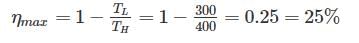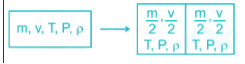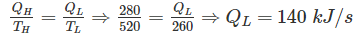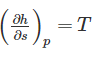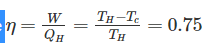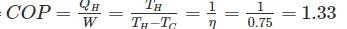Thermodynamics - 2 - Mechanical Engineering MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Thermodynamics - 2
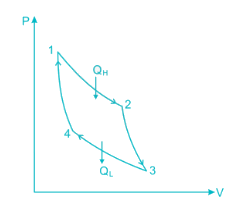
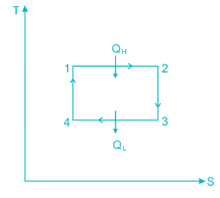
A scientist says that the efficiency of his heat engine which operates at source temperature 127°C and sink temperature 27°C is 26%, then
Which one of the following is extensive property of a thermodynamics system
A heat engine is supplied with 280 kJ/s of heat at a constant fixed temperature of 520 K and heat rejection takes place at 260 K temperature. If the engine is reversible, the heat rejected would be approximate equal to:
Properties of substances like pressure, temperature and density, in thermodynamic co-ordinates are _____.
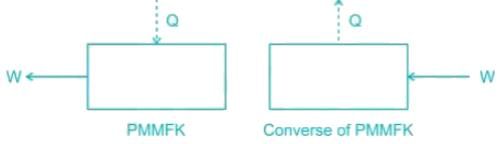
Which of the following represents the perpetual motion of the first kind
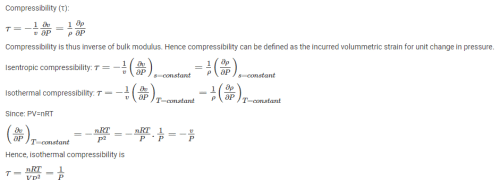
The property of a working substance, which increases or decreases according to the heat supplied or removed in a reversible manner, is called ________.
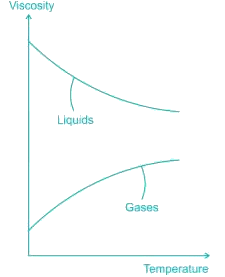
Dynamic viscosity of most of the gases with rise in temperature...
A closed bottle containing water at 30°C is carried to the moon in a space-ship. If it is placed on the surface of the moon, what will happen to the water as soon as the lid is opened
The universal gas constant of a gas is the product of molecular weight of the gas and
One kg of steam sample contains 0.8 kg dry steam; it’s dryness fraction is
A process in which no heat is supplied or rejected from the system and entropy is not constant is known as
Efficiency of a Carnot engine is 75%. If the cycle direction is reverse, COP of the heat pump working on reversed Carnot cycle will be