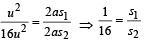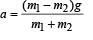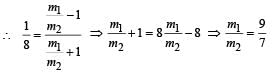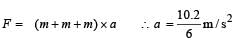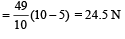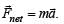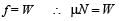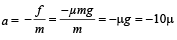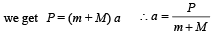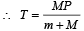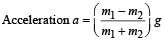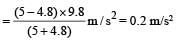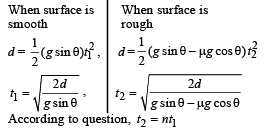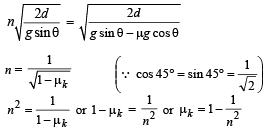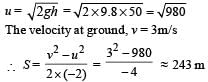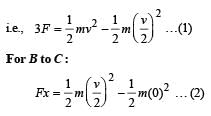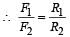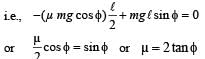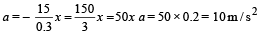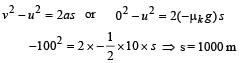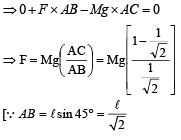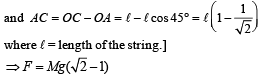Test: JEE Main 35 Year PYQs- Laws of Motion - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: JEE Main 35 Year PYQs- Laws of Motion
A frame of reference that is accelerated with respect to an inertial frame of reference is called a non-inertial frame of reference. A coordinate system fixed on a circular disc rotating about a fixed axis with a constant angular velocity ω is an example of noninertial frame of reference. The relationship between the force  experienced by a particle of mass m moving on the rotating disc and the force
experienced by a particle of mass m moving on the rotating disc and the force 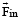 experienced by the particle in an inertial frame of reference is
experienced by the particle in an inertial frame of reference is
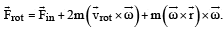
where 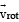 is the velocity of the particle in the rotating frame of reference and
is the velocity of the particle in the rotating frame of reference and 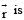 is the position vector of the particle with respect to the centre of the disc.
is the position vector of the particle with respect to the centre of the disc.
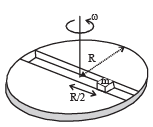
Now consider a smooth slot along a diameter of a disc of radius R rotating counter-clockwise with a constant angular speed ω about its vertical axis through its center. We assign a coordinate system with the origin at the center of the disc, the x-axis along the slot, the y-axis perpendicular to the slot and the z-axis along the rotation axis 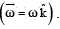 A small block of mass m is gently placed in the slot at
A small block of mass m is gently placed in the slot at 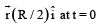 and is constrained to move only along the slot.
and is constrained to move only along the slot.
Q. The distance r of the block at time t is
 experienced by a particle of mass m moving on the rotating disc and the force
experienced by a particle of mass m moving on the rotating disc and the force 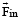 experienced by the particle in an inertial frame of reference is
experienced by the particle in an inertial frame of reference is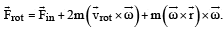
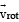 is the velocity of the particle in the rotating frame of reference and
is the velocity of the particle in the rotating frame of reference and 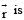 is the position vector of the particle with respect to the centre of the disc.
is the position vector of the particle with respect to the centre of the disc.
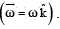 A small block of mass m is gently placed in the slot at
A small block of mass m is gently placed in the slot at 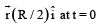 and is constrained to move only along the slot.
and is constrained to move only along the slot.A frame of reference that is accelerated with respect to an inertial frame of reference is called a non-inertial frame of reference. A coordinate system fixed on a circular disc rotating about a fixed axis with a constant angular velocity ω is an example of noninertial frame of reference. The relationship between the force  experienced by a particle of mass m moving on the rotating disc and the force
experienced by a particle of mass m moving on the rotating disc and the force  experienced by the particle in an inertial frame of reference is
experienced by the particle in an inertial frame of reference is
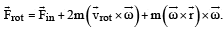
where 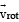 is the velocity of the particle in the rotating frame of reference and
is the velocity of the particle in the rotating frame of reference and 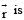 is the position vector of the particle with respect to the centre of the disc.
is the position vector of the particle with respect to the centre of the disc.

