Revision Notes, Kinesiology, Biomechanics and Sports, Physical Education | Physical Education Class 11 (XI) - CBSE and NCERT Curriculum PDF Download
Kinesiology, Biomechanics, and Sports
9.1 Meaning and importance of kinesiology and Biomechanics in Physical Education and sports
9.2 Lever and its types and its application in sports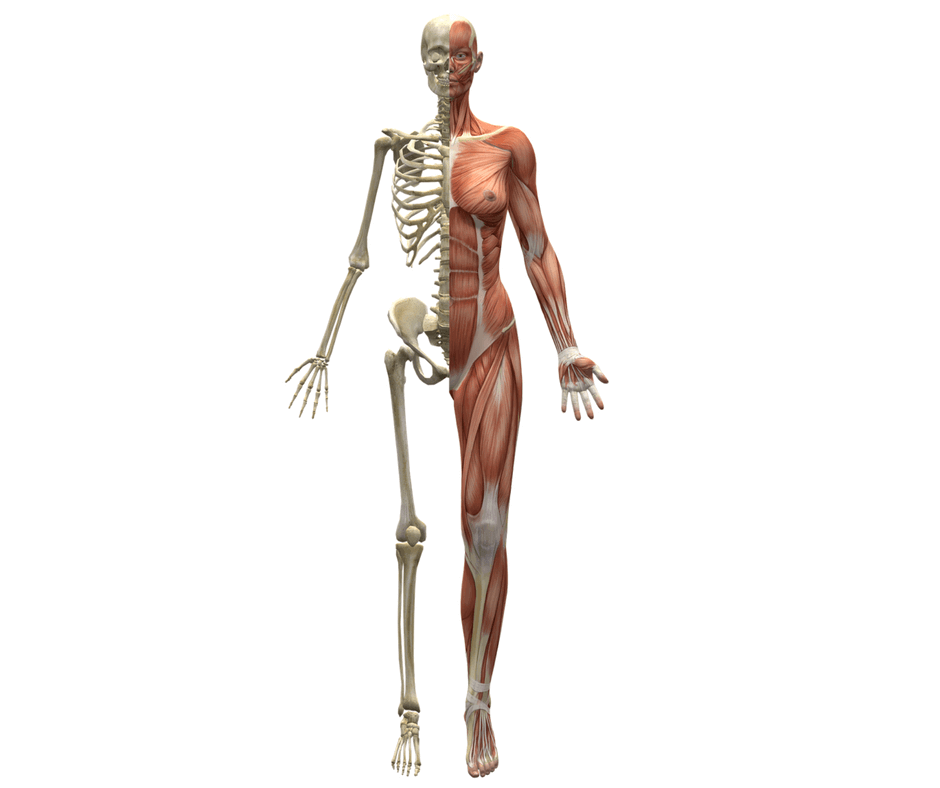 Fig: Kinesiology9.3 Equilibrium – Dynamic and static, the center of Gravity and its application in sports9.4 Force – Centrifugal and centripetal and its application in sports
Fig: Kinesiology9.3 Equilibrium – Dynamic and static, the center of Gravity and its application in sports9.4 Force – Centrifugal and centripetal and its application in sports
9.5 Introduction to the buoyancy force
9.1 (a) Meaning of Kinesiology
Kinesiology is the study of human or non-human and movement Kinesiology is the study of human and animal body movements, performance, and function by applying the sciences of biomechanics, anatomy, physiology, psychology, and neuroscience.
