Heredity & Mendel's Laws of Inheritance | Biology for ACT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Heredity? |

|
| What is Inheritance? |

|
| Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance |

|
| Mendel’s Experiments |

|
| Monohybrid Cross |

|
| Dihybrid Cross |

|
| Mendel’s laws |

|
What is Heredity?
Heredity refers to the transmission of traits or characteristics from parents to offspring through either asexual or sexual reproduction. These traits are carried on chromosomes in the form of genes. Essentially, heredity determines the genetic makeup of an individual, influencing their physical and behavioral traits.
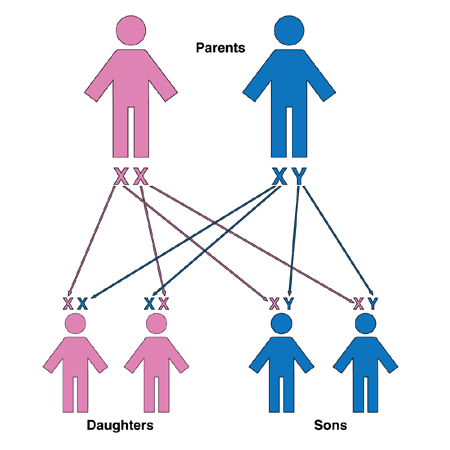 How heredity occurs in human beings
How heredity occurs in human beings
What is Inheritance?
Inheritance can be defined as the process of how a child receives genetic information from the parent. The whole process of heredity is dependent upon inheritance and it is the reason that the offsprings are similar to the parents. This simply means that due to inheritance, the members of the same family possess similar characteristics.
It was only during the mid 19th century that people started to understand inheritance in a proper way. This understanding of inheritance was made possible by a scientist named Gregor Mendel, who formulated certain laws to understand inheritance known as Mendel’s laws of inheritance.
Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance
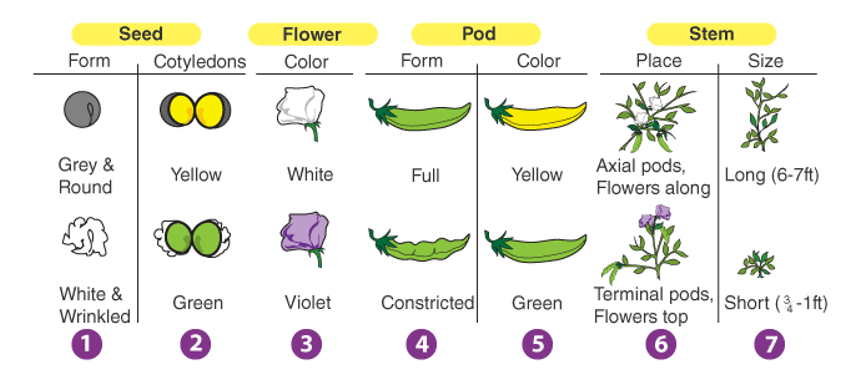
Between 1856-1863, Mendel conducted the hybridization experiments on the garden peas. During that period, he chose some distinct characteristics of the peas and conducted some cross-pollination/ artificial pollination on the pea lines that showed stable trait inheritance and underwent continuous self-pollination. Such pea lines are called true-breeding pea lines.
Why was Pea Plant Selected for Mendel’s Experiments?
He selected a pea plant for his experiments:
- The pea plant can be easily grown and maintained.
- They are naturally self-pollinating but can also be cross-pollinated.
- It is an annual plant, therefore, many generations can be studied within a short period of time.
- It has several contrasting characters.
Mendel conducted 2 main experiments to determine the laws of inheritance. These experiments were:
- Monohybrid Cross Experiment
- Dihybrid Cross Experiment
While experimenting, Mendel found that certain factors were always being transferred down to the offspring in a stable way. Those factors are now called genes i.e. genes can be called the units of inheritance.
Mendel’s Experiments
Mendel experimented on a pea plant and considered 7 main contrasting traits in the plants. Then, he conducted both the experiments to determine the aforementioned inheritance laws. A brief explanation of the two experiments is given below.
Monohybrid Cross
In this experiment, Mendel took two pea plants of opposite traits (one short and one tall) and crossed them. He found the first generation offsprings were tall and called it F1 progeny. Then he crossed F1 progeny and obtained both tall and short plants in the ratio 3:1. To know more about this experiment, visit Monohybrid Cross – Inheritance Of One Gene.
Mendel even conducted this experiment with other contrasting traits like green peas vs yellow peas, round vs wrinkled, etc. In all the cases, he found that the results were similar. From this, he formulated the laws of Segregation And Dominance.
Dihybrid Cross
In a dihybrid cross experiment, Mendel considered two traits, each having two alleles. He crossed wrinkled-green seed and round-yellow seeds and observed that all the first generation progeny (F1 progeny) were round-yellow. This meant that dominant traits were the round shape and yellow colour.
He then self-pollinated the F1 progeny and obtained 4 different traits wrinkled-yellow, round-yellow, wrinkled-green seeds and round-green in the ratio 9:3:3:1.
Check Dihybrid Cross and Inheritance of Two Genes to know more about this cross.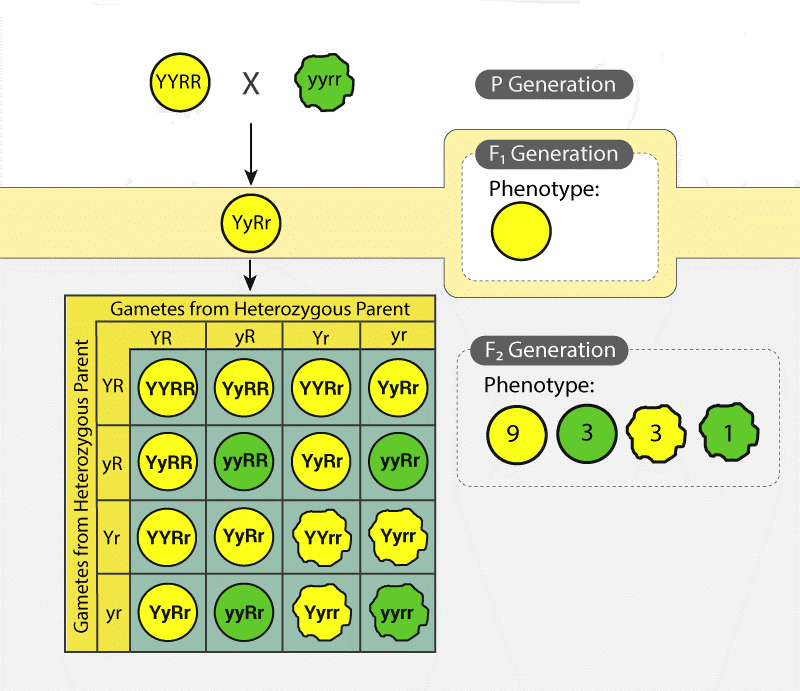
After conducting for other traits, the results were found to be similar. From this experiment, Mendel formulated his second law of inheritance i.e law of Independent Assortment.
