JEE Advanced (Single Correct MCQs): Simple Harmonic Motion (Oscillations) - JEE MCQ
11 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Advanced (Single Correct MCQs): Simple Harmonic Motion (Oscillations)
Two bodies M and N of equal masses are suspended from two separate massless springs of spring constants k1 and k2 respectively. If the two bodies oscillate vertically such that their maximum velocities are equal, the ratio of the amplitude of vibration of M to that of N is
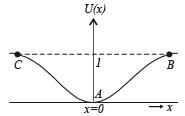
A particle free to move along the x-axis has potential energy given by U(x) = k [1–exp(–x2)] for -∞ < x < + ∞, where k is a positive constant of appropriate dimensions. Then
The period of oscillation of a simple pendulum of length L suspended from the roof of a vehicle which moves without friction down an inclined plane of inclination α , is given by
A particle executes simple harmonic motion between x = -A and x = +A. The time taken for it to go from 0 to A/2 is T1 and to go from A/2 to A is T2. Then
For a particle executing SHM the displacement x is given by x = A coswt. Identify the graph which represents the variation of potential energy (PE) as a function of time t and displacement x
A simple pendulum has time period T1. The point of suspension is now moved upward according to the relation y = Kt2, (K = 1 m/s2) where y is the vertical displacement. The time period now becomes T2. The ratio of 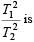
(g = 10 m/s2)
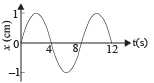
The x-t graph of a particle undergoing simple harmonic motion is shown below. The acceleration of the particle at t = 4 / 3 s is
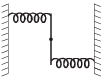
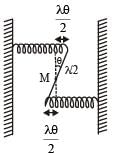
A uniform rod of length L and mass M is pivoted at the centre. Its two ends are attached to two springs of equal spring constants k. The springs are fixed to rigid supports as shown in the figure, and the rod is free to oscillate in the horizontal plane.
The rod is gently pushed through a small angle θ in one direction and released. The frequency of oscillation is
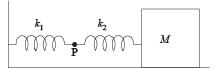
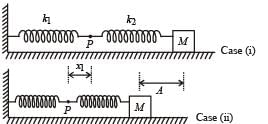
The mass M shown in the figure oscillates in simple harmonic motion with amplitude A. The amplitude of the point P is
A point mass is subjected to two simultaneous sinusoidal displacements in x-direction, x1(t) = A sin wt and x2(t) = 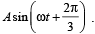 Adding a third sinusoidal displacement x3(t) = B sin (ωt + φ) brings the mass to a complete rest. The values of B and φ are
Adding a third sinusoidal displacement x3(t) = B sin (ωt + φ) brings the mass to a complete rest. The values of B and φ are
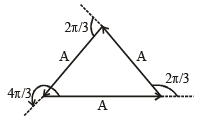
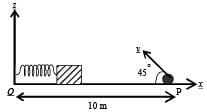
A small block is connected to one end of a massless spring of un-stretched length 4.9 m. The other end of the spring (see the figure) is fixed. The system lies on a horizontal frictionless surface. The block is stretched by 0.2 m and released from rest at t = 0. It then executes simple harmonic motion with angular frequency ω = π/3 rad/s. Simultaneously at t = 0, a small pebble is projected with speed v form point P at an angle of 45° as shown in the figure. Point P is at a horizontal distance of 10 m from O. If the pebble hits the block at t = 1 s, the value of v is (take g = 10 m/s2)


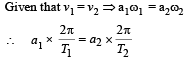
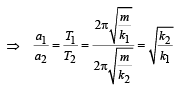
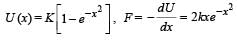
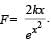 Therefore for small
Therefore for small
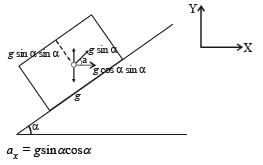
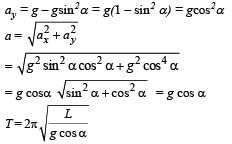
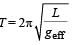
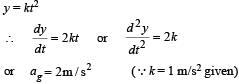
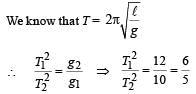
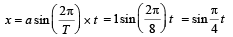
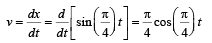
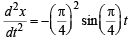
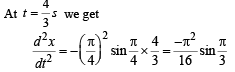

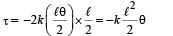 ... (i)
... (i)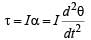 … (ii)
… (ii)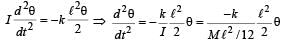
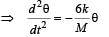
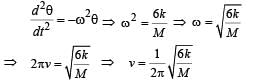
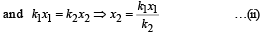
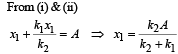
 It is given that sinusoidal displacement x3(t) brings the mass to a complete rest. This is possible when the amplitude of third is A and is having a phase difference of
It is given that sinusoidal displacement x3(t) brings the mass to a complete rest. This is possible when the amplitude of third is A and is having a phase difference of 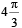 with
with