Revision Notes, Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology, Physical Education | Physical Education Class 11 (XI) - CBSE and NCERT Curriculum PDF Download
Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology
8.1 Definition of Anatomy, Physiology and its importance
8.2 Functions of the skeleton system, classification of bones and types of joints
8.3 Function and structure of the Respiratory system
8.4 Structure of Heart and Introduction to circulatory system
8.1 Anatomy: Anatomy is the study of the shape and structure of the body Physiology: It is the study of functions systems of the human body.
8.2 Skeleton System: This is the bony framework of the body consisting of numbers of bones. Total bones in the human body are 206.
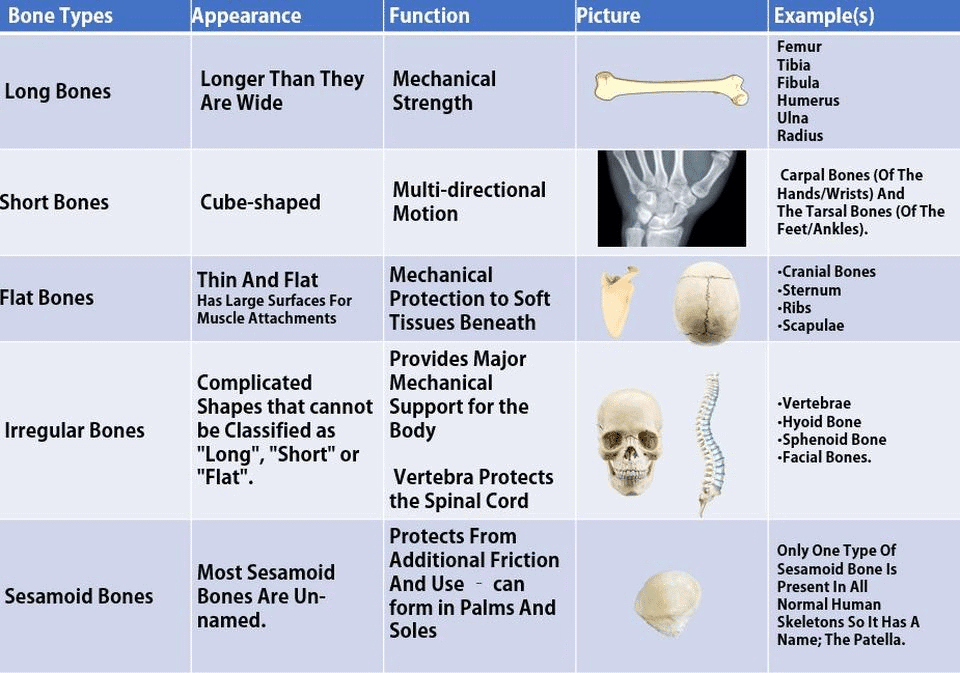
Classification of Bones
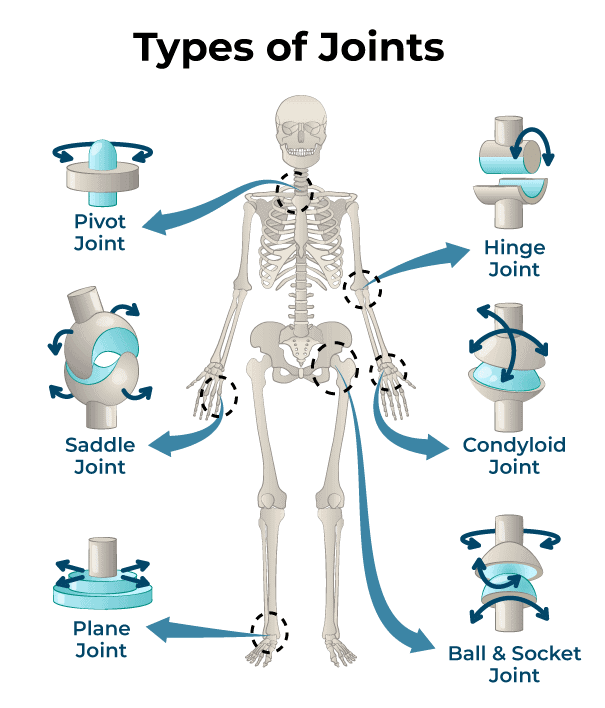
Types of Joints
1. Immovable Joints: These joints are fixed and do not move eg. skull Joint
2. Slightly Movable Joints: The movement of such joints is very limited eg. Inter-vibrations.
3. Freely Movable Joints: Such joints are freely movable.
8.3 Muscular System:- Properties of Muscles
The Definition of Muscle: Muscle is the tissue composed of fibers capable to effect bodily movement or muscle is the body tissue that can contract to produce movement.
- Movement is possible in the human body due to movement contraction and expansion of muscles.
- The human muscular system is made up of 600 muscles which act in a group.
- The study of muscles is known as 'Myology'
- They also give shape to the individual.
- 40% to 50% of body weight is the weight of muscles in the body.
- Muscles also assist in the circulation of blood.
Structure of Muscle: Every muscle fiber made up of a very large number of microscopic threads called myofibril. Each myofibril consists of protein molecules called Active and myosin.
