(Part - 2) - Self and Personality Class 12 Psychology
Post-Freudian Approaches
- Several theorists have built upon Freud's ideas, but their theories differ in that they place less emphasis on the sexual and aggressive instincts of the Id and instead expand on the concept of Ego.
- These theories emphasize human qualities such as creativity, competence, and problem-solving abilities.
Carl Jung: Aims and Aspirations
- Jung, a collaborator of Freud early in his career, diverged from Freud's ideas later on.
- Jung believed that human beings are influenced by aims and aspirations as much as by instincts like sex and aggression.
- He formulated his own theory of personality known as analytical psychology.
- In his theory, Jung proposed that personality is shaped by internal conflicts and structures that need to be harmonized.
- Contrary to societal or external pressures, Jung focused on the individual's internal dynamics.
- He introduced the concept of a collective unconscious housing archetypes or inherited symbolic images.
- Archetypes, such as the God or Mother Earth, are deeply ingrained in human culture, appearing in myths, dreams, and art.
- Jung emphasized the pursuit of unity and wholeness within the self, embodied by the archetype of the self.
- He stressed the importance of accessing one's personal and collective unconscious to achieve harmony and completeness.
- Jung's work involved exploring expressions of unity across different cultural traditions.
Karen Horney: Optimism
- Like another follower of Freud, she expanded upon his principles to develop her own theory. However, she held a more positive view of human life, believing that people are motivated by both growth and self-actualization.
- Furthermore, she challenged Freud's notion that women were inferior by arguing that each gender possesses admirable qualities that are equal in value. She acknowledged that women are more susceptible to societal and cultural pressures.
- According to her, childhood experiences play a crucial role in the development of psychological disorders such as anxiety. Specifically, disturbed interpersonal relationships with indifferent, discouraging, or excessively dominating individuals can contribute to these disorders.
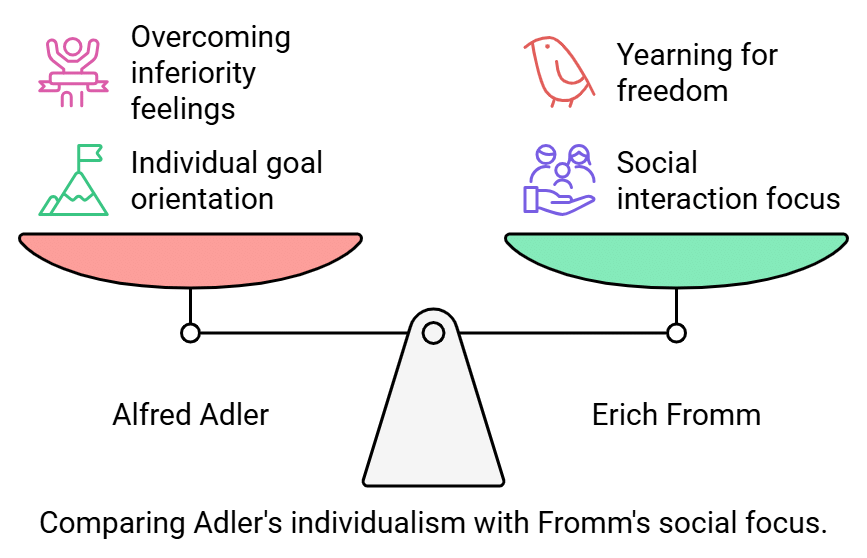
Alfred Adler: Lifestyle and Social Interest
- Alfred Adler's theory posits that human behavior is directed towards goals and serves a purpose.
- He believes that every person experiences feelings of inferiority at some point in their life, but this can be overcome by striving for superiority and accomplishing one's goals. According to Adler, achieving one's purpose in life is essential for achieving optimal personality development.
Erich Fromm: The Human Concerns
- In opposition to Freud's focus on biology, Fromm formulated his theory based on societal viewpoints.
- Fromm perceived humans as fundamentally social creatures, comprehensible through their interactions with others.
- He posited that attributes like personal growth and the realization of capabilities stem from a yearning for freedom, as well as efforts towards justice and truth.
- Fromm suggested that one's character traits and personality evolve from interactions with fellow individuals.
- The culture of a society is influenced by the collective way of life within it, while the prevalent character traits of individuals within that society serve as influential factors in shaping social dynamics and the culture itself.
- Fromm's research underscores the significance of positive attributes, such as gentleness and affection, in the development of one's personality.
Erik Erikson: Search for identity
- This theory emphasizes the role of rational, conscious ego processes in shaping personality development.
- In this theory, identity is given significant importance, particularly during the adolescent stage when individuals undergo an identity crisis, which has garnered substantial attention.
Reasons for criticism of Psychodynamics theories
These theories have been heavily criticized for the following reasons:
- Firstly, they rely heavily on case studies and lack scientific evidence to support their claims.
- Secondly, small and atypical sample sizes were often used to make generalizations about the wider population.
- Thirdly, the concepts used in these theories are often poorly defined, making it difficult to subject them to scientific testing.
- Finally, Freud's theory is criticized for using male experiences as the basis for understanding all human personality development, disregarding the unique experiences and perspectives of females.
Behavioural Approach
- This approach does not consider the internal psychological processes that influence behavior. Behaviorists emphasize the importance of observable, measurable, and definable data.
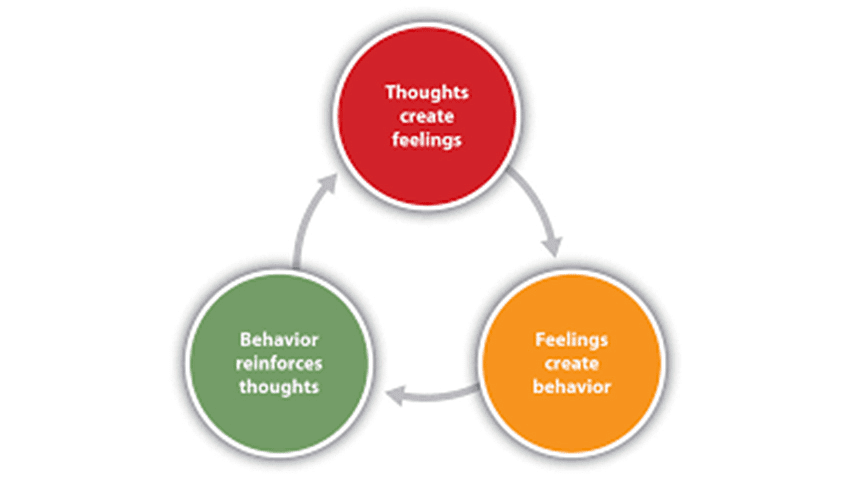
- Their theory centers around the study of stimulus-response and reinforcement. They believe that personality can be understood as an individual's response to their environment. According to behaviorists, personality development involves changes in an individual's response characteristics as they learn new behaviors in response to new stimuli and environments.
Cultural Approach
- This approach seeks to understand personality by examining the influence of ecological and cultural factors. The climate, terrain, and availability of food in a particular area determine economic conditions, lifestyle, social structures, and settlement patterns.
- The cultural approach posits that personality is an adaptation of individuals and groups to the demands of their ecology and culture. People modify their personalities and develop various qualities to fit in and adapt to their culture.
Humanistic Approach
- Carl Rogers and Abraham Maslow had a positive view of human nature and believed that individuals possess the potential for love, joy, and cooperation. Maslow believed that individuals have the freedom to shape their lives and realize their potential through self-actualization. Rogers posited that personality development is a continuous process and discussed the concept of a fully functioning person.
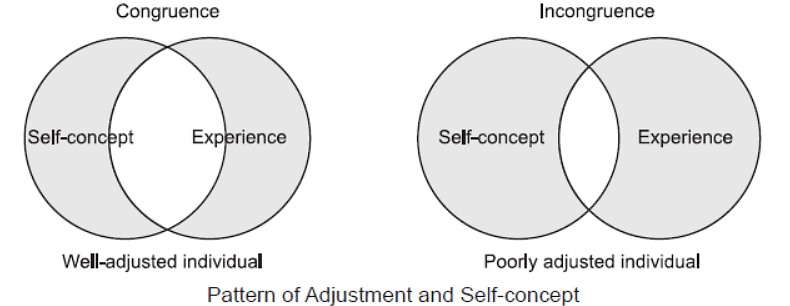
- According to Rogers, individuals strive to align their ideal self with their real self to achieve genuine happiness, and failing to do so results in unhappiness. He also believed that people have an innate tendency to maximize their self-concept through self-actualization. Positive social conditions contribute to high self-esteem and a positive self-concept, while negative social conditions can lead to the opposite.
