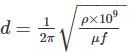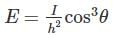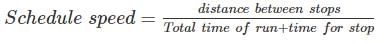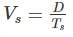Test: Utilization of Electrical Energy- 2 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Utilization of Electrical Energy- 2
In dielectric heating, the current flows through:
In induction heating, the depth up to which the current will penetrate is proportional to:
In submerged arc furnaces, the power is controlled by:
In direct arc furnace, which of the following is of high value?
During the resistance welding, the heat produced at the joint is proportional to:
The main drawbacks of the resistance welding are:
A substance that changes its electrical resistance when illuminated by light is called:
The illumination of various points on a horizontal surface illuminated by the same source varies as:
In the electric discharge lamps, the light is produced by:
An auto-transformer used with a sodium vapour lamp should have:
Which law states that the mass of substance liberated from an electrolyte is proportional to the quantity of electricity passing through it?
The process of depositing one metal over the other metal is known as:
The speed-time curve for the urban service has no:
The speed of a train estimated taking into account the stoppage time at a station in addition to the actual running time between stops is called the:
The coefficient of the adhesion is the ratio of tractive effort to slip the wheels and:
Load equalization is desirable in the case of
Which of the following material is most commonly used for the filaments in incandescent lamps?
Centrifugal pumps are usually driven by: