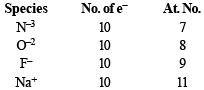JEE Advanced (Single Correct MCQs): Classification of Elements & Periodicity in Properties - JEE MCQ
16 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Advanced (Single Correct MCQs): Classification of Elements & Periodicity in Properties
The correct order of second ionisation potential of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and fluorine is (1981 - 1 Mark)
TThe element with highest value of first ionization potential is (1982 - 1 Mark)
The first ionisation potential in electron volts of nitrogen and oxygen atoms are respectively given by (1987 - 1 Mark)
Atomic radii of fluorine and neon in Ångstorm units are respectively given by-
The electronegativity of the following elements increases in the order (1987 - 1 Mark)
The first ionisation potential of Na, Mg, Al and Si are in the order (1988 - 1 Mark)
Which one of the following is the strongest base?
Which one of the following is the smallest in size?
Amon gst the followin g elemen ts (whose electr on ic configurations are given below), the one having the highest ionization energy is : (1990 - 1 Mark)
The statement that is not correct for the periodic classification of element is (1992 - 1 Mark)
Which has most stable +2 oxidation state : (1995S)
Which of the following has the maximum number of unpaired electrons? (1996 - 1 Mark)
The correct order of radii is (2000S)
The correct order of acidic strength is (2000S)
Amongst H2O, H2S, H2Se and H2Te, the one with the highest boiling point is (2000S)
Identify the correct order of acidic strengths of CO2, CuO, CaO, H2O (2002S)