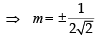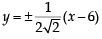Test: Comprehension Based Questions: Circle - JEE MCQ
8 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Comprehension Based Questions: Circle
PASSAGE-1
ABCD is a square of side length 2 units. C1 is the circle touching all the sides of the square ABCD and C2 is the circumcircle of square ABCD. L is a fixed line in the same plane and R is a fixed point.
Q. If P is any point of C1 and Q is another point on C2, then
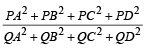 is equal to (2006 - 5M, –2)
is equal to (2006 - 5M, –2)
ABCD is a square of side length 2 units. C1 is the circle touching all the sides of the square ABCD and C2 is the circumcircle of square ABCD. L is a fixed line in the same plane and R is a fixed point.
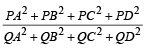 is equal to (2006 - 5M, –2)
is equal to (2006 - 5M, –2) PASSAGE-1
ABCD is a square of side length 2 units. C1 is the circle touching all the sides of the square ABCD and C2 is the circumcircle of square ABCD. L is a fixed line in the same plane and R is a fixed point.
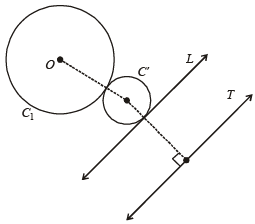
Q. If a circle is such that it touches the line L and the circle C1 externally, such that both the circles are on the same side of the line, then the locus of centre of the circle is (2006 - 5M, –2)
ABCD is a square of side length 2 units. C1 is the circle touching all the sides of the square ABCD and C2 is the circumcircle of square ABCD. L is a fixed line in the same plane and R is a fixed point.
PASSAGE-1
ABCD is a square of side length 2 units. C1 is the circle touching all the sides of the square ABCD and C2 is the circumcircle of square ABCD. L is a fixed line in the same plane and R is a fixed point.
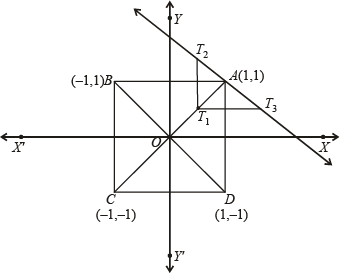
Q. A line L' through A is drawn parallel to BD. Point S moves such that its distances from the line BD and the vertex A are equal. If locus of S cuts L' at T2 and T3 and AC at T1, then area of ΔT1T2T3 is (2006 - 5M, –2)
ABCD is a square of side length 2 units. C1 is the circle touching all the sides of the square ABCD and C2 is the circumcircle of square ABCD. L is a fixed line in the same plane and R is a fixed point.
PASSAGE-2
A circle C of radius 1 is inscribed in an equilateral triangle PQR.
The points of contact of C with the sides PQ, QR, RP are D, E, F, respectively. The line PQ is given by the equation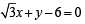 and the point D is
and the point D is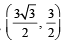
Further, it is given that the origin and the centre of C are on the same side of the line PQ.
Q. The equation of circle C is (2008)
PASSAGE-2
A circle C of radius 1 is inscribed in an equilateral triangle PQR.
The points of contact of C with the sides PQ, QR, RP are D, E, F, respectively. The line PQ is given by the equation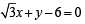 and the point D is
and the point D is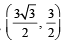
Further, it is given that the origin and the centre of C are on the same side of the line PQ.
Q. Points E and F are given by (2008)
PASSAGE-2
A circle C of radius 1 is inscribed in an equilateral triangle PQR.
The points of contact of C with the sides PQ, QR, RP are D, E, F, respectively. The line PQ is given by the equation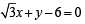 and the point D is
and the point D is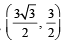
Further, it is given that the origin and the centre of C are on the same side of the line PQ.
Q. Equations of the sides QR, RP are (2008)
PASSAGE-3
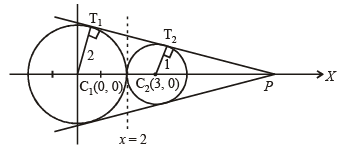
A tangent PT is drawn to the circle x2 + y2 = 4 at the point 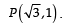 . A straight line L, perpendicular to PT is a tangent to the circle (x – 3)2 + y2 = 1. (2012)
. A straight line L, perpendicular to PT is a tangent to the circle (x – 3)2 + y2 = 1. (2012)
Q. A possible equation of L is
PASSAGE-3
A tangent PT is drawn to the circle x2 + y2 = 4 at the point 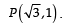 . A straight line L, perpendicular to PT is a tangent to the circle (x – 3)2 + y2 = 1. (2012)
. A straight line L, perpendicular to PT is a tangent to the circle (x – 3)2 + y2 = 1. (2012)
Q. A common tangent of the two circles is


 ,0 ).
,0 ).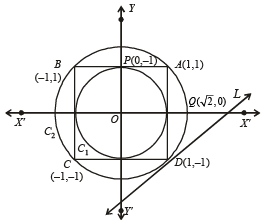
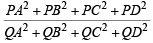
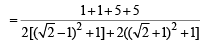
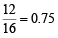

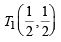 is the vertex of parabola.
is the vertex of parabola.
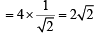
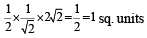
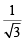
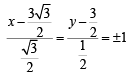
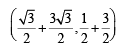 or
or 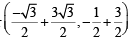
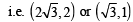
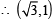 should be the coordinates of C.
should be the coordinates of C.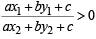
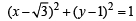
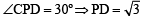
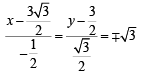
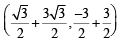
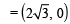 and
and 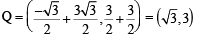
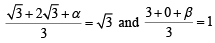
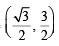
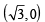
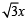 and equation of side RP is y = 0
and equation of side RP is y = 0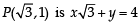
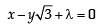
 = – 1 or – 5
= – 1 or – 5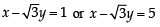
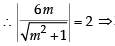 36 m2 = 4(m2 + 1)
36 m2 = 4(m2 + 1)