Test: Molecular Basis Of Inheritance 4 - From Past 28 Years Questions - NEET MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Molecular Basis Of Inheritance 4 - From Past 28 Years Questions
An environmental agent, which triggers transcription from an operon, is a
[1995]
The lac operon is an example of
[1995]
Anticodon is an unpaired triplet of bases in an exposed position of
[1995, 2000]
Okazaki fragments are seen during
[1996]
The translation termination triplet is
[1996]
The basis for DNA fingerprinting is
[1996]
Which step of translation does not consume a high energy phosphate bond ?
[1997]
Three codons causing chain termination are
[1997]
A mutation at one base of the first codon, of a gene, produces a non-functional protein. Such a mutation is called
[1997]
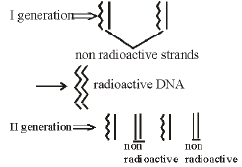
If a completely radioactive double stranded DNA molecule undergoes two rounds of replication in a non-radioactive medium, what will be the radioactive status of the four resulting molecules?
[1997]
Different mutations referrable to the same locus of a chromosome give rise to
[1997]
During development of an organism, the product of one gene is required to activate another gene. Such gene products are called
[1997]
In eukaryotes, after transcription of mRNA, some of its nucleotides are removed before it is translated into polypeptide. The nucleotides which are removed from mRNA are called
[1997]
What base is responsible for hot spots for spontaneous point mutations?
[1998]
The eukar yotic genome differs from the prokaryotic genome because [1998]
DNA elements which can switch their position are called
[1998]
Genes that are involved in turning on or off the transcription of a set of structural genes are called
[1998]
In DNA, when AGCT occurs, their association is as per which of the following pairs?
[1999]
The Pneumococcus experiment proves that
[1999]
In operon concept , regulator gene functions as
[1999]
How many base pairs (bp) are found in the haploid genome of humans?
[1999]
Mutation generally produces
[2000]
Protein synthesis occurs
[2000]
One function of the telomeres in a chromosome is to
[2000]
In negative operon
[2001]