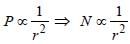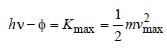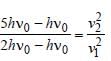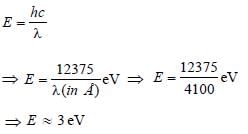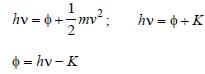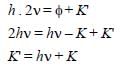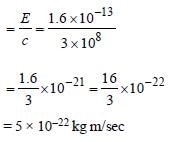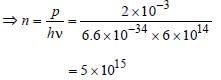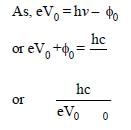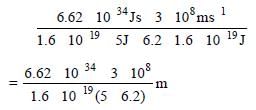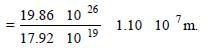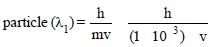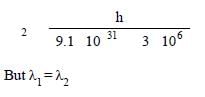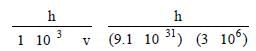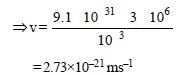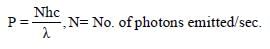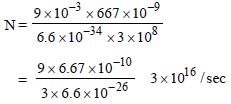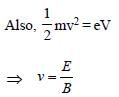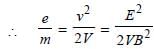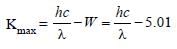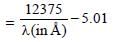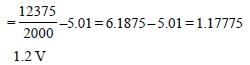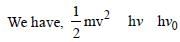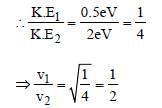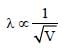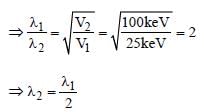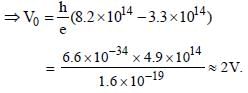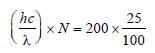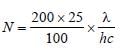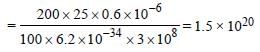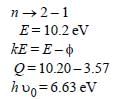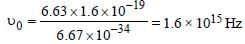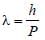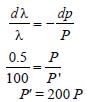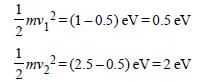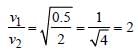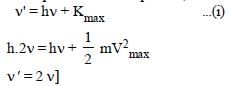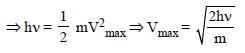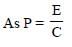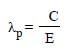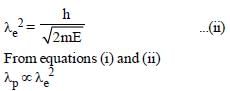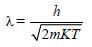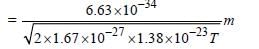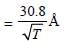31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Dual Nature of Radiation & Matter - 1 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - 31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Dual Nature of Radiation & Matter - 1
When ultraviolet radiation is incident on asurface, no photoelectrons are emitted. If asecond beam causes photoelectrons to beejected, it may consists of [2002]
A photoelectric cell is illuminated by a pointsource of light 1m away. When the source isshifted to 2m then [2003]
According to Einstein’s photoelectric equation, the graph between the kinetic energy of photoelectrons ejected and the frequency of
incident radiation is [2004]
incident radiation is [2004]
A photosensitive metallic surface has workfunction, hv0. If photons of energy 2 hv0 fallon this surface, the electrons come out with amaximum velocity of 4 ×106 m/s. When thephoton energy is increased to 5 hv0, thenmaximum velocity of photoelectrons will be
[2005]
The work functions for metals A, B and C arerespectively 1.92 eV, 2.0 eV and 5 eV.According to Einstein s equation, the metalswhich will emit photoelectrons for a radiationof wavelength 4100 Å is/are [2005]
When photons of energy hv fall on an aluminiumplate (of work function E0), photoelectrons ofmaximum kinetic energy K are ejected. If thefrequency of the radiation is doubled, themaximum kinetic energy of the ejectedphotoelectrons will be [2006]
In a discharge tube ionization of enclosed gas isproduced due to collisions between [2006]
A photo-cell employs photoelectric effect toconvert [2006]
The momentum of a photon of energy 1 MeV inkg m/s, will be [2006]
Monochromatic light of frequency 6.0 × 1014 Hzis produced by a laser. The power emitted is 2 × 10–3 ω. The number of photons emitted, onthe average, by the sources per second is [2007]
The work function of a surface of aphotosensitive material is 6.2 eV. The wavelengthof incident radiation for which the stoppingpotential is 5 V lies in the: [2008]
In the phenomenon of electric discharge throughgases at low pressure, the coloured glow in thetube appears as a result of: [2008]
A particle of mass 1 mg has the same wavelengthas an electron moving with a velocity of 3×106 ms–1. The velocity of the particle is: [2008]
(mass of electron = 9.1×10–31 kg)
The number of photo electrons emitted for lightof a frequency v (higher than the threshold frequency v0) is proportional to: [2009]
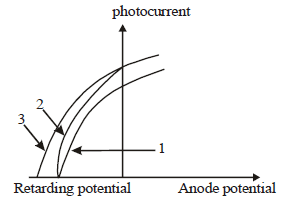
The figure shows a plot of photo current versus anode potential for a photo sensitive surface for three different radiations. Which one of the following is a correct statement? [2009]
Monochromatic light of wavelength 667 nm isproduced by a helium neon laser. The poweremitted is 9 mW. The number of photons arrivingper sec on the average at a target irradiated bythis beam is: [2009]
A beam of cathode rays is subjected to crossed Electric (E) and Magnetic fields (B). The fields are adjusted such that the beam is not deflected. The specific charge of the cathode rays is given by: [2010]
The potential difference that must be applied tostop the fastest photoelectrons emitted by anickel surface, having work function 5.01 eV,when ultraviolet light of 200 nm falls on it, mustbe: [2010]
Photoelectric emmision occurs only whenthe incident light has more than a certainminimum [2011]
Light of two different frequencies whosephotons have energies 1 eV and 2.5 eVrespectively illuminate a metallic surface whosework function is 0.5 eV successively. Ratioof maximum speeds of emitted electrons will be[2011]
Electrons used in an electron microscope areaccelerated by a voltage of 25 kV. If the voltageis increased to 100kV then the de–Brogliewavelength associated with the electrons would
The threshold frequency for a photosensitivemetal is 3.3 × 1014 Hz. If light of frequency 8.2 × 1014 Hz is incident on this metal, the cut-offvoltage for the photoelectric emission is nearly [2011M]
A 200 W sodium street lamp emits yellow lightof wavelength 0.6 μm. Assuming it to be 25% efficient in converting electrical energy to light,the number of photons of yellow light it emitsper second is [2012]
Monochromatic radiation emitted when electronon hydrogen atom jumps from first excited tothe ground state irradiates a photosensitivematerial. The stopping potential is measured tobe 3.57 V. The threshold frequency of the materialsis : [2012]
If the momentum of electron is changed by P,then the de Broglie wavelength associated withit changes by 0.5%. The initial momentum ofelectron will be : [2012M]
Two radiations of photons energies 1 eV and 2.5 eV, successively illuminate a photosensitivemetallic surface of work function 0.5 eV. The ratioof the maximum speeds of the emitted electronsis : [2012M]
For photoelectric emission from certain metal the cut-off frequency is v. If radiation of frequency 2v impinges on the metal plate, the maximum possible velocity of the emitted electron will be (m is the electron mass) [NEET 2013
The wavelength λe of an electron and λp of a photon are of same energy E are related by [NEET 2013]
A source of light is placed at a distance of 50 cm from a photocell and the stopping potential is found to be V0. If the distance between the lightsource and photocell is made 25 cm, the newstopping potential will be [NEET Kar. 2013]
The de-Broglie wavelength of neutron in thermal equilibrium at temperature T is [NEET Kar. 2013]