9.1 (b) BIOMECHANICS
Biomechanics is derived from Greek words. Bio-means living things and mechanics is a field of physics. Thus, the branch of science, which deals with the forces related to body movements.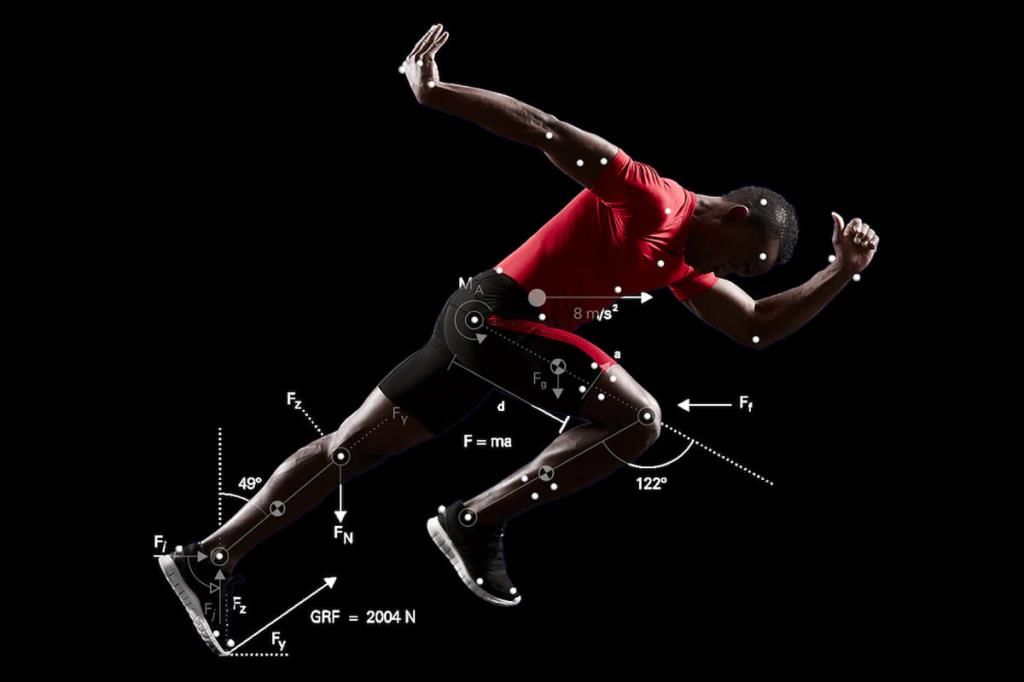 Fig: BiomechanicsBiomechanics is defined as the systematic study of the mechanics of body joints.
Fig: BiomechanicsBiomechanics is defined as the systematic study of the mechanics of body joints.
According to Wikipedia, "biomechanics is the study of structure and function of the biological system of humans."
9.1 (c) IMPORTANCE OF BIOMECHANICS IS SPORTS
• Improve performance in sports
• Improvements in technique.
• Development of sports equipment.
• Prevents in training technique
• Helps in understanding the human body.
• Knowledge of safety principles.
• Helps in research work.
• Creates confidence in the player.
• Helps in maintaining a healthy body.
• Increase the popularity of sports.
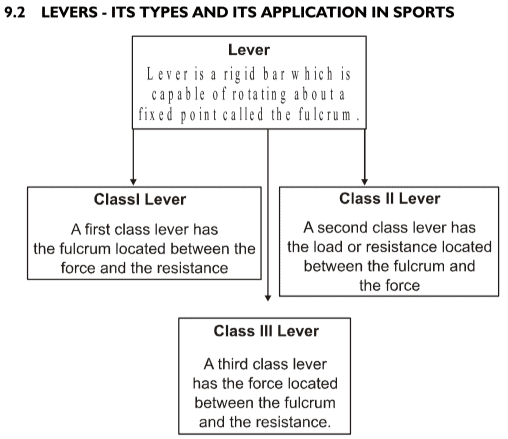 Class I Lever: A first class lever has the fulcrum located between the force and the resistance.
Class I Lever: A first class lever has the fulcrum located between the force and the resistance.
Example: See saw a pair of sensors, cycle bracket etc.
Class II Lever: A second class lever has the load or resistance located between the fulcrum and the force.
Example: Punching machine, calisthenics and straight push-ups etc.
