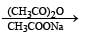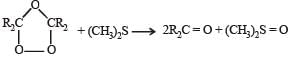Test: Comprehension Based Questions: Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids - JEE MCQ
19 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Comprehension Based Questions: Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acids
PASSAGE -1
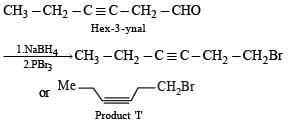
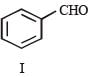
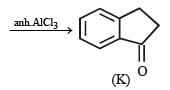
In the following reaction sequence, product I, J and L are formed.
K represents a reagent.
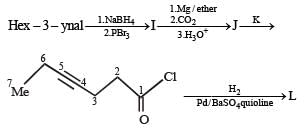
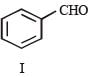
Q.The structure of the product I is –

In the following reaction sequence, product I, J and L are formed.
K represents a reagent.

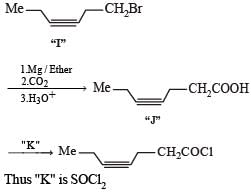
Q. The structures of compound J and K, respectively, are

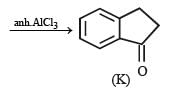
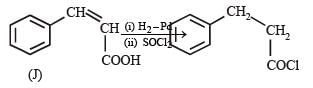
In the following reaction sequence, product I, J and L are formed.
K represents a reagent.

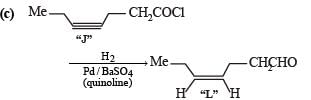
Q. The structure of product L is

PASSAGE-2
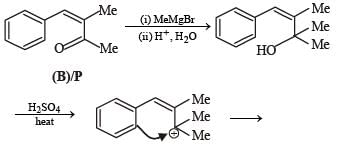
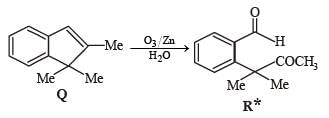
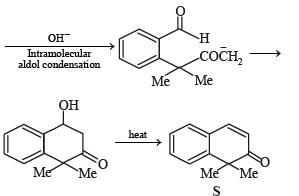
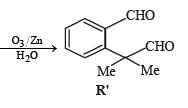
A carbonyl compound P, which gives positive iodoform test, undergoes reaction with MeMgBr followed by dehydration to give an olefin Q. Ozonolysis of Q leads to a dicarbonyl compound R, which undergoes intramolecular aldol reaction to give predominantly S.
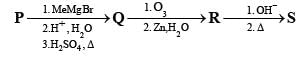
Q. The structure of the carbonyl compound P is
PASSAGE-2
A carbonyl compound P, which gives positive iodoform test, undergoes reaction with MeMgBr followed by dehydration to give an olefin Q. Ozonolysis of Q leads to a dicarbonyl compound R, which undergoes intramolecular aldol reaction to give predominantly S.
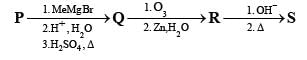
Q. The structures of the products Q and R, respectively, are
PASSAGE-2
A carbonyl compound P, which gives positive iodoform test, undergoes reaction with MeMgBr followed by dehydration to give an olefin Q. Ozonolysis of Q leads to a dicarbonyl compound R, which undergoes intramolecular aldol reaction to give predominantly S.
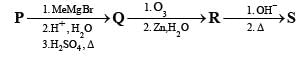
Q. The structure of the product S is
PASSAGE-3
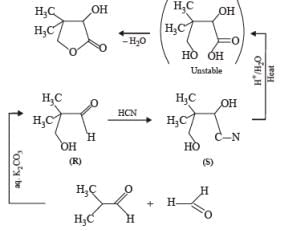
Two aliphatic aldehydes P and Q react in the presence of aqueous K2CO3 to give compound R, which upon treatment with HCN provides compound S. On acidification and heating, S gives the product shown below
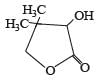
Q. The compounds P and Q respectively are :
PASSAGE-3
Two aliphatic aldehydes P and Q react in the presence of aqueous K2CO3 to give compound R, which upon treatment with HCN provides compound S. On acidification and heating, S gives the product shown below.
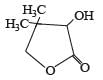
Q. The compound R is :
PASSAGE-3
Two aliphatic aldehydes P and Q react in the presence of aqueous K2CO3 to give compound R, which upon treatment with HCN provides compound S. On acidification and heating, S gives the product shown below.
Q. The compound S is :
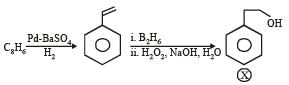
PASSAGE-4
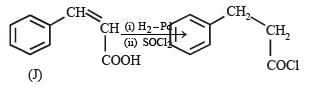
In the following reaction sequence, the compound J is an intermediate.
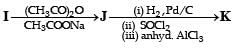
J (C9H8O2) gives effervescence on treatment with NaHCO3 and a positive Baeyer’s test.
Q. The compound I is
PASSAGE-4
In the following reaction sequence, the compound J is an intermediate.
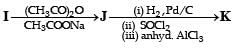
J (C9H8O2) gives effervescence on treatment with NaHCO3 and a positive Baeyer’s test.
Q. The compound K is
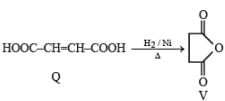
PASSAGE-5
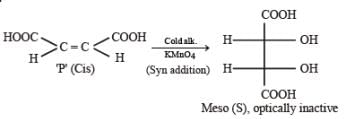
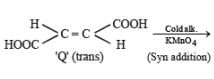
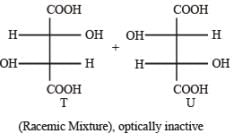
P and Q are isomers of dicarboxylic acid C4H4O4. Both decolorize Br2/H2O. On heating, P forms the cyclic anhydride. Upon treatment with dilute alkaline KMnO4, P as well as Q could produce one or more than one from S, T and U.
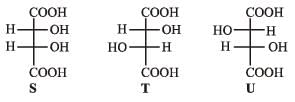
PASSAGE-5
P and Q are isomers of dicarboxylic acid C4H4O4. Both decolorize Br2/H2O. On heating, P forms the cyclic anhydride. Upon treatment with dilute alkaline KMnO4, P as well as Q could produce one or more than one from S, T and U.

