Introduction to Logic Families | Digital Electronics - Electrical Engineering (EE) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Classification of Logic Families |

|
| Bipolar Logic Family |

|
| Unipolar Logic Family |

|
| Features of Logic Families |

|
| Characteristics of the digital logic family |

|
A logic family is a collection of different integrated circuit chips that have similar input, output, and internal circuit characteristics, but they perform different logic gate functions such as AND, OR, NOT, etc. The idea is that different logic gate functions, when fabricated in the form of an integrated circuit with the same approach, or which belongs to the same logic family, will have identical electrical characteristics (electrically compatible with each other). These families may vary by speed, power consumption, cost, voltage and current levels.
Classification of Logic Families
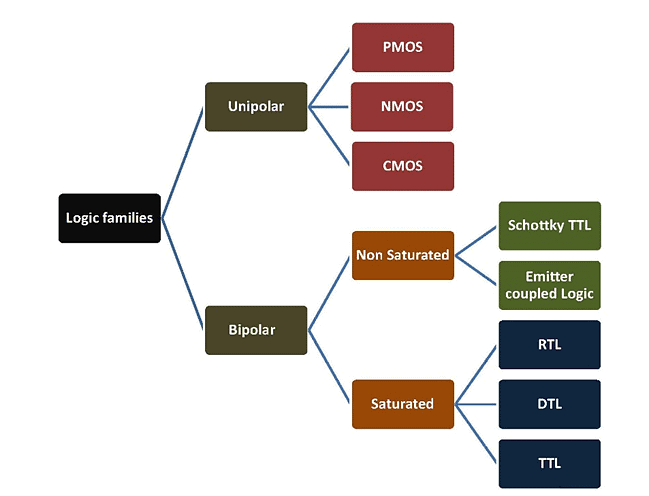
The most common logic family in modern semiconductor devices is Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) logic, due to lower power consumption, small sized transistor, and high transistor density.
The digital integrated circuits are designed using bipolar devices or Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) or a combination of both. There are two kinds of semiconductor devices. The logic family which falls under the first kind Bipolar logic family and the other is Unipolar logic family.
Bipolar Logic Family
It mainly uses bipolar devices like diodes, transistors in addition to passive elements like resistors and capacitors.
There are two kinds of operations in bipolar integrated circuits: Saturated Bipolar Logic family and Non-saturated Bipolar Logic family.
Saturated Bipolar Logic Families: In this family the transistors used in ICs are driven into saturation.
- Diode logic (DL)
- Resistor Transistor Logic (RTL)
- Diode Transistor Logic (DTL)
- Integrated Injection Logic (IIL or I2L)
- Transistor Transistor Logic (TTL)
- High Threshold Logic (HTL)
Non-saturated Bipolar Logic Families: In this family the transistors used in IC is not driven into saturation.
- Schottky TTL
- Emitter Coupled Logic (ECL)
Unipolar Logic Family
Unipolar logic family consists of Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) logic families. It mainly uses Unipolar devices like MOSFETs in addition to passive elements like resistors and capacitors. These logic families have the advantages of high speed and lower power consumption than Bipolar families. They are:
- P - type MOS (PMOS) Logic
- N - type MOS (NMOS) logic
- Complementary MOS (CMOS) logic
- Bipolar MOS (BiMOS) logic
- Bipolar CMOS (BiCMOS) logic
Features of Logic Families
- TTL - Transistor-Transistor Logic: Standard logic family; used for the longest time.
- ECL - Emitter Coupled Logic: Suitable for systems requiring high-speed operations.
- MOS - Metal Oxide Semiconductor Logic: Suitable for systems with high component density.
- CMOS - Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor Logic: Suitable for systems with low power consumption (VLSI circuits). Gradually becomes the dominant logic family.
Characteristics of the digital logic family
(i) Propagation Delay
- It is the time interval between the application of the input pulse and the occurrence of the output. It is an important characteristic of the digital logic family.
- If the propagation delay is less, then the speed at which the IC operates will be faster.
- Let THL is the propagation delay when the output changes from logic 0 to 1 and TLH is the delay when the output changes from logic 1 to 0. The maximum value of THL and TLH is considered as the propagation delay for that logic gate.
(ii) Fan in and Fan out
- Fan-in refers to the number of inputs in a digital logic gate family. For the example given in the figure below, the EX-OR gate has three inputs. So, fan-in for the given EX-OR gate is 3.
- Fan-out refers to the number of inputs that is driven by the output of another logic gates.
- For example, the following circuit has an EX-OR gate, which drives 4 NOT gates. So fan-out of EX-OR gate is 4.
- Both fan-in and fan-out values are given by the manufacturer at the time of designing and the data is specified in the datasheet. When the number of inputs or outputs are changed, it may cause some malfunction to the device.
(iii) Power Dissipation
- It is the amount of power that the digital circuit dissipates. The power dissipated is determined by the average current, that is drawn from the supply voltage.
- The average current is the average value of the current at LOW gate output(logic ‘o’) and the current at HIGH gate output (logic ‘1’).
Noise Immunity and Noise Margin
(a) What is Noise?
- It is an unwanted signal that is superimposed on the normal operating signal. Noise may be due to various factors like operating environment, radiations, stray electrical and magnetic fields.
- In digital logic circuits, the binary values 0 and 1 represent the LOW and HIGH voltage levels. Due to the interference of the noises, the voltage levels may increase or decrease. This may lead to the wrong operation of the device.
- The noise immunity is the ability of the logic device to tolerate the noise without causing spurious change to the output voltage. Noise margin allows the logic device to function properly within the specified limits.
(b) Figure of Merit
- For an efficient operation of any device, whether it may be digital or analog, the power dissipation and the speed are notable characteristics. Achieving a higher speed with less power dissipation is a highly challenging task.
- In the digital logic circuit, a trade-off exists between these two characteristics. That is, for higher speed, the power dissipation will be more.
- The figure of merit or Speed Power Product is a common means of measuring the performance of circuits in the digital logic family.
|
125 videos|83 docs|58 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction to Logic Families - Digital Electronics - Electrical Engineering (EE)
| 1. What is the difference between bipolar and unipolar logic families? |  |
| 2. What are some examples of bipolar logic families? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of unipolar logic families? |  |
| 4. What are the main features of logic families? |  |
| 5. What are the characteristics of digital logic families? |  |
















