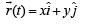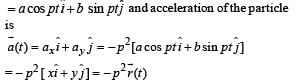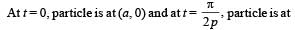JEE Advanced (Single Correct MCQs): Motion - JEE MCQ
12 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Advanced (Single Correct MCQs): Motion
A river is flowing from west to east at a speed of 5 metres per minute. A man on the south bank of the river, capable of swimming at 10 metres per minute in still water, wants to swim across the river in the shortest time. He should swim in a direction
A boat which has a speed of 5 km/hr in still water crosses a river of width 1 km along the shortest possible path in 15 minutes. The velocity of the river water in km/hr is
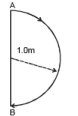
In 1.0 s, a particle goes from point A to point B, moving in a semicircle of radius 1.0 m (see Figure). The magnitude of the average velocity

A ball is dropped vertically from a height d above the ground.
It hits the ground and bounces up vertically to a height d/2.
Neglecting subsequent motion and air resistance, its velocity v varies with the height h above the ground as
A particle starts sliding down a frictionless inclined plane.
If Sn is the distance travelled by it from time t = n – 1 sec to t = n sec, the rati o Sn/Sn+1 is
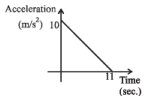
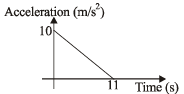
A body starts from rest at time t = 0, the acceleration time graph is shown in the figure. The maximum velocity attained by the body will be
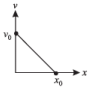
The velocity-displacement graph of a particle moving along a straight line is shown
The most suitable acceleration-displacement graph will be
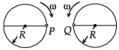
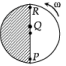
Two identical discs of same radius R are rotating about their axes in opposite directions with the same constant angular speed w. The discs are in the same horizontal plane. At time t = 0, the points P and Q are facing each other as shown in the figure. The relative speed between the two points P and Q is vr. In one time period (T) of rotation of the discs, vr as a function of time is best represented by
Consider a disc rotating in the horizontal plane with a constant angular speed w about its centre O. The disc has a shaded region on one side of the diameter and an unshaded region on the other side as shown in the figure. When the disc is in the orientation as shown, two pebbles P and Q are simultaneously projected at an angle towards R. The velocity of projection is in the y-z plane and is same for both pebbles with respect to the disc. Assume that (i) they land back on the disc before the disc has completed 1/8 rotation, (ii) their range is less than half the disc radius, and (iii) w remains constant throughout. Then .
A particle is moving eastwards with a velocity of 5 m/s. In 10s the velocity changes to 5 m/s northwards. The average acceleration in this time is
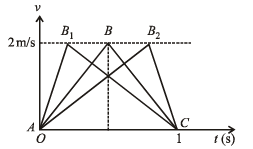
A particle of mass m moves on the x-axis as follows : it starts from rest at t = 0 from the point x = 0, and comes to rest at t = 1 at the point x = 1. NO other information is available about its motion at intermediate times (0 < t< 1). If a denotes the instantaneous acceleration of the particle, then:
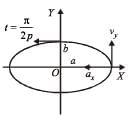
The coordinates of a particle moving in a plane are given by x(t) = a cos (pt) and y (t) = b sin (pt) where a, b (< a) and p are positive constants of appropriate dimensions. Then


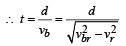
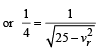
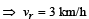

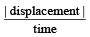
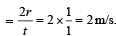
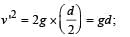
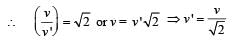
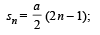
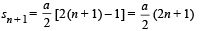
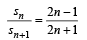
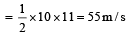
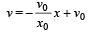
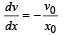
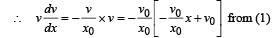
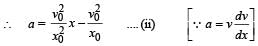
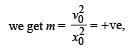
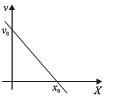
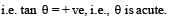
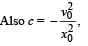
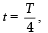 , the relative velocity will be maximum in magnitude.
, the relative velocity will be maximum in magnitude.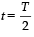 , the relative velocity will be zero.
, the relative velocity will be zero.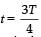 , the relative velocity will be maximum in magnitude
, the relative velocity will be maximum in magnitude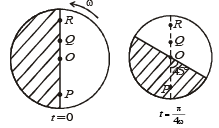
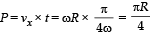
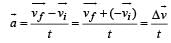
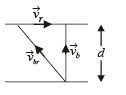
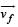 and
and 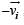 , we draw a diagram
, we draw a diagram 
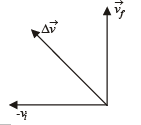
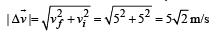
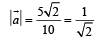
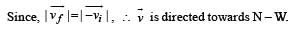
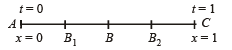
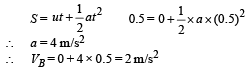
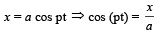
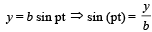
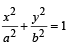
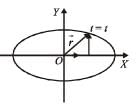
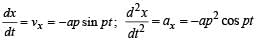
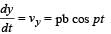
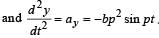
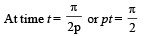
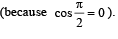 Only
Only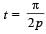 velocity and acceleration of theparticle are normal to each other.
velocity and acceleration of theparticle are normal to each other.