Conclusions from Mendel’s Experiments
- The genetic makeup of the plant is known as the genotype. On the contrary, the physical appearance of the plant is known as phenotype
- The genes are transferred from parents to the offsprings in pairs known as allele.
- During gametogenesis when the chromosomes are halved, there is a 50% chance of one of the two alleles to fuse with the other parent.
- When the alleles are the same, they are known as homozygous alleles and when the alleles are different they are known as heterozygous alleles.
Mendel’s laws
The two experiments lead to the formulation of Mendel’s laws known as laws of inheritance which are:
- Law of Dominance
- Law of Segregation
- Law of Independent Assortment
Law of Dominance
This is also called Mendel’s first law of inheritance. According to the law of dominance, hybrid offsprings will only inherit the dominant trait in the phenotype. The alleles that are suppressed are called as the recessive traits while the alleles that determine the trait are known as the dormant traits.
Law of Segregation
The law of segregation states that during the production of gametes, two copies of each hereditary factor segregate so that offspring acquire one factor from each parent. In other words, allele (alternative form of the gene) pairs segregate during the formation of gamete and re-unite randomly during fertilization. This is also known as Mendel’s third law of inheritance.
Law of Independent Assortment
Also known as Mendel’s second law of inheritance, the law of independent assortment states that a pair of trait segregates independently of another pair during gamete formation. As the individual heredity factors assort independently, different traits get equal opportunity to occur together.
Key Points on Mendel’s Laws
- The law of inheritance was proposed by Gregor Mendel after conducting experiments on pea plants for seven years.
- The Mendel’s laws of inheritance include law of dominance, law of segregation and law of independent assortment.
- The law of segregation states that every individual possesses two alleles and only one allele is passed on to the offspring.
- The law of independent assortment states that the inheritance of one pair of genes is independent of inheritance of another pair.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the three laws of inheritance proposed by Mendel?
The three laws of inheritance proposed by Mendel include:
- Law of Dominance
- Law of Segregation
- Law of Independent Assortment
Which is the universally accepted law of inheritance?
Law of segregation is the universally accepted law of inheritance. It is the only law without any exceptions. It states that each trait consists of two alleles which segregate during the formation of gametes and one allele from each parent combines during fertilization.
Why is the law of segregation known as the law of purity of gametes?
The law of segregation is known as the law of purity of gametes because a gamete carries only a recessive or a dominant allele but not both the alleles.
Why was the pea plant used in Mendel’s experiments?
Mendel picked pea plant in his experiments because the pea plant has different observable traits. It can be grown easily in large numbers and its reproduction can be manipulated. Also, pea has both male and female reproductive organs, so they can self-pollinate as well as cross-pollinate.
What was the main aim of Mendel’s experiments?
The main aim of Mendel’s experiments was:
- To determine whether the traits would always be recessive.
- Whether traits affect each other as they are inherited.
- Whether traits could be transformed by DNA.
|
226 videos|247 docs|150 tests
|
FAQs on Heredity & Mendel's Laws of Inheritance - Biology for ACT
| 1. What is heredity and how does it relate to Mendel's laws of inheritance? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between heredity and inheritance in terms of genetics? |  |
| 3. What were Mendel's key experiments that led to the discovery of his laws of inheritance? |  |
| 4. How do monohybrid and dihybrid crosses demonstrate Mendel's laws of inheritance? |  |
| 5. What are the three main laws of inheritance proposed by Mendel and how do they apply to genetic inheritance? |  |
