Class III Lever:- A third class lever has the force located between the fulcrum and the resistance.
Example: - Baseball bat, tennis racket, and boat paddles etc.
9.3 Equilibrium DYNAMIC AND STATIC AND CENTER OF GRAVITY AND ITS APPLICATION IN SPORTS
Equilibrium:- It is defined as a state of balance or a stable situation, where opposite forces cancel each other out and there is no changes are occurring. Fig: EquilibriumTypes of Equilibrium
Fig: EquilibriumTypes of Equilibrium
(i) Dynamic Equilibrium:- It is the balance of the body during movement.
(ii) Static Equilibrium:- Dynamic stability is a balance of the body during its rest or stable position.
Or
Static equilibrium is when the center of gravity is in a stable position.
GUIDANCE PRINCIPLES TO DETERMINE THE DEGREE OF STABILITY
1. Broader the base, greater the stability.
2. Lower the center of gravity, higher the stability
3. When the body is free in the air if the head and feet moves then hips help move up and vice-versa.
4. Body weight is directly proportional to stability.
Centre of gravity:- Centre of gravity is that point in a body or system around which its mass or weight is evenly distributed or balanced and through which they force of gravity acts. The center of gravity is fixed, provided the size and shape of the body do not change.
9.4 Force - CENTRIFUGAL AND CENTRIPETAL AND ITS APPLICATION IN SPORTS
Force - Force can be defined as a push or pull by one body acting upon another. Force is a product of mass and acceleration of an object or person.
F = ma
TYPES OF FORCES
1. Centripetal force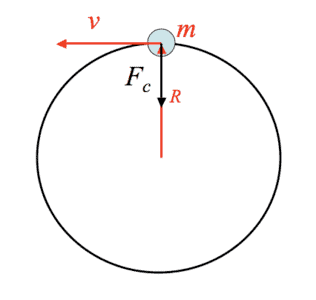 Fig: Centripetal force2. Centrifugal force
Fig: Centripetal force2. Centrifugal force
3. Gravitational
4. Fractional force
5. Static force
IMPORTANCE AND APPLICATION OF FORCE IN SPORTS
1. Help to move:
2. Stop the moving object.
3. Helps to accelerate.
4. Helps in throwing an object.
5. Helps to lift the object.
6. Helps to pull the object.
9.5 Introduction of Buoyancy
The Buoyancy refers to a force that arises from the pressure exerted on an object by a fluid.
The buoyancy force always points upwards because the pressure of a fluid increases with depth.
The buoyant force on an object can be calculated using the Archimedes principle.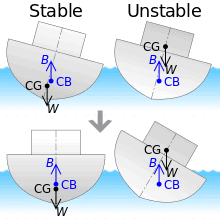 Fig: BuoyancyTypes of Buoyancy
Fig: BuoyancyTypes of Buoyancy
Positive Buoyancy: The object or person floats upward in the water or remains floating on the water or remain floating on the surface.
Negative Buoyancy: The object or person sinks downwards in the water or remains on the bottom.
Neutral Buoyancy: The objects or person neither sinks downwards nor floats upward but remains suspended in the water at a single depth.
Archimedes principle states what the upward buoyant force that is exerted in a body immersed in a fluid, whether fully or partially submerged, is equal to the weight of the fluid that the body displaces and acts in an upward direction at the center of mass of the displaced fluid.
|
33 videos|47 docs|23 tests
|
FAQs on Revision Notes, Kinesiology, Biomechanics and Sports, Physical Education - Physical Education Class 11 (XI) - CBSE and NCERT Curriculum
| 1. What is kinesiology? |  |
| 2. What is biomechanics and how is it related to sports? |  |
| 3. How is kinesiology related to physical education? |  |
| 4. What are some common career options in kinesiology and biomechanics? |  |
| 5. How can knowledge of kinesiology and biomechanics benefit athletes? |  |

















