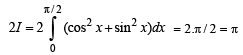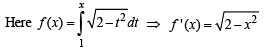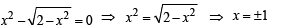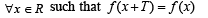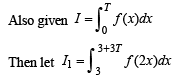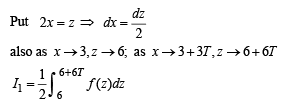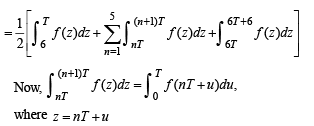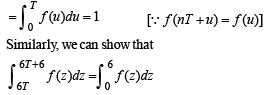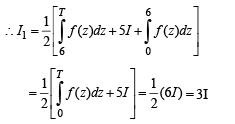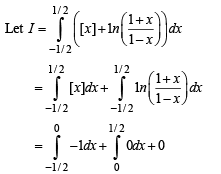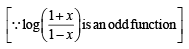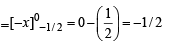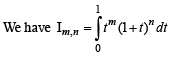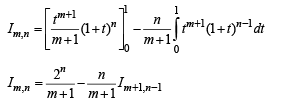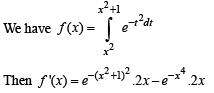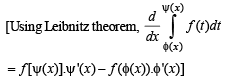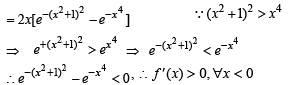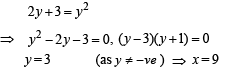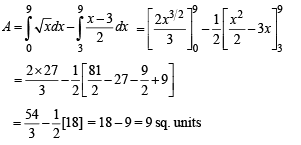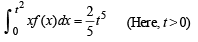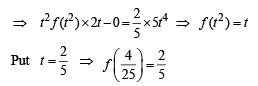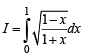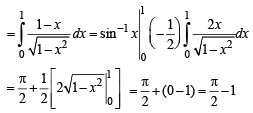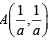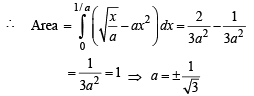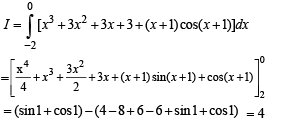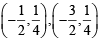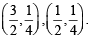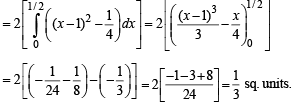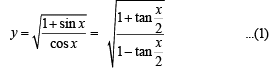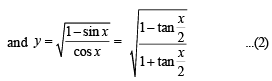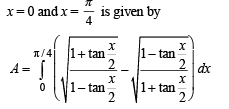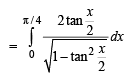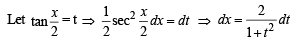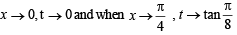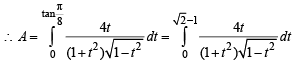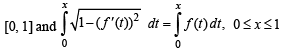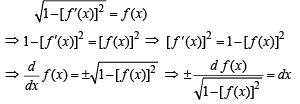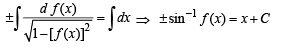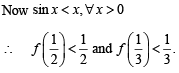JEE Advanced (Single Correct MCQs): Definite Integrals and Applications of Integrals - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Advanced (Single Correct MCQs): Definite Integrals and Applications of Integrals
The value of the definite integra 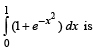 equal to a.
equal to a.
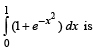 equal to a.
equal to a.Let a, b, c be non-zero real numbers such that
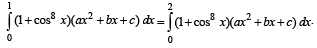
Then the quadratic equation ax2 + bx +c= 0 has
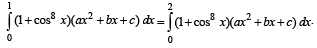
The area bounded by the curves y = f(x), the x-axis and the ordinates x = 1 and x = b is (b – 1) sin (3b + 4). Then f(x) is
The value of the integral 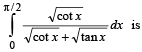
For any integer n the integral ––
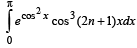 has the value
has the value
Let f : R → R and g : R → R be continous functions. Then the value of the integral
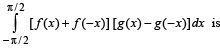
The value of 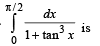
If f (x)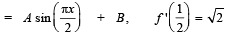 and
and 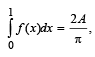 then constants A and B are
then constants A and B are
The value of  represents the greatest integer function is
represents the greatest integer function is
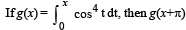 equals
equals
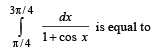
If for a real number y, [y] is the greatest integer less than or equal to y, then the value of the integral 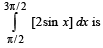
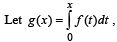 where f is such that
where f is such that 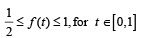
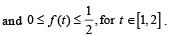
Then g(2) satisfies the inequality
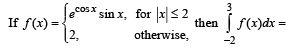
The value of the integral 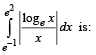
The value of 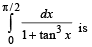
The area bounded by the curves y = |x| –1 and y = –|x| + 1 is
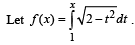 Then the real roots of the equation x2 – f '(x) = 0 are
Then the real roots of the equation x2 – f '(x) = 0 are