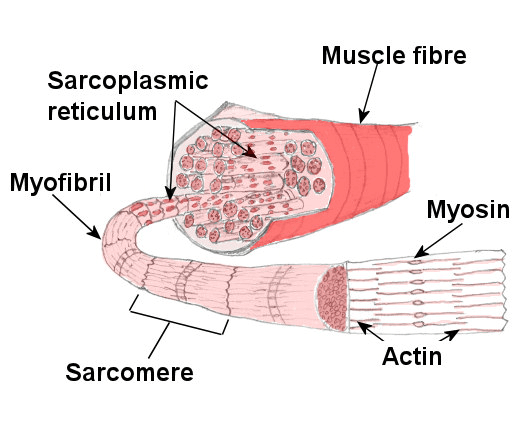 Fig: Structure of muscle.
Fig: Structure of muscle.
8.4 Structure and functions of the Respiratory system:
Respiratory System: Respiratory system is a system which regulates the exchange of gases.
Structure of the respiratory system involves the following organs in human beings.
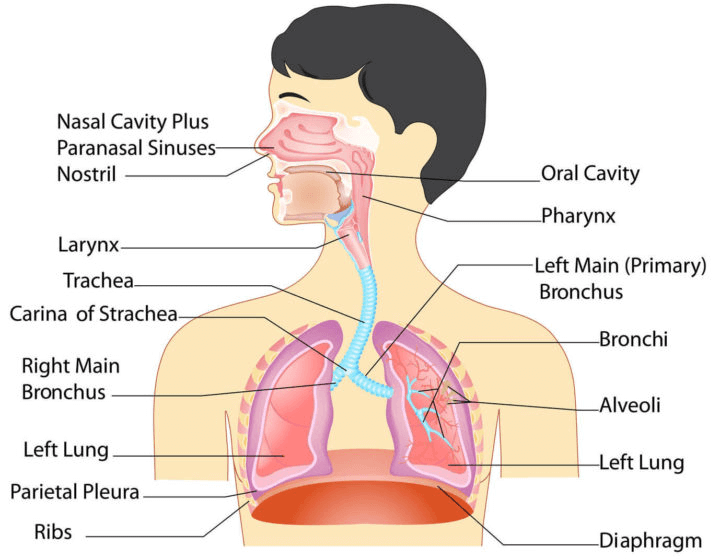 Fig: Respiratory systems in humans.Types of Respiration
Fig: Respiratory systems in humans.Types of Respiration
1. External Respiration
2. Internal tissues Respiration
Functions of Respiration System
— To provide oxygen to the blood
— Removal of waste products forms the body eg. CO2
— Maintain body temperature
— It affects the circulation of blood
Structure of Heart and introduction of a circulatory system
Circulatory System: Circulatory system serves the function of transporting materials in the body. It consists of the heart, blood vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries)
Heart: The human heart is a hollow cone-shaped muscular organ. It is a pumping system inside the body.
Structure of Heart: The heart is divided into four chambers. A septum divides it into a left and right side. Each side is further divided into an upper and lower chamber. The upper two chambers called auricles and the bottom chambers are ventricles.
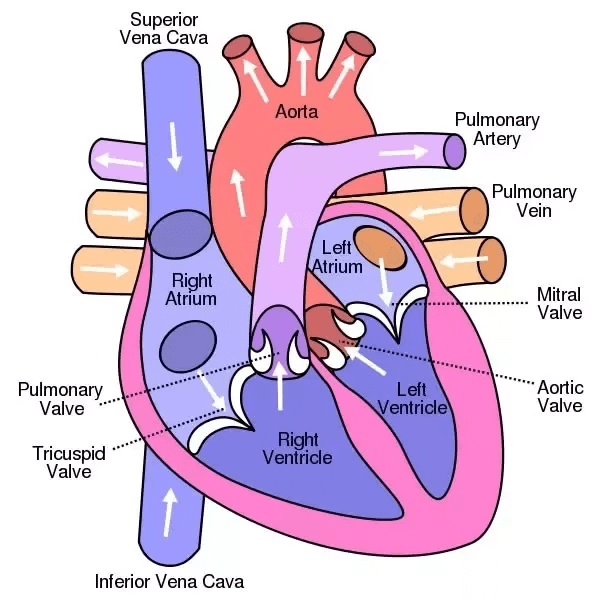 Fig: Structure of heart.
Fig: Structure of heart.
The function of Heart : Arteries - |
Arteries are blood vessels that take blood away from the heart, except for the pulmonary artery, which carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs. |
| |
Veins | : Veins are blood vessels that return blood to the heart. |
Capillaries | : Exchange of material take-place in capillaries. There are about 7000 m of blood capillaries inside the body of an adult. |
Blood | : Blood is a special mixture of fluid which acts as a medium of transporting nutrients and gases from one part of the body to another. |
Heart Rate | : It is a number of pumping of heart in one minute. |
Stroke Volume | : It is the volume of blood pumped by the heart in one beat. It is approximately 80 ml beat in a normal adult, whereas trained players have 100 ml beat as stroke. |
Cardiac Output | : Stroke volume x heart rate. It is 5 to 6 liters at a basal level. |
Blood Pressure | : It is the force exerted by the blood on the walls of the blood vessels |
Second Wind | : The breathlessness caused due to prolonged exercises is removed automatically by our body. It is called a second wind. |
Oxygen Debt | : The amount of oxygen taken by an athlete during the recovery period after the strenuous activity is called oxygen debt. |
|
33 videos|47 docs|23 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes, Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology, Physical Education - Physical Education Class 11 (XI) - CBSE and NCERT Curriculum
| 1. What are the main components of the human skeletal system? |  |
| 2. How does the muscular system contribute to body movement? |  |
| 3. What is the role of the respiratory system in human physiology? |  |
| 4. How do the circulatory and respiratory systems work together? |  |
| 5. What are the key functions of the digestive system in the human body? |  |

















