NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Political Science - The End of Bipolarity
Q1: Which among the following statements that describe the nature of Soviet economy is wrong?
(a) Socialism was the dominant ideology.
(b) State ownership/control existed over the factors of production.
(c) People enjoyed economic freedom.
(d) Every aspect of the economy was planned and contained by the state.
Ans: (c) People enjoyed economic freedom
The Soviet economy was characterized by state control and central planning. Economic freedom was highly restricted, with the government controlling most aspects of economic activity.
Q2: Arrange the following in chronological order:
(a) Soviet invasion of Afghanistan
(b) Fall of the Berlin Wall
(c) Disintegration of Soviet Union
(d) Russian Revolution
Ans:
(d) Russian Revolution (1917)
(a) Soviet invasion of Afghanistan (1979)
(b) Fall of the Berlin Wall (Nov 1989)
(c) Disintegration of Soviet Union
Q3: Which among the following is NOT an outcome of the disintegration of the USSR?
(a) End of the ideological war between the US and USSR
(b) Birth of CIS
(c) Change in the balance of power in the world order
(d) Crises in the Middle East
Ans: (d) Crises in the Middle East
While the disintegration of the USSR had global implications, the crises in the Middle East were not a direct outcome of it. The other options are directly related to the aftermath of the USSR's collapse.
Q4: Match the following:
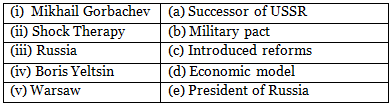 Ans: (i)-(c); (ii)-(d); (iii)-(a); (iv)-(e); (v)-(b)
Ans: (i)-(c); (ii)-(d); (iii)-(a); (iv)-(e); (v)-(b)
(i) Mikhail Gorbachev, General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union in 1985. introduced reforms to keep the USSR abreast of the information and technological revolutions taking place in the West.
(ii) Shock Therapy, the approach to economic transition in Russia, Central Asia, and Eastern Europe influenced by the World Bank and the IMF, became a widely recognized model after the collapse of communism.
(iii) Russia came to be known as the successor of USSR after it disintegrated.
(iv) Boris Yeltsin was the first elected President of Russia (1991- 1999).
(v) The Warsaw Pact was a military alliance that unified the Soviet-controlled Eastern European countries, known as the socialist bloc, under the leadership of the USSR after World War II.
Q5: Fill in the blanks:
(a) The Soviet Political System was based on _______ ideology.
(b) _______ was the military alliance started by the USSR.
(c) _______ party dominated the Soviet Union’s political system.
(d) _______ initiated the reforms in the USSR in 1985.
(e) The fall of the _______ symbolised the end of the Cold War.
Ans:
(a) Marxist/Communist
The Soviet Political System was fundamentally rooted in Marxist ideology, which emphasized the principles of socialism and communism as guided by the ideas of Karl Marx.
(b) Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact, also known as the Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation, and Mutual Assistance, was a collective defense treaty established in 1955 by the Soviet Union and seven other Eastern Bloc socialist republics in Europe during the Cold War. It was created in response to the integration of West Germany into NATO.
(c) Communist
The Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) was the founding and ruling political party of the Soviet Union. It held a monopoly on political power, with no other parties allowed to exist.
(d) Gorbachev
Mikhail Gorbachev was the General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1985 until 1991. He introduced significant reforms known as perestroika (restructuring) and glasnost (openness) which aimed to revitalize the Soviet economy and make the government more transparent.
(e) Berlin wall
The Berlin Wall, which had divided East and West Berlin since 1961, fell on November 9, 1989. This event marked the beginning of the end for the Cold War, symbolizing the collapse of communist control in Eastern Europe and the eventual dissolution of the Soviet Union.
Q6: Mention any three features that distinguish the Soviet economy from that of a capitalist country like the US.
Ans: The three features that distinguish the Soviet economy from that of a capitalist country like the US, can be summed up as follows:
- Soviet economy experienced a complex communication network, vast energy resources and an efficient transport sector to connect its remotest areas.
- Soviet Union industries produced every domestic product from pin to cars, whose quality might not match with that of the west technology.
- Soviet Union ensured a minimum standard of living for all its citizens. Consequently Government subsidised basic necessities including health, education, children and other welfare schemes.
- There was an absence of unemployment in Soviet Union.
- Land and productive assets were owned by the state only.
