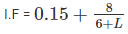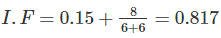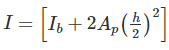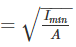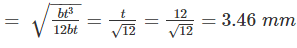Test: Steel Design- 2 - SSC JE MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Steel Design- 2
The effective length of a fillet weld should not be less than
According to the Unwin’s formula, if t is the thickness of the plate in mm, the nominal diameter of the rivet is
According to IS 800-1984, the minimum thickness of vertically stiffened web plate shall not be less than:
The best arrangement to provide unified behaviour in built up steel column is by:
The internal pressure coefficient on walls for buildings with large permeability is taken as:
If the loaded length of span in meters of a railway steel bridge carrying a single track is 6 m, then impact factor is taken as:
If “Ib” is the moment of the inertia of the rolled beam section, “Ap” is the area of the cover plates in one flange and “h” is the distance between the centroid of the top and bottom flange plates, Moment of inertia of Built-up plate girder is given by:
The fillet weld whose axis is perpendicular to the direction of the applied load is known as:
The beam sections in which the extreme fibre in compression can yield stress, but cannot develop the plastic moment of resistance, due to local buckling are classified as
If fillet weld is applied to the rounded toe of a rolled steel section having thickness of "t" at toe, the specified size of weld generally not to exceed
If a plate with small hole is kept over another plate and the entire hole is filled with weld material, the welded joint is known as
A simply supported beam of rectangular section and span L is subjected to a concentrated load at the mid span. The length of the plastic hinge is–
Consider the following with respect to lacing for steel column:
1. It is required to resist a total transverse shear of 2.5 percent of the axial and bending stress.
2. The slenderness ratio of lacing bars shall not exceed 135.
3. For single lacing, effective length is the distance between the inner rivets of the bars.
4. For double lacing, effective length is the distance between the outer most rivets of the bars.
Which one of the above statements are correct?
In case of tension member consisting of two angles back to back of same side of gusset plate, and members are tack riveted. what is K equal to?
Where, A1 – Area of connected leg
A2 – Area of outstanding leg
If a rolled steel flat designated as 55 I.S.F. 12 mm is used as lacing, then minimum radius of gyration will be ________.
When two plates are placed end to end and are joined by two cover plates, the joint is known as _____.
According to IS 800 – 2007, the permissible bending stress in column base in case of Fe415 is:
The critical section for web crippling in case of flexure members is at:



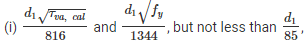 for unstiffened web.
for unstiffened web. for vertically stiffened web.
for vertically stiffened web. for webs stiffened both vertically and horizontally with a horizontal stiffener at a distance from the compression flange equal to 2/5th of the distance from the compression flange to the neutral axis.
for webs stiffened both vertically and horizontally with a horizontal stiffener at a distance from the compression flange equal to 2/5th of the distance from the compression flange to the neutral axis. when there is also a horizontal stiffener at the neutral axis, where d2 is twice the clear distance from the compression flange angles, or plate or tongue plate to the neutral axis.
when there is also a horizontal stiffener at the neutral axis, where d2 is twice the clear distance from the compression flange angles, or plate or tongue plate to the neutral axis.