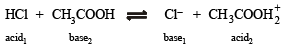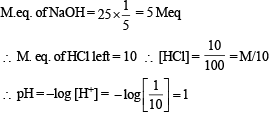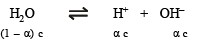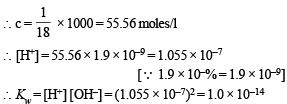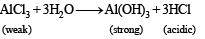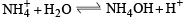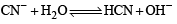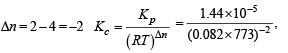JEE Advanced (Single Correct MCQs): Equilibrium - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Advanced (Single Correct MCQs): Equilibrium
An acidic buffer solution can be prepared by mixing the solutions of
The pH of a 10–8 molar solution of HCl in water is
The oxidation of SO2 by O2 to SO3 is an exothermic reaction. The yield of SO3 will be maximum if
For the reaction :
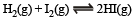
the equilibrium constant Kp changes with
Of the given anions, the strongest Bronsted base is
At 90ºC, pure water has [H3O+] 10–6 mole litre–1. What is the value of Kw at 90ºC?
The precipitate of
CaF2(Ksp = 1.7 × 10–10)
is obtained when equal volumes of the following are mixed
A liquid is in equilibrium with its vapour at its boiling point. On the average, the molecules in the two phases have equal :
Pure ammonia is placed in a vessel at a temperature where its dissociation constant (a) is appreciable. At equilibrium :
A certain buffer solution contains equal concentration of X– and HX. The Kb for X– is 10–10. The pH of the buffer is :
A certain weak acid has a dissociation constant of 1.0 × 10–4. The equilibrium constant for its reaction with a strong base is :
An example of a reversible reaction is :
The best indicator for detection of end point in titration of a weak acid and a strong base is :
The compound that is not a Lewis acid is :
The compound insoluble in acetic acid is :
The compound whose 0.1 M solution is basic is :
When equal volumes of the following solutions are mixed, precipitation of AgCl (Ksp = 1.8×10–10) will occur only with
The pKa of acetylsalicyclic and (aspirin) is 3.5. The pH of gastric juice in human stomach is about 2-3 and the pH in the small intestine is about 8. Aspirin will be
Which one of the following is the strongest acid?
Amongst the following hydroxides, the one which has the lowest value of Ksp at ordinary temperature (about 25ºC) is
The reaction which proceeds in the forward direction is
The following equilibrium in established when hydrogen chloride is dissolved in acetic acid.
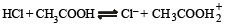
The set that characterises the conjugate acid-base pairs is
Which of the following solutions will have pH close to 1.0?
The degree of dissociation of water at 25ºC is 1.9 × 10–7% and density is 1.0 g cm–3. The ionic constant for water is :
Which one is more acidic in aqueous solution
The following acids have been arranged in the order of decreasing acid strength. Identify the correct order.
ClOH (I), BrOH(II), IOH(III)
The pH of 0.1 M solution of the following salts increases in the order.
For the chemical reaction 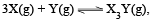 the amount of X3Y at equilibrium is affected by
the amount of X3Y at equilibrium is affected by
For the reversible reaction, 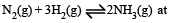 500°C, the value of Kp is 1.44 x10-5 when partial pressure is measured in atmospheres. The corresponding value of Kc, with concentration in mole litre–1, is
500°C, the value of Kp is 1.44 x10-5 when partial pressure is measured in atmospheres. The corresponding value of Kc, with concentration in mole litre–1, is


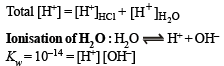
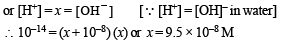
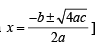

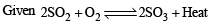
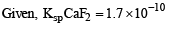
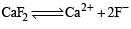
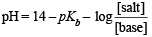
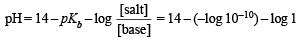
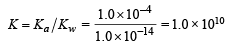
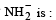
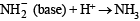 (conjugate acid)
(conjugate acid)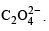
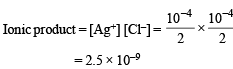
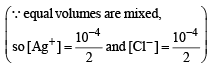
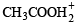 and is the conjugate base of HCl.
and is the conjugate base of HCl.