Let T > 0 be a fixed real number. Suppose f is a continuous function such that for all 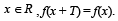

The integral 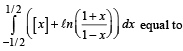
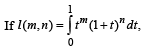 then the expression for l(m, n) in terms of l(m + 1, n – 1) is
then the expression for l(m, n) in terms of l(m + 1, n – 1) is
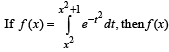 increases in
increases in
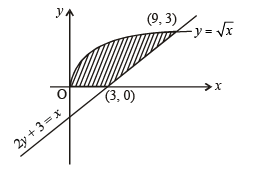
The area bounded by the curves 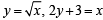 and x-axis in the 1st quadrant is
and x-axis in the 1st quadrant is
If f (x) is differentiable and 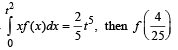 equals
equals
The value of the integral 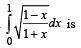
The area enclosed between the curves y = ax2 and x = ay2 (a > 0) is 1 sq. unit, then the value of a is
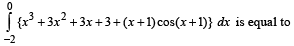
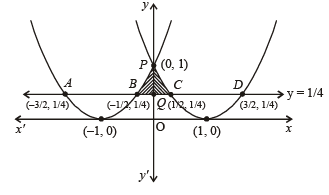
Th e area bounded by the par abolas y = (x + 1)2 and y = (x – 1)2 and the line y = 1/4 is
The area of the region between the curves 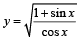 and
and 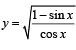 bounded by the lines x = 0 and
bounded by the lines x = 0 and 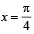 is
is
Let f be a non-negative function defined on the interval 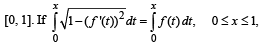
and f (0) = 0, then


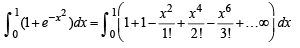
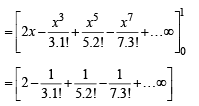
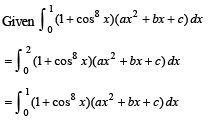
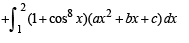
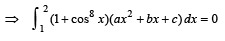
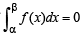 then it means that
then it means that
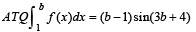
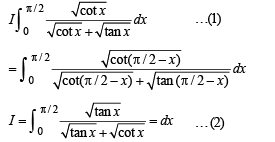
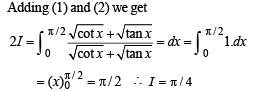
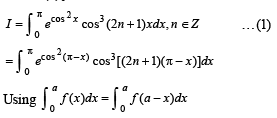
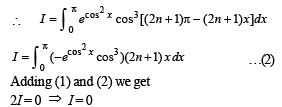
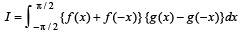
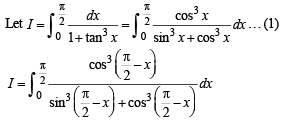
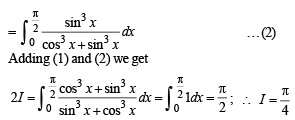
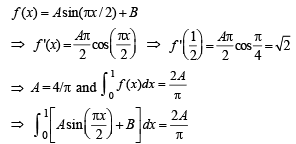
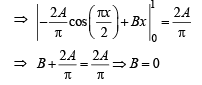
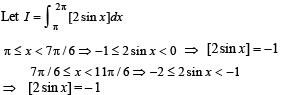
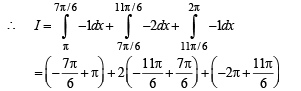
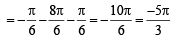
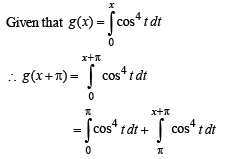
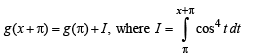
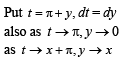
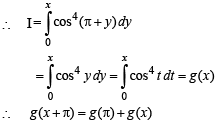
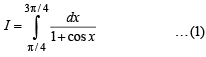
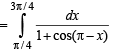
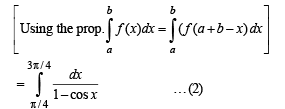
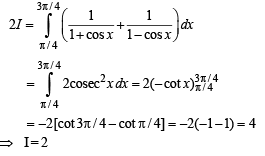
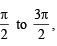 we have to find the value of
we have to find the value of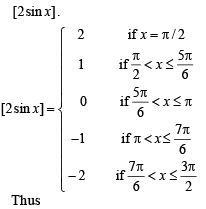
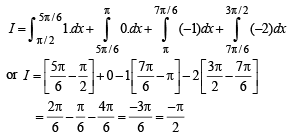
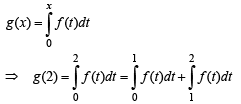
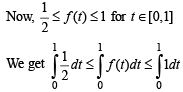
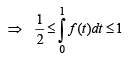 … (1)
… (1)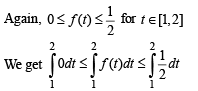
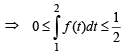 … (2)
… (2)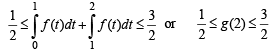
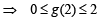
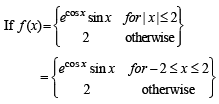
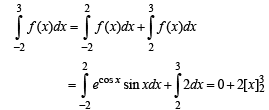
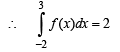
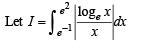
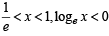 and hence
and hence 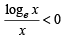
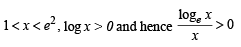
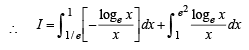
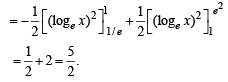
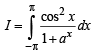 .....(1)
.....(1)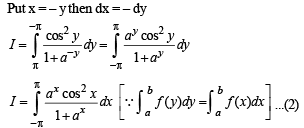
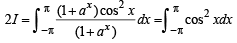
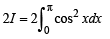 (even function)
(even function)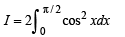 ...(3)
...(3)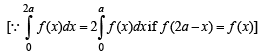
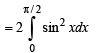 ....(4)
....(4)