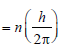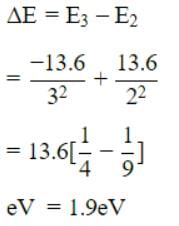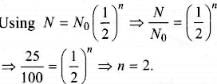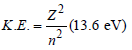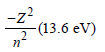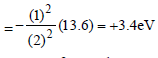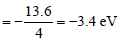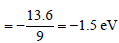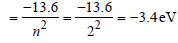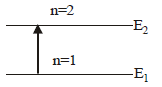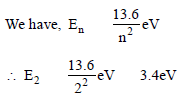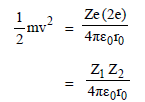31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Atoms - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - 31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Atoms
What is the radius of iodine atom (At. no. 53,mass no. 126) [1988]
The ionisation energy of hydrogen atom is 13.6eV, the ionisation energy of helium atom wouldbe [1988]
To explain his theory, Bohr used [1989]
The ground state energy of H-atom 13.6 eV. Theenergy needed to ionize H-atom from its secondexcited state. [1991]
In terms of Bohr radius a0, the radius of the second Bohr orbit of a hydrogen atom is given by [1992]
The ionization energy of hydrogen atom is 13.6eV. Following Bohr’s theory, the energycorresponding to a transition between 3rd and4th orbit is [1992]
Which source is associated with a line emissionspectrum ? [1993]
In Rutherford scattering experiment, what willbe the correct angle for α-scattering for an impactparameter, b = 0 ? [1994]
The radius of hydrogen atom in its ground stateis 5.3 × 10–11 m. After collision with an electron itis found to have a radius of 21.2 × 10–11 m. Whatis the principal quantum number n of the finalstate of the atom [1994]
The spectrum obtained from a sodium vapourlamp is an example of [1995]
When a hydrogen atom is raised from the groundstate to an excited state, [1995]
If the threshold wavelength for a certain metal is 2000 Å, then the work-function of the metal is [1995]
When hydrogen atom is in its first excited level,its radius is [1997]
In the Bohr model of a hydrogen atom, the centripetal force is furnished by the coulomb attraction between the proton and the electron. If a0 is the radius of the ground state orbit, m is the mass, e is the charge on the electron and ε0 is the vacuum ermittivity, the speed of the electron is [1998]
Who indirectly determined the mass of theelectron by measuring the charge of the electron? [2000]
When an electron jumps from the fourth orbit tothe second orbit, one gets the [2000]
Which of the following transitions in a hydrogenatom emits the photon of highest frequency? [2000]
An electron changes its position from orbit n = 2 to the orbit n = 4 of an atom. The wavelength of the emitted radiations is (R = Rydberg’s constant)
The energy of hydrogen atom in nth orbit is En, then the energy in nth orbit of single ionised helium atom will be [2001]
J.J. Thomson’s cathode-ray tube experimentdemonstrated that [2003]
In which of the following systems will the radiusof the first orbit (n = 1) be minimum ? [2003]
Energy E of a hydrogen atom with principal quantum number n is given by E = – 13.6/n2 eV. The energy of photon ejected when the electronjumps from n = 3 state to n = 2 state of hydrogenis approximately [2004]
The half life of radium is about 1600 years. Of 100 g of radium existing now, 25 g will remainunchanged after [2004]
The total energy of an electron in the firstexcited state of hydrogen atom is about –3.4eV. Its kinetic energy in this state is [2005]
Ionization potential of hydrogen atom is 13.6eV.Hydrogen atoms in the ground state are excitedby monochromatic radiation of photon energy12.1 eV. According to Bohr’s theory, the spectrallines emitted by hydrogen will be [2006]
The total energy of electron in the ground stateof hydrogen atom is – 13.6 eV. The kinetic energyof an electron in the first excited state is [2007]
The ground state energy of hydrogen atom is 13.6eV. When its electron is in the first excited state, its excitation energy is [2008]
In a Rutherford scattering experiment when a projectile of charge Z1 and mass M1 approaches a target nucleus of charge Z2 and mass M2, the distance of closest approach is r0. The energy of the projectile is [2009]
The ionization energy of the electron in thehydrogen atom in its ground state is 13.6 eV.The atoms are excited to higher energy levels toemit radiations of 6 wavelengths. Maximumwavelength of emitted radiation corresponds tothe transition between [2009]


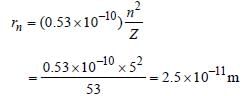

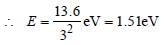
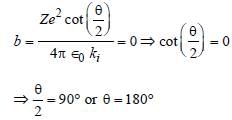
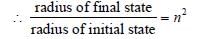
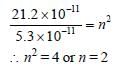
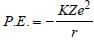 and
and 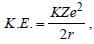 where,
where,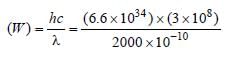


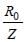
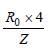
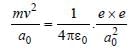
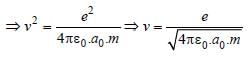
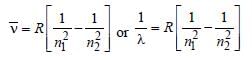
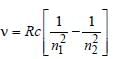
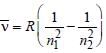 , where n1 = 2, n2 = 4
, where n1 = 2, n2 = 4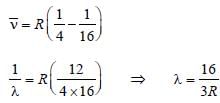
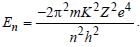 For helium
For helium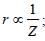 Z(=3) is maximum for Li2+.
Z(=3) is maximum for Li2+.