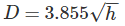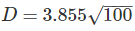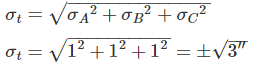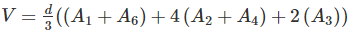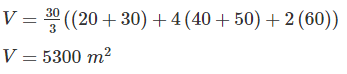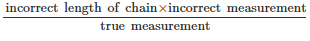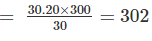Test: Surveying- 3 - SSC JE MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Surveying- 3
A scale of 1 inch = 50 ft. is mentioned on an old map. What is the corresponding equivalent scale?
An object on the top of a hill 100 m high is just visible above the horizon from a station at sea level. The distance between the station and the object is:
If every one of the three angles of a triangle have a probable error of ±1′′, then what will be the probable error in the sum of the measured internal angles of the triangle?
Which type of errors introduces due to clogging of chain rings with mud?
If whole circle bearing of any line is W1, that of the preceding line is W2 and “d” is the deflection angles to the right, then choose the correct expression:
The back sight reading on bench mark of R.L 500.00 m is 2.685 m. If foresight reading on the point is 1.345 m, the reduced level of the point is?
The following consecutive readings were taken with a dumpy level and a 3 m staff on a continuous sloping ground:
0.425, 1.035, 1.950, 2.360, 2.950, 0.750, 1.565, 2.455.
Which of the following readings are back sights?
If cross sectional area of an embankment at 30 m intervals are 20, 40, 60, 50 and 30 m2 respectively, then volume of the embankment on the basis of prismoidal rule is:
To orient a plane table at a point with two inaccessible points, the method generally adopted is:
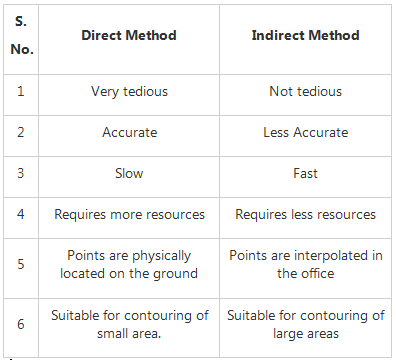
The indirect method of contouring has all the following advantages over direct method except:
If the degree of curve is 1, then radius of the curve for 30 m chain is
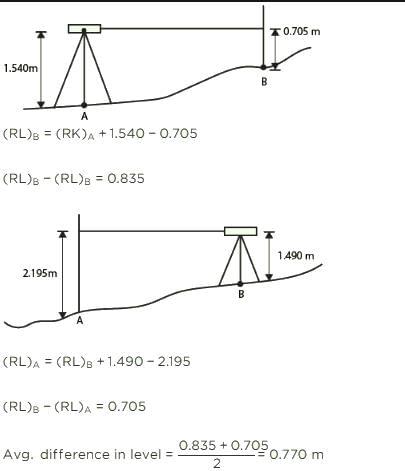
A dumpy level is set up with its eyepiece vertically over a peg A. The height from the top of peg A to the centre of the eyepiece is 1.540 m and the reading on peg B is 0.705 m. The level is then set up over B. The height of the eyepiece above peg B is 1.490 m and a reading on A is 2.195 m. The difference in level between A and B is ________.
A level when set up 25 m from peg A and 50 m from peg B reads 2.847 m on staff held on A and 3.462 m on staff held on B, keeping bubble at its centre while reading. If the reduced levels of A and B are 283.665 m and 284.295 m respectively, what is the collimation error per 100.0 m?
A 30 m metric chain is found to be 20 cm too long throughout a measurement. If the distance measured is recorded as 300 m, what is the actual distance?
The difference between face left and face right observation of a theodolite is 3’. The error is: