JEE Advanced (Single Correct MCQs): Thermodynamics - JEE MCQ
16 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Advanced (Single Correct MCQs): Thermodynamics
The difference between heats of reaction at constant pressure and constant volume for the reaction : 2 C6H6(l) + 15O2(g) → 12CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) at 25ºC in kJ is (1991)
For which change ΔH ≠ ΔE : (1995S)
The ΔH0f for CO2(g), CO(g) and H2O(g) are –393.5, –110.5 and –241.8 kJ mol–1 respectively. The standard enthalpy change (in kJ) for the reaction CO2(g) + H2(g) → CO(g) + H2O(g) is (2000S)
In thermodynamics, a process is called reversible when (2001S)
Which one of the following statements is false? (2001S)
One mole of a non-ideal gas undergoes a change of state (2.0 atm, 3.0L, 95(K) → (4.0 atm, 5.0 L, 245K) with a change in internal energy, ΔU= 30.0L atm . The change in enthalpy (ΔH) of the process in L atm is (2002S)
Which of the reaction defines ΔH°f ? (2003S)
Two moles of an ideal gas is expanded isothermally and reversibly from 1 litre to 10 litre at 300 K. The enthalpy change (in kJ) for the process is (2004S)
The enthalpy of vapourization of liquid is 30 kJ mol–1 and entropy of vapourization is 75 J mol–1 K. The boiling point of the liquid at 1 atm is (2004S)
The direct conversion of A to B is difficult, hence it is carried out by the following shown path :
Given 
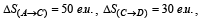

where e.u. is the entropy unit, then ΔS(A→B) is (2006 - 3M, –1)
The value of log10 K for a reaction A  B is (Given : 1 ΔrH°298K =-54.07 kJ mol-1, ΔrS°298K = 10 JK–1 mol–1 and R = 8.314 JK–1 mol–1; 2.303 × 8.314 × 298 = 5705) (2007)
B is (Given : 1 ΔrH°298K =-54.07 kJ mol-1, ΔrS°298K = 10 JK–1 mol–1 and R = 8.314 JK–1 mol–1; 2.303 × 8.314 × 298 = 5705) (2007)
For the process H2O(l) (1 bar, 373 K) → H2O(g) (1 bar, 373 K), the correct set of thermodynamic parameters is (2007)
The species which by definition has ZERO standard molar enthalpy of formation at 298 K is (2010)
The standard enthalpies of formation of CO2(g), H2O(l) and glucose(s) at 25°C are –400 kJ/mol, –300 kJ/mol and –1300 kJ/mol, respectively. The standard enthalpy of combustion per gram of glucose at 25°C is (JEE Advanced 2013-I)
For the process (JEE Adv. 2014) H2O(l) → H2O(g) at T = 100°C and 1 atmosphere pressure, the correct choice is
One mole of an ideal gas at 300 K in thermal contact with surroundings expands isothermally from 1.0 L to 2.0 L against a constant pressure of 3.0 atm. In this process, the change in entropy of surroundings (ΔSsurr) in JK–1 is (1 L atm = 101.3 J) (JEE Adv. 2016)




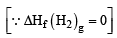
 ∴ T = 400 K
∴ T = 400 K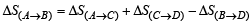
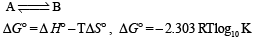



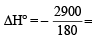 - 16.11 kJ / gm
- 16.11 kJ / gm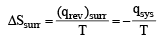
 = –1 .01 3 J/K
= –1 .01 3 J/K