Now consider a smooth slot along a diameter of a disc of radius R rotating counter-clockwise with a constant angular speed ω about its vertical axis through its center. We assign a coordinate system with the origin at the center of the disc, the x-axis along the slot, the y-axis perpendicular to the slot and the z-axis along the rotation axis 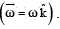 A small block of mass m is gently placed in the slot at
A small block of mass m is gently placed in the slot at 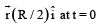 and is constrained to move only along the slot.
and is constrained to move only along the slot.
Q. The net reaction of the disc on the block is
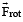 experienced by a particle of mass m moving on the rotating disc and the force
experienced by a particle of mass m moving on the rotating disc and the force 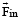 experienced by the particle in an inertial frame of reference is
experienced by the particle in an inertial frame of reference is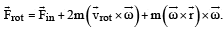
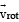 is the velocity of the particle in the rotating frame of reference and
is the velocity of the particle in the rotating frame of reference and 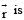 is the position vector of the particle with respect to the centre of the disc.
is the position vector of the particle with respect to the centre of the disc.
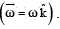 A small block of mass m is gently placed in the slot at
A small block of mass m is gently placed in the slot at 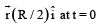 and is constrained to move only along the slot.
and is constrained to move only along the slot.STATEMENT-1 : A cloth covers a table. Some dishes are kept on it. The cloth can be pulled out without dislodging the dishes from the table.
STATEMENT-2 : For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
STATEMENT-2 : For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
STATEMENT-1 : It is easier to pull a heavy object than to push it on a level ground and
STATEMENT-2 : The magnitude of frictional force depends on the nature of the two surfaces in contact.
If a body looses half of its velocity on penetrating 3 cm in a wooden block, then how much will it penetrate more before coming to rest?
A lift is moving down with acceleration a. A man in the lift drops a ball inside the lift. The acceleration of the ball as observed by the man in the lift and a man standing stationary on the ground are respectively
When forces F1, F2, F3 are acting on a particle of mass m such that F2 and F3 are mutually perpendicular, then the particle remains stationary. If the force F1 is now removed then the acceleration of the particle is
Two forces are such that the sum of their magnitudes is 18 N and their resultant is 12 N which is perpendicular to the smaller force. Then the magnitudes of the forces are
Speeds of two identical cars are u and 4u at the specific instant. The ratio of the respective distances in which the two cars are stopped from that instant is
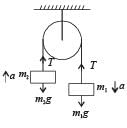
A light string passing over a smooth light pulley connects two blocks of masses m1 and m2 (vertically). If the acceleration of the system is g/8, then the ratio of the masses is
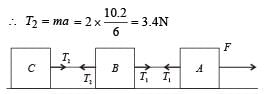
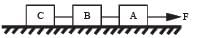
Three identical blocks of masses m = 2 kg are drawn by a force F = 10.2 N with an acceleration of 0. 6 ms–2 on a frictionless surface, then what is the tension (in N) in the string between the blocks B and C?
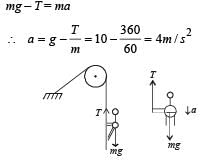
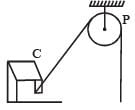
One end of a massless rope, which passes over a massless and frictionless pulley P is tied to a hook C while the other end is free. Maximum tension that the rope can bear is 360 N. With what value of maximum safe acceleration (in ms–2) can a man of 60 kg climb on the rope?
