Digital Electronics & Logic Gates | Physics Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
What is Digital Electronics?
Digital electronics is defined as
 View Answer
View Answer 
The branch of electronics that deals with digital data in the form of codes. There are only two codes in digital electronics, and they are 0 and 1. 0 is considered to be low logic while 1 is considered to be high logic.
Components of Digital Electronics
Digital electronics or the digital circuit comprises various components that perform specific functions. These components are divided into two categories:
- Active components
- Passive components
The active components are the transistors and diodes while the passive components are the capacitors, resistors, inductors, etc.
Active Components
- Diodes:
Diodes are manufactured using semiconductor materials. They are used for allowing the flow of current in a particular direction. Different types of diodes are used in the construction of the digital circuit. - Transistors:
A semiconductor device with three terminals is known as a transistor. The main function of the transistor is to amplify the signal, and it is also used as a switching device.
Passive Components
- Capacitors and Inductors:
The main function of the capacitor is to store electrical energy. A capacitor is made using two conducting plates and between these plates, an insulator is placed. The change in the current is resisted with the help of an inductor. They are used for storing electric energy in the magnetic field. - Battery and Switch:
The conversion of chemical energy into electric energy takes place because of the battery. It is used as a source of energy. The flow of electric current is controlled by using a switch. - Resistors:
The flow of current in the circuit is opposed by the resistor. The fixed resistor and variable resistor are the two types of resistors. All the resistors work on the basis of Ohm’s law.
Advantages of Digital System Over Analog System
- The transmission of data in digital systems takes place without degradation due to noise when compared to an analog system.
- The digital system comes with noise-immunity, which makes the storage of data easier. Whereas the analog system undergoes wear and tear, which degrades the information in storage.
- The digital system comes with an interface with computers which makes it easy to control the data. The system can be kept bug free by updating the software. This feature is not available in the analog system.
Disadvantages of Digital System
Though the digital system has noise-immunity and better storage it does have disadvantages too:
- The energy consumed by the digital system is more compared to the analog system. This energy is consumed in calculations and signal processing which results in the generation of heat.
- These systems are expensive.
- The digital systems are fragile, that is if one of the digital data is misinterpreted, the final data will change completely.
- Taking care of analog issues in digital systems could be demanding as analog components are used in designing the digital system.
Applications of Digital Circuits
Digital electronics or digital circuits are an integral part of electronic devices and here are the uses of digital circuits:
- The display of digital watches is designed based on digital circuits.
- Rocket science and quantum computing use digital electronics.
- The automatic doors work on the principle of digital electronics.
- Everyday encounters with traffic lights are based on digital circuits.
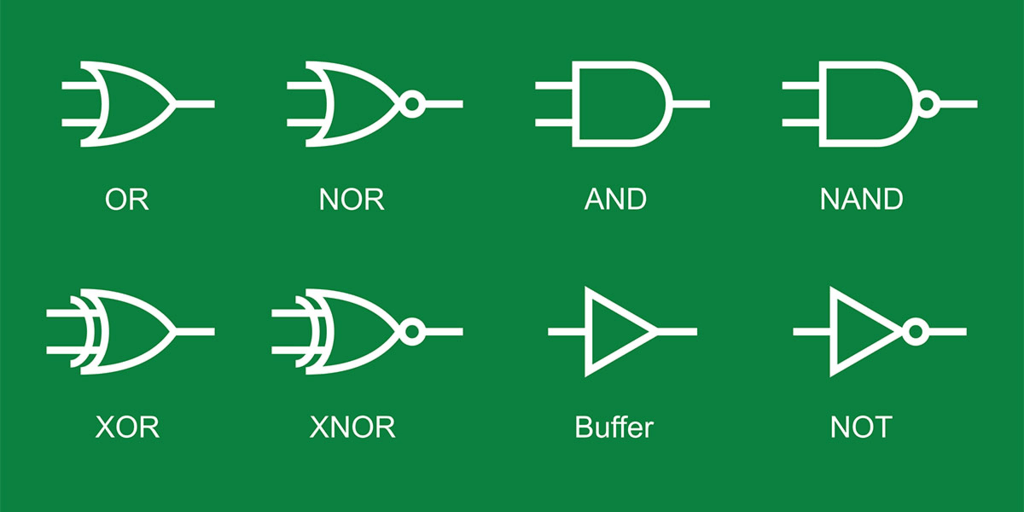
Logic Gate
A digital circuit that allows a signal to pass through it, only when few logical relations are satisfied, is called a logic gate.
Truth Table
A table that shows all possible input and output combinations is called a truth table.
Basic Logic Gates
(i) OR Gate It is a two input and one output logic gate.
Boolean expression Y = A + B (Y equals A OR B)
(ii) AND Gate It is a two input and one output logic gate
Boolean expression Y = A . B (Y equals A AND B)
(iii) NOT Gate It is a one input and one output logic gate.
Combination of Gates
(i) NAND Gate When output of AND gate is applied as input to a NOT gate, then it is called a NAND gate.
Boolean expression Y = A * B (Y equals negated of A AND B)
(ii) NOR Gate When output of OR gate is applied as input to a NOT gate, then it is called a NOR gate.
Boolean expression Y = A + B ( Y equals negated of A OR B)
- The Boolean expression obey commutative law associative law as well as distributive law.
- A + B = B+ A
- A· B = B· A
- A + (B + C) = (A + B) + C
- Demorgan’s theorems
|
74 videos|314 docs|88 tests
|
FAQs on Digital Electronics & Logic Gates - Physics Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is digital electronics? |  |
| 2. What are the components of digital electronics? |  |
| 3. What is a logic gate in digital electronics? |  |
| 4. How do logic gates work in digital electronics? |  |
| 5. What are some applications of digital electronics? |  |

