Who is a Healthy Person?
The humanistic theory proposes that simply conforming to society is not enough to achieve a healthy personality.
This theory includes the following characteristics:
- Self-awareness, which involves recognizing one's emotions and limitations and accepting oneself.
- Living in the present moment and practicing mindfulness.
- Avoiding dwelling in the past or being overly focused on the future through anxious expectations and distorted defenses.
Assessment of Personality
- To know, understand and describe people is a task in which everybody is involved in day-to-day life. When we meet new people, we often try to understand them and even predict what they may do before we interact with them. In our personal lives, we rely on our past experiences, observations, conversations and information obtained from other persons.
- This approach to understanding others may be influenced by a number of factors that may color our judgment and reduce objectivity. Hence, we need to organize our efforts more formally to analyze personalities.
- A formal effort aimed at understanding personality of an individual is termed as personality assessment. Assessment refers to the procedures used to evaluate or differentiate people on the basis of certain characteristics. The goal of assessment is to understand and predict behavior with minimum error and maximum accuracy.
- In assessment, we try to study what a person generally does, or how he behaves, in a given situation. Besides promoting our understanding, assessment is also useful for diagnosis, training, placement, counseling, and other purposes.
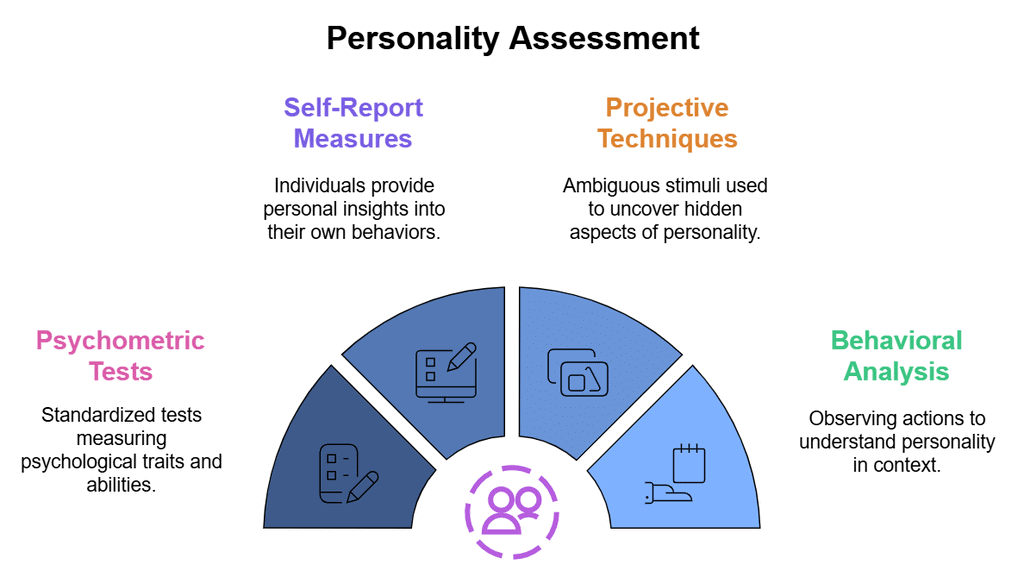
- Psychologists have tried to assess personality in various ways. The most commonly used techniques are Psychometric Tests, Self-Report Measures, Projective Techniques, and Behavioral Analysis. These techniques are rooted in different theoretical orientations; hence they throw light on different aspects of personality. You have read about psychometric tests in the previous chapter. We will discuss the other methods.
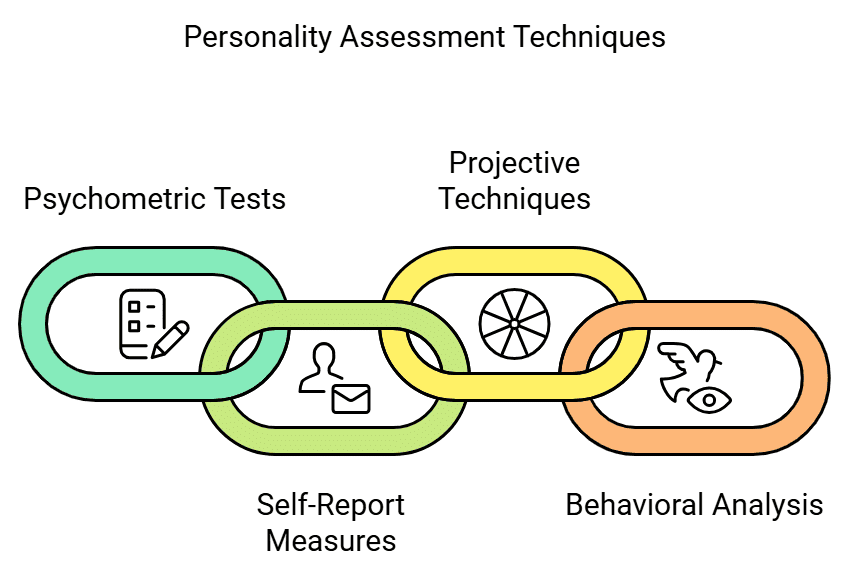
There are several techniques utilized in personality assessment, including:
- Psychometric Tests
- Self-Report Measures
- Projective Techniques
- Behavioral Analysis
Self-report Measures
This technique involves the individual providing factual information about themselves, including their beliefs and opinions.
Various self-report measures are used in personality assessment:
1. Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory(MMPI): The Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI) was created by Hathaway and McKinley for the purpose of psychiatric diagnosis. It comprises of 567 statements that the subject must evaluate as true or false. The test is divided into ten subscales, which are:
- Hypochondriasis
- Depression
- Hysteria
- Psychopathic Deviate
- Masculinity-Femininity
- Paranoia
- Psychasthenia
- Schizophrenia
- Mania
- Social Introversion
2. Eysenck Personality Questionnaire(EPQ): This personality test evaluates two aspects of personality known as Introversion-Extraversion and Emotional Stability-Instability. 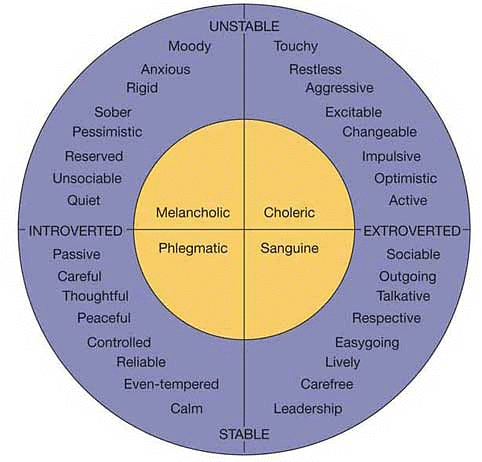 A third dimension named Psychoticism vs Sociability was subsequently added. Individuals who scored high on Psychoticism were seen as self-centered and antisocial, while those who scored high on Sociability were viewed as collaborative and affable. This test is broadly utilized.
A third dimension named Psychoticism vs Sociability was subsequently added. Individuals who scored high on Psychoticism were seen as self-centered and antisocial, while those who scored high on Sociability were viewed as collaborative and affable. This test is broadly utilized.
3. Sixteen Personality Factor Questionnaire(16 PF): Raymond Cattell and his colleagues created a personality assessment tool using factor analysis to identify and measure basic personality traits. The test presents declarative statements, and the individual responds by selecting from a set of predetermined alternatives based on a specific scenario. This assessment is commonly used for career counseling, occupational testing, and with high school students.
