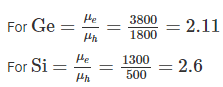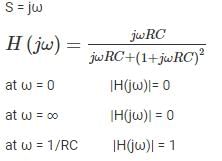Test: Basic Electronics- 3 - Electrical Engineering (EE) MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Basic Electronics- 3
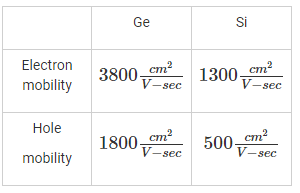
Generally, mobility of electrons in semiconductor is _________ times the mobility of holes:
In a p-n Junction with no externally applied voltage, the drift and diffusion components of the hole and electron currents:
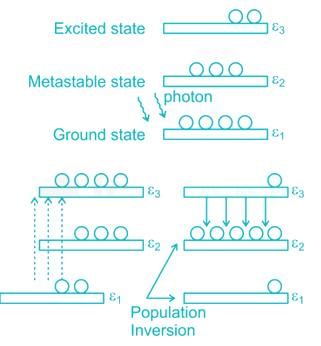
Semiconductor lasers are based on the following principle:
A Bipolar Junction Transistor saturation point may be defined as
In a rectifier, commutation of diodes refers to transferring energy from –
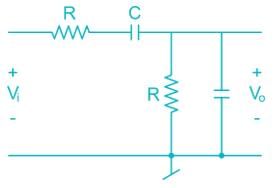
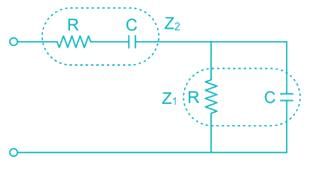
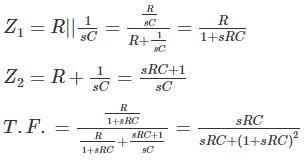
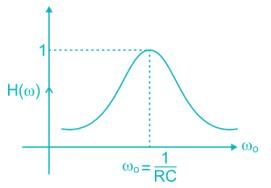
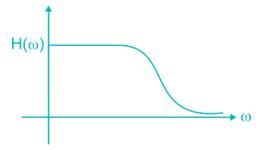
Which among the following has a frequency selective amplifier whose gain decreases from a finite value to zero as the frequency of the sinusoidal input increase form dc to infinity?
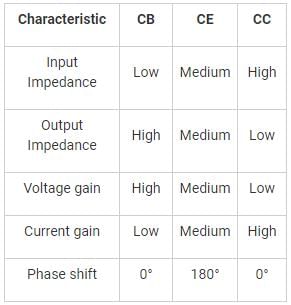
Consider the following circuit configurations:
1. Common emitter
2. Common base
3. Emitter follower
The correct sequence in increasing input impedance is
The h-parameter equivalent circuit of a BJT is valid for:
In a BJT, collector region width is maximum when it.
1. Collects maximum number of charge carrier
2. Reduces heat dissipation per unit area Out of these
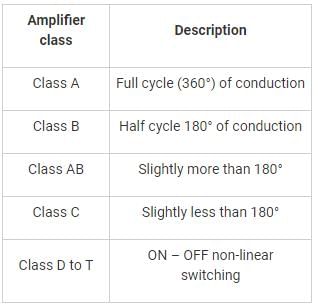
DC bias is adjusted greater than its cut-off value so that the output current flow for less than half of the input voltage cycle, in:
What is the required connection for an enhancement type N-MOSFET to function as a resistor?