Q. In the following reaction sequences V and W are respectively
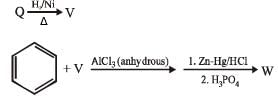
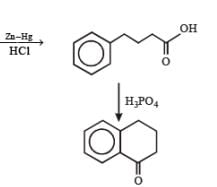
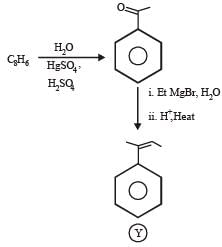
PASSAGE-6
In the following reactions
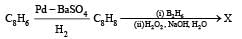
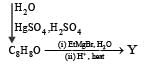
Q. Compound X is
PASSAGE-6
In the following reactions
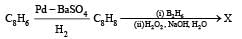
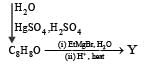
Q. The major compound Y is
Each of this question contains STATEMENT-1 (Assertion/ Statement ) and STATEMENT-2 (Reason/Explanation) and has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d) out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
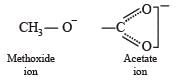
Statement-1 : Acetate ion is more basic than the methoxide ion.
Statement-2 : The acetate ion is resonance stabilized
Statement-1 : Acetic acid does not undergo haloform reaction.
Statement-2 : Acetic acid has no alpha hydrogens.
Statement-1 : Dimethyl sulphide is commonly used for the reduction of an ozonide of an alkene to get the carbonyl compounds.
Statement-2 : It reduces the ozonide giving water soluble dimethyl sulphoxide and excess of it evaporates.
Statement-1 : p-Hydroxybenzoic acid has a lower boiling point than o-hydroxybenzoic acid.
Statement-2 : o-Hydroxybenzoic acid has intramolecular hydrogen bonding.