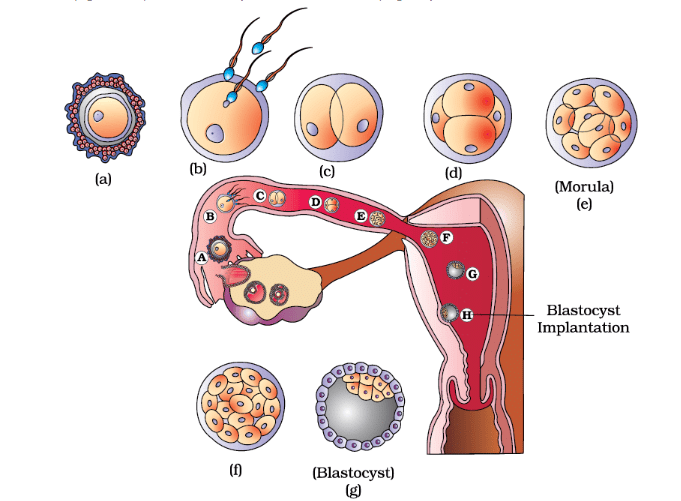 Transport of ovum, fertilisation and passage of growing embryo through fallopian tube
Transport of ovum, fertilisation and passage of growing embryo through fallopian tube
Attachment and Implantation
- The trophoblast layer attaches to the endometrium, and the inner cell mass differentiates into the embryo.
- After attachment, the uterine cells divide rapidly and cover the blastocyst, leading to its embedding in the endometrium of the uterus. This process is called implantation, which marks the beginning of pregnancy.
Question for Fertilization and ImplantationTry yourself: Which parent determines the sex of the baby?View Solution
The document Fertilization and Implantation | Biology Class 12 - NEET is a part of the NEET Course Biology Class 12.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
59 videos|290 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on Fertilization and Implantation - Biology Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is the process of fertilization in humans? |  |
Ans.Fertilization in humans occurs when a sperm cell from a male penetrates and merges with an egg cell from a female. This typically takes place in the fallopian tubes and results in the formation of a zygote, which contains genetic material from both parents.
| 2. How long after fertilization does implantation occur? |  |
Ans.Implantation usually occurs about 6 to 10 days after fertilization. During this time, the zygote, now a blastocyst, travels down the fallopian tube and embeds itself into the uterine lining, where it can begin to develop into an embryo.
| 3. What factors can affect the success of implantation? |  |
Ans.Factors that can affect the success of implantation include the quality of the embryo, the thickness and receptiveness of the uterine lining, hormonal balance in the body, and the presence of any underlying health conditions such as endometriosis or uterine abnormalities.
| 4. What are the signs of successful implantation? |  |
Ans.Signs of successful implantation may include light spotting or bleeding (often referred to as implantation bleeding), mild cramping, and changes in hormone levels that can lead to early pregnancy symptoms such as nausea or breast tenderness.
| 5. Can fertilization occur without ovulation? |  |
Ans.No, fertilization cannot occur without ovulation. Ovulation is the process where an egg is released from the ovary, making it available for fertilization by sperm. If ovulation does not occur, there will be no egg for the sperm to fertilize.
Related Searches
















