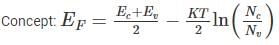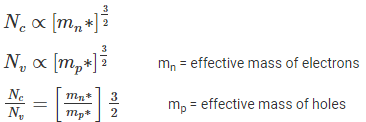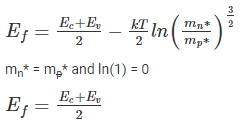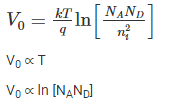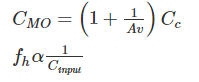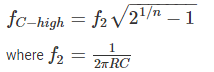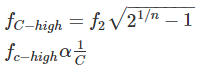Test: Basic Electronics- 2 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Basic Electronics- 2
In the silicon crystal structure, the recombination rate is proportional to the number of;
The Fermi level EF in an intrinsic semiconductor, if effective masses of holes and electrons are same is:
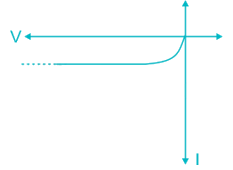
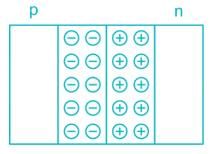
During reverse bias operation of PN junction, a low current flows known as…….. which is……… barrier voltage:
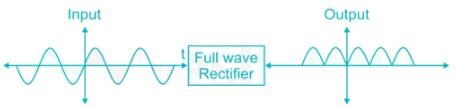
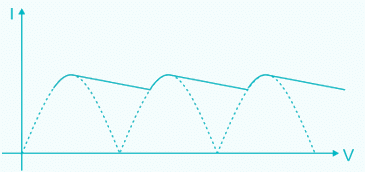
A centre tapped full wave rectifier output contains only-
What is the effect on the diode current in a forward biased photo diode with increase in incident light intensity?
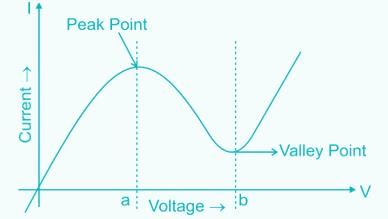
Which diode has negative resistance region in its characteristics?
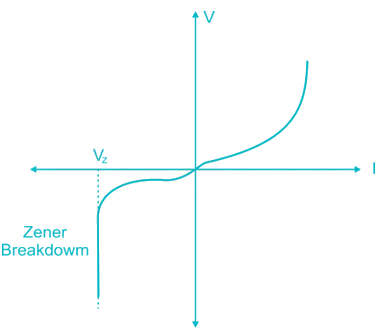
Which of the following diode is used for voltage stabilization?
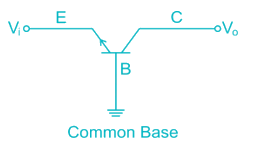
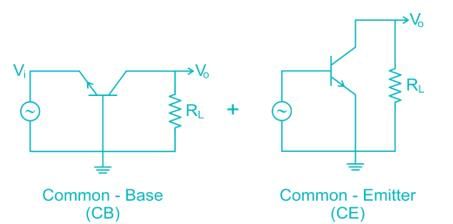
A transistor connected in common base configuration has:
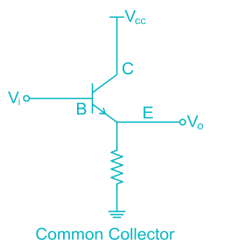
Which of the following is not possible BJT configuration?
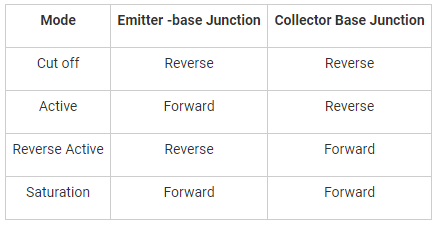
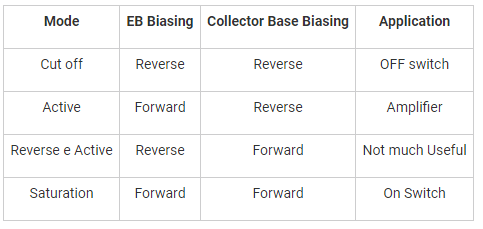
When a BJT is used as switch, its mode of operation switches between:
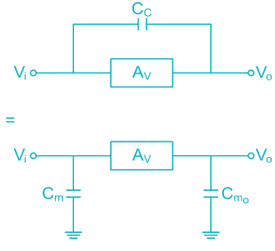
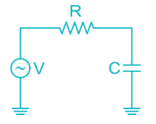
The upper cut-off frequency of an RC coupled amplifier mainly depends upon:
The cascade amplifier is a multistage configuration of:
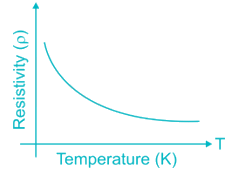
at room temperature intrinsic carrier concentration is higher in germanium than in silicon because __________.