Projective Techniques
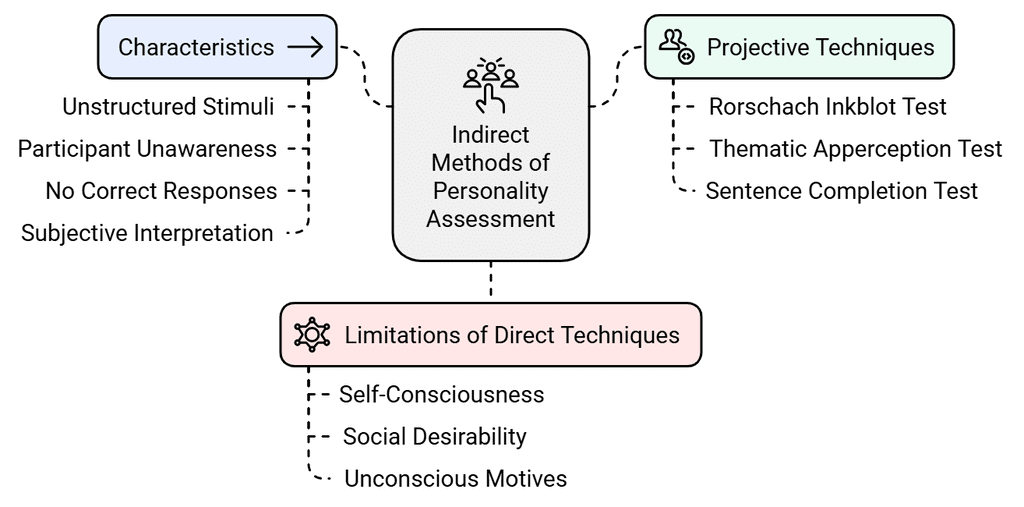
- The techniques of personality assessment discussed so far are termed as direct techniques. These methods rely on information acquired directly from individuals aware of being evaluated. However, individuals in such scenarios may feel self-conscious, leading them to withhold private thoughts, feelings, and motivations. They often present themselves in a socially desirable manner during these assessments.
- According to psychoanalytic theory, a substantial portion of human behavior is steered by unconscious motives. Direct methods of personality assessment are unable to unveil this unconscious part of behavior. Consequently, they fall short in portraying an accurate image of an individual’s personality.
- To address these limitations, indirect methods of assessment can be employed. Projective techniquesbelong to this category. These techniques encompass a wide spectrum of stimuli and responses. Despite their diversity, they share common features:
- The stimuli utilized are either relatively or completely unstructured and vaguely defined.
- The individual under assessment is generally kept uninformed about the assessment's purpose, the scoring method, and the interpretation process.
- Participants are explicitly informed that there are no correct or incorrect responses.
- Each response is believed to divulge a significant facet of the individual's personality.
- The scoring and interpretation of responses can be extensive and at times subjective.
Here are some projective techniques:
1. Rorschach Inkblot Test: Harmann Rorschach developed a test consisting of 10 inkblots (5 black and white, 2 red and the rest pastel colors) printed in the center of a 7 to 10-inch cardboard. 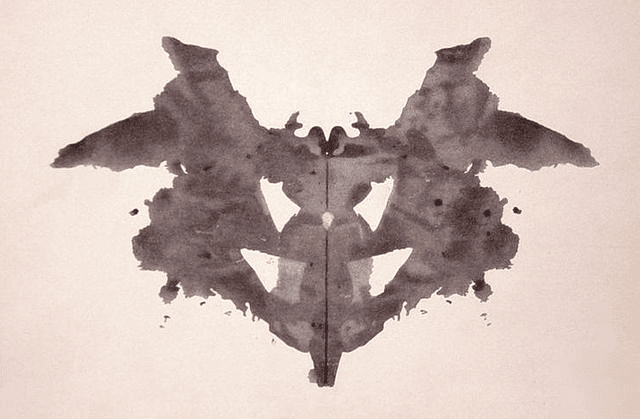 Example of Rorschach Inkbolt TestThe test has two phases:
Example of Rorschach Inkbolt TestThe test has two phases:
- In the first phase, the subject is shown the cards and asked to report what they see in each.
- In the second phase, an extensive report of the responses is prepared by asking the subject to explain where, how, and on what basis a particular response was made. However, using this test requires extensive training to make accurate judgments and interpretations.