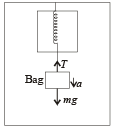
A spring balance is attached to the ceiling of a lift. A man hangs his bag on the spring and the spring reads 49 N, when the lift is stationary. If the lift moves downward with an acceleration of 5 m/s2, the reading of the spring balance will be
Three forces start acting simultaneously on a particle moving with velocity, 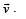 These forces are represented in magnitude and direction by the three sides of a triangle ABC. The particle will now move with velocity
These forces are represented in magnitude and direction by the three sides of a triangle ABC. The particle will now move with velocity
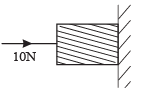
A horizontal force of 10 N is necessary to just hold a block stationary against a wall. The coefficient of friction between the block and the wall is 0.2. The weight of the block is
A marble block of mass 2 kg lying on ice when given a velocity of 6 m/s is stopped by friction in 10 s. Then the coefficient of friction is
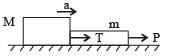
A block of mass M is pulled along a horizontal frictionless surface by a rope of mass m. If a force P is applied at the free end of the rope, the force exerted by the rope on the block is
A light spring balance hangs from the hook of the other light spring balance and a block of mass M kg hangs from the former one. Then the true statement about the scale reading is
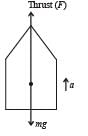
A rocket with a lift-off mass 3.5 × 104 kg is blasted upwards with an initial acceleration of 10m/s2. Then the initial thrust of the blast is
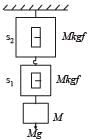
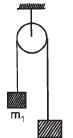
Two masses m1 = 5 kg and m2 = 4.8 kg tied to a string are hanging over a light frictionless pulley. What is the acceleration of the masses when left free to move ?
(g = 9.8m / s2)
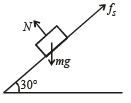
A block rests on a rough inclined plane making an angle of 30° with the horizontal. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the plane is 0.8. If the frictional force on the block is 10 N, the mass of the block (in kg) is
(take g = 10 m /s2)
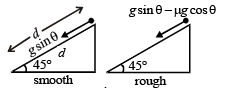
A smooth block is released at rest on a 45° incline and then slides a distance ‘d’. The time taken to slide is ‘n’ times as much to slide on rough incline than on a smooth incline.
The coefficient of friction is
A parachutist after bailing out falls 50 m without friction.
Wh en par achute open s, it decelerates at 2 m /s2 . He reaches the ground with a speed of 3 m/s. At what height, did he bail out ?
A bullet fired into a fixed target loses half of its velocity after penetrating 3 cm. How much further it will penetrate before coming to rest assuming that it faces constant resistance to motion ?
An annular ring with inner and outer radii R1 and R2 is rolling without slipping with a uniform angular speed. The ratio of the forces experienced by the two particles situated on the inner and outer parts of the ring, 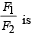
The upper half of an inclined plane with inclination φ is perfectly smooth while the lower half is rough. A body starting from rest at the top will again come to rest at the bottom if the coefficient of friction for the lower half is given by
A particle of mass 0.3 kg subject to a force F = – kx with k = 15 N/m . What will be its initial acceleration if it is released from a point 20 cm away from the origin ?
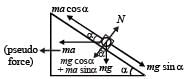
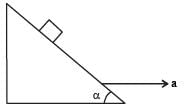
A block is kept on a frictionless inclined surface with angle of inclination ‘α’ . The incline is given an acceleration ‘a’ to keep the block stationary. Then a is equal to
Consider a car moving on a straight road with a speed of 100 m/s . The distance at which car can be stopped is [μk = 0.5]
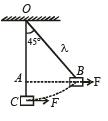
A mass of M kg is suspended by a weightless string. The horizontal force that is required to displace it until the string makes an angle of 45° with the initial vertical direction is


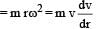
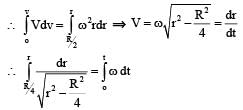
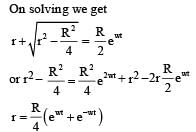
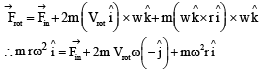
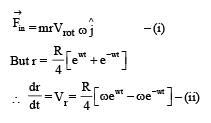

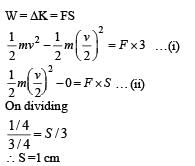
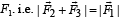
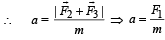
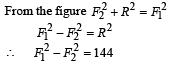
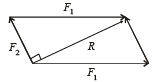
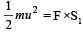 … (i)
… (i)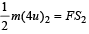 ...(ii)
...(ii)