Q7: What were the factors that forced Gorbachev to initiate the reforms in the USSR?
Ans: Mikhail Gorbachev was the General Secretary of Communist Party of Soviet Union in 1985. He was forced to initiate the reforms in the USSR due to following reasons:
- To keep the USSR abreast of information and technological revolutions at par the West.
- To normalise the relations with that of the West.
- To democratise the Soviet System.
- To loosen the administrative system which exempted ordinary people from the privileges.
Q8: What were the major consequences of the disintegration of the Soviet Union for countries like India?
Ans: The major consequences of the disintegration of the Soviet Union for countries like India can be analysed as follows:
- Disintegration of Soviet Union gave an end to Cold War confrontations and to ideological disputes between two superpowers.
- Military alliances had been abolished and demand arose for world peace and security.
- Multipolar system was surpassed to exist where no single power could dominate and a group of countries could play a crucial role in world politics like NAM Countries.
- The US became the sole superpower and capitalist economy became dominant at international level. World Bank and IMF became powerful advisors due to their economic support to these countries during transitional period.
- The motion of liberal democracy emerged as a way to organise political life.
- Due to disintegration of Soviet Union many new countries emerged with the independent aspirations and choices.
- The Baltic and East European states wanted to join European Union and became the part of NATO. The Central Asian countries took the advantage of their geographical location and continued close ties with Russia, West, China and others.
Q9: What was Shock Therapy? Was this the best way to make a transition from communism to capitalism?
Ans: Shock Therapy was a painful process of transition from an authoritarian socialist system to a democratic capitalist system. This transformation system was influenced by the world bank and the IMF in Russia, Central Asia and East Europe. Though it varies in intensity and speed amongst the former second world countries but its direction and features were quite similar.
This was not the best way to make a transition from communism to capitalism due to following drawbacks:
- Russia, the large state controlled industrial complex lost about 90 per cent of its industries through sales to private individuals and companies
- It created “the largest garage sale in history” which led virtual disappearance of entire industries for the restructuring was carried out by market forces in place of government owned policies.
Hence, industries were undervalued and sold at throwaway prices. - It systematically destroyed the old system of social welfare.
- The value of ‘Ruble’, the Russian currency, declined dramatically due to high rate of inflation and real GDP of Russia also declined between 1989 to 1999.
- The withdrawal of government subsidies pushed large sections of society into poverty and it emerged mafia to start controlling many economic activities.
- Privatisation led to new disparities which divided Russia between rich and poor people creating economic inequality.
- Hence, Shock Therapy brought ruin to economies and disaster upon the people of entire region.
Q10: Write an essay for or against the following proposition. “With the disintegration of the second world, India should change its foreign policy and focus more on friendship with the US rather than with traditional friends like Russia”.
Ans: India’s foreign policy should continue to prioritize its traditional partnership with Russia rather than pivoting entirely toward the United States. The Indo-Russian relationship is not merely historical but rests on strong foundations of trust, strategic cooperation, and mutual benefit.
Both nations share a vision of a multipolar world, where global power is balanced and institutions like the UN play a central role in maintaining peace and security. Over the years, their ties have been institutionalized through numerous agreements, particularly the Indo-Russia Strategic Partnership of 2001, which has deepened cooperation in key sectors.
Russia has consistently supported India on sensitive issues, including Kashmir, and has helped India secure energy resources and maintain strategic access to Central Asia. The partnership extends to critical areas such as nuclear energy and space exploration, with Russia providing vital technologies that have advanced India’s capabilities. Economically, Russia has enabled significant Indian investments in oil fields, especially in Central Asia, enhancing India’s energy security.
Defense cooperation remains a backbone of the relationship, with Russia being a primary supplier of military equipment to India. Scientific and technological collaborations have also flourished, strengthening bilateral ties.
Therefore, while India must engage with the US to meet its global aspirations, its enduring friendship with Russia remains indispensable for its strategic autonomy and balanced foreign policy.
|
151 videos|780 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Political Science - The End of Bipolarity
| 1. What were the factors contributing to the end of bipolarity in international relations? |  |
| 2. How did the end of bipolarity impact the balance of power in the world? |  |
| 3. What role did the United States play in the post-bipolar world order? |  |
| 4. How did the end of bipolarity impact regional conflicts around the world? |  |
| 5. What are the implications of the end of bipolarity on international institutions and organizations? |  |

