2. The Thematic Appreciation Test (TAT): The Thematic Apperception Test (TAT) is a structured test created by Morgan and Murray, which consists of 30 black and white picture cards and 1 blank card. Each card depicts one or more people in various situations. Out of the 30 cards, 20 to 5 cards are used for assessment purposes. The test is conducted by presenting one card at a time to the subject and asking them to describe the situation presented in the picture, including what led up to the situation, what is happening at the moment, what will happen in the future, and what the characters are thinking and feeling. A standard procedure is followed for scoring the responses. An Indian adaptation of the test has been done by Uma Chaudhary.
3. Rozensweig’s Picture-Frustration study ( P-F Study): Rozenweig developed a test to evaluate how individuals express aggression in situations where they are being frustrated. This test includes cartoon-like pictures that illustrate scenarios where one person is causing frustration to another. The subject is then asked to describe what the frustrated person might say or do in response. The analysis of the results focuses on the type and direction of aggression, including whether it is directed towards oneself or the environment, and whether the focus is on the frustrating object, protecting the frustrated person, or finding a constructive solution.
4. Sentence Completion Test: The Sentence Completion Test is a method that utilizes several unfinished sentences. The subject is given the beginning of a sentence and asked to provide an ending to it. The type of response given by the subject is used to evaluate their unconscious attitude, motivation, and conflicts.
For example:
"My father..."
"My greatest fear is..."
"The best thing about my mother is..."
"I am proud of..."
5. Draw-a-Person Test: The Drawing Test is a psychological assessment where the subject is given a sheet of paper, a pencil, and an eraser, and asked to draw a picture of a person. After completing the first drawing, the subject is then asked to draw a person of the opposite gender and create a story about that person as if they were a character in a movie or novel. The interpretation of the test involves analyzing the drawing for various graphic elements. For example, an omission of facial features may suggest a tendency to avoid interpersonal conflict, an emphasis on the neck may suggest a lack of control over impulses, and an abnormally large head may suggest organic brain disease or preoccupation with headaches.
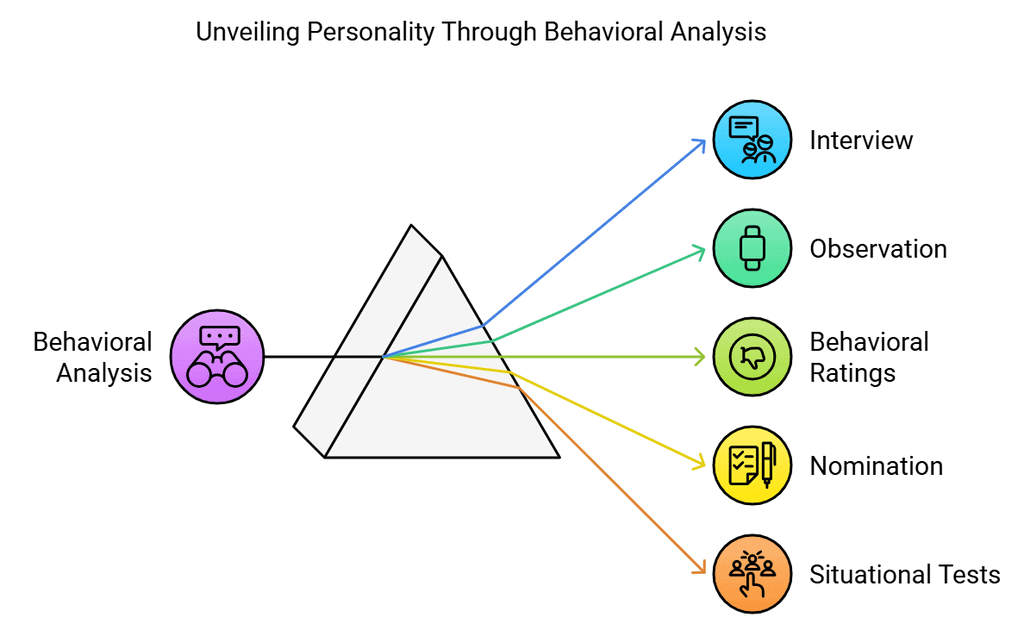
Behavioural Analysis
This analysis can provide us with a meaningful information about his/her personality.
