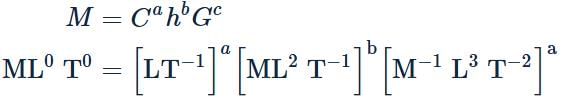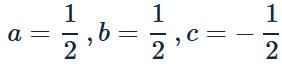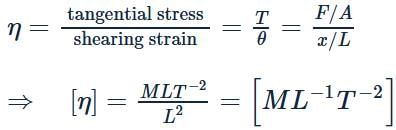Test: Dimensions of Physical Quantities - JEE MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Dimensions of Physical Quantities
Which of the following system of units is NOT based on the unit of mass, length and time alone
Which of the following statement is wrong ?
The angular frequency is measured in rad s-1. Its dimension in length are :
The dimensional formula of coefficient of viscosity is
A pair of physical quantities having the same dimensional formula is :
If momentum (P), area (A) and time (T) are taken to be fundamental quantities, then energy has the dimensional formula
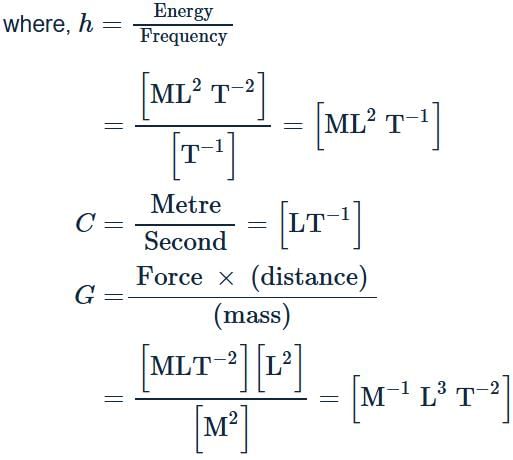
If C the velocity of light, h Planck's constant and G gravitational constant are taken as fundamental quantities, then the dimensional formula of mass is
The dimensional representation of Planck's constant is identical to that of
The dimensions of shear modulus of rigidity are
Suppose refractive index μ is given as μ = A + B/λ2 where A and B are constants and λ is wavelength, then dimensions of B are same as that of
The M.K.S. units of coefficient of viscosity is-
The pressure of 106 dyne/cm2 is equivalent to
The sum of the numbers 436.32, 227.2 and 0.301 in appropriate significant figures is
The SI unit of length is the meter. Suppose we adopt a new unit of length which equals to x meters. The area 1m2 expressed in terms of the new unit has a magnitude-
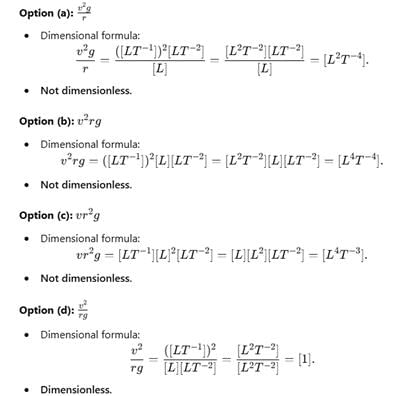
Given that v is the speed, r is radius and g is acceleration due to gravity. Which of the following is dimension less
The value of G = 6.67 × 10_11 N m2 (kg)_2. Its numerical value in CGS system will be :