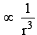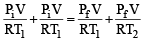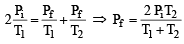Test: JEE Main 35 Year PYQs- States of Matter - JEE MCQ
15 Questions MCQ Test - Test: JEE Main 35 Year PYQs- States of Matter
For an ideal gas, number of moles per litre in terms of its pressure P, gas constant R and temperature T is
Kinetic theory of gases proves [2002]
According to the kinetic theory of gases, in an ideal gas, between two successive collisions a gas molecule travels
As the temperature is raised from 20ºC to 40ºC, the average kinetic energy of neon atoms changes by a factor of which of the following ? [2004]
In van der Waals equation of state of the gas law, the constant ‘b’ is a measure of [2004]
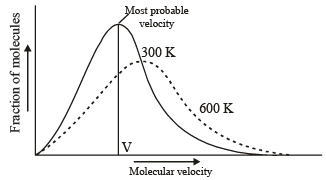
Which one of the following statements is NOT true about the effect of an increase in temperature on the distribution of molecular speeds in a gas? [2005]
If 10–4 dm3 of water is introduced into a 1.0 dm3 flask at 300 K, how many moles of water are in the vapour phase when equilibrium is established ? [2010]
(Given : Vapour pressure of H2O at 300 K is 3170 Pa; R = 8.314 J K–1 mol–1)
‘a’ and ‘b’ are van der Waals’ constants for gases. Chlorine is more easily liquefied than ethane because [2011]
The compressibility factor for a real gas at high pressure is : [2012]
For gaseous state, if most probable speed is denoted by C*, average speed by 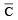 and mean square speed by C, then for a large number of molecules the ratios of these speeds are : [JEE M 2013]
and mean square speed by C, then for a large number of molecules the ratios of these speeds are : [JEE M 2013]
If Z is a compressibility factor, van der Waals equation at low pressure can be written as: [JEE M 2014]
The ratio of masses of oxygen and nitrogen in a particular gaseous mixture is 1 : 4. The ratio of number of their molecule is: [JEE M 2014]
The intermolecular interaction that is dependent on the inverse cube of distance between the molecules is : [JEE M 2015]
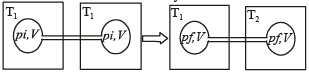
Two closed bulbs of equal volume (V) containing an ideal gas initially at pressure pi and temperature T1 are connected through a narrow tube of negligible volume as shown in the figure below. The temperature of one of the bulbs is then raised to T2. The final pressure pf is : [JEE M 2016]



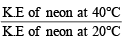
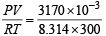 = 1.27 × 10–3
= 1.27 × 10–3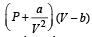 = RT at high pressure
= RT at high pressure 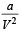 can be
can be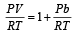
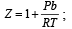 Z > 1 at high pressure
Z > 1 at high pressure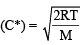
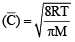
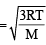
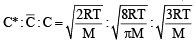
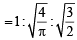 = 1 :1.128 : 1.225
= 1 :1.128 : 1.225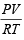
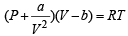
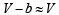
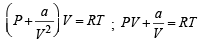
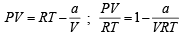
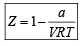
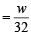
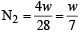
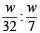 = 7 : 32
= 7 : 32