An observer’s report contains data obtained from:
1. Interview:
- A structured interview involves asking a predetermined set of specific questions in a particular order, allowing for objective comparison between interviewees. The use of rating scales can further enhance objectivity.

- On the other hand, an unstructured interview involves asking open-ended questions to develop an overall impression of the interviewee's personality. The way the interviewee answers and presents themselves can provide valuable insight into their personality.
2. Observation:
- Observation is a complex method used for personality assessment that should only be conducted by trained individuals. It requires careful training of the observer and detailed guidelines to analyze the data collected through observation.
- Although this method is widely used, it has some limitations, such as the need for professional training to collect useful data, which is time-consuming and demanding. The observer's maturity is also essential to prevent personal biases from affecting the assessment. Moreover, the presence of the observer may contaminate the results.
3. Behavioural Ratings
- The technique of behavioral ratings is commonly utilized to assess the personality of individuals in educational or industrial environments.
- The ratings are typically obtained from individuals who have interacted with the person being assessed over an extended period of time and have a good understanding of their behavior.
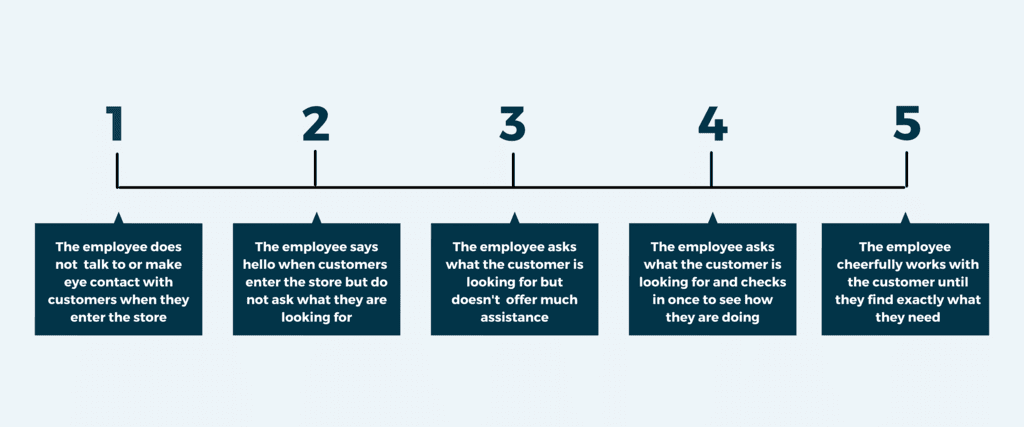 To use this method, the traits being evaluated must be precisely defined and accompanied by well-stated behavioral indicators.
To use this method, the traits being evaluated must be precisely defined and accompanied by well-stated behavioral indicators.
Limitations of Behavioural Rating method:
- Typically, evaluators exhibit prejudices that taint their assessments of various characteristics. One illustration of this is when most of them are swayed by one positive or negative feature, which then affects their overall evaluation of all the traits.
- This phenomenon is known as the "Halo effect." Furthermore, assessors tend to assign individuals either to the median of the scale (known as the middle category bias) or to the extremes (referred to as extreme response bias).
4. Nomination: This approach involves requesting individuals within a group who have known each other for an extended period of time to nominate another person from the group with whom they would like to collaborate, engage in leisure activities, or participate in some other activity. Afterward, they are requested to provide a justification for their nomination.
5. Situational tests: Various situational tests have been developed to evaluate personality. The most commonly used test is the Situational Stress test, which provides insight into how an individual behaves when subjected to stressful circumstances. During this test, the person is assigned a task in a stressful environment where others are instructed not to offer any assistance and act uncooperatively. This involves role-playing, and the subject is observed while a report is compiled. The situations can be recorded on video and later evaluated.
FAQs on (Part - 2) - Self and Personality Class 12 Psychology
| 1. What are the key components of personality assessment? |  |
| 2. How does self-concept influence personality development? |  |
| 3. What role do nature and nurture play in shaping personality? |  |
| 4. What are some common methods used in personality assessment? |  |
| 5. How can understanding personality traits benefit personal and professional relationships? |  |






















