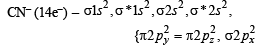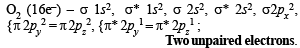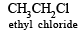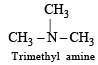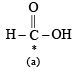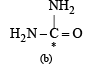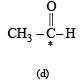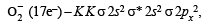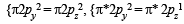JEE Advanced (Single Correct MCQs): Chemical Bonding & Molecular Structure- 1 - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Advanced (Single Correct MCQs): Chemical Bonding & Molecular Structure- 1
The compound which contains both ionic and covalent bonds is(1979)
The octet rule is not valid for the molecule (1979)
Element X is strongly electropositive and element Y is strongly electronegative. Both are univalent. The compound formed would be (1980)
Which of the following compounds are covalent? (1980)
The total number of electrons that take part in forming the bond in N2 is (1980)
Which of the following is soluble in water (1980)
If a molecule MX3 has zero dipole moment, the sigma bonding orbitals used by M (atomic number < 21) are (1981 - 1 Mark)
The ion that is isoelectronic with CO is (1982 - 1 Mark)
Among the following, the molecule that is linear is
The compound with no dipole moment is (1982 - 1 Mark)
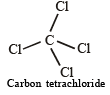
Carbon tetrachloride has no net dipole moment because of
Which one among the following does not have the hydrogen bond? (1983 - 1 Mark)
The types of bonds present in CuSO4.5H2O are only
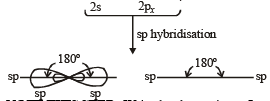
On hybridization of one s and one p orbitals we get :
The molecule having one unpaired electron is : (1985 - 1 Mark)
The bond between two identical non-metal atoms has a pair of electrons : (1986 - 1 Mark)
The hydrogen bond is strongest in : (1986 - 1 Mark)
The hybridisation of sulphur in sulphur dioxide is : (1986 - 1 Mark)
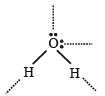
Hydrogen bonding is maximum in (1987 - 1 Mark)
The species in which the central atom uses sp2 hybrid orbitals in its bonding is (1988 - 1 Mark)
The molecule that has linear structure is (1988 - 1 Mark)
The molecule which has zero dipole moment is :
The molecule which has pyramidal shape is :
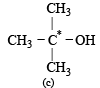
The compound in which C* uses its sp3 hybrid orbitals for bond formation is : (1989 - 1 Mark)
Which of the following is paramagnetic? (1989 - 1 Mark)
The type of hybrid orbitals used by the chlorine atom in ClO-2 is (1992 - 1 Mark)
The maximum possible number of hydrogen bonds a water molecule can form is (1992 - 1 Mark)
The cyanide ion , CN– and N2 are isoelectron ic. But in contrast to CN–, N2 is chemically inert, because of (1992 - 1 Mark)
Pick out the isoelectronic structures from the following; (1993 - 1 Mark)
I.CH+3 II.H3O+ III. NH3 IV CH3–
Which one is most ionic : (1995S)



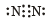
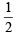 (V + M – C + A)
(V + M – C + A)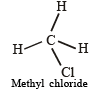

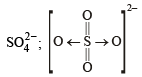 ion.
ion.