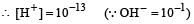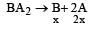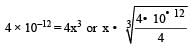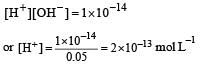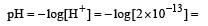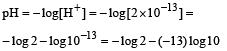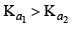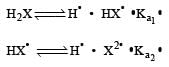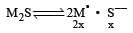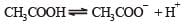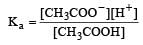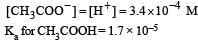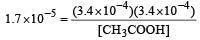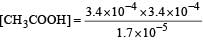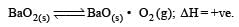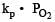31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Equilibrium - 3 - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - 31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Equilibrium - 3
The compound whose aqueous solution has the highest pH is [1988]
K1 and K2 are equilibrium constant for reactions (1) and (2)
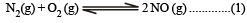
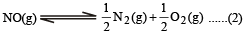
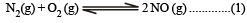
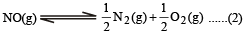
Aqueous solution of acetic acid contains [1991]
0.1 M solution of which one of these substances will be basic ? [1992]
Which one of the following information can be obtained on the basis of Le Chatelier principle?
In which of the following solvents, AgBr will have the highest solubility ? [1992]
According to Le-chatelier ’s principle, adding heat to a solid 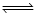 liquid equilibrium will cause the
liquid equilibrium will cause the
In which of the following the solubility of AgCl will be minimum ? [1993]
Which of the following is most soluble ? [1994]
The pH value of a 10 M solution of HCl is [1995]
The rate constant for forward and backward reaction of hydrolysis of ester are 1.1x10-2 and 1.5x10-3 per minute respectively. Equilibrium constant for the reaction [1995]
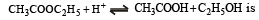
Th e pH value of blood does not appreciably change by a small addition of an acid or a base, because the blood [1995]
If α is the fraction of HI dissociated at equilibrium in the reaction, 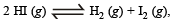 starting with 2 moles of HI, the total number of moles of reactants and products at equilibrium are[1996]
starting with 2 moles of HI, the total number of moles of reactants and products at equilibrium are[1996]
The equilibrium con stant for the reaction A2  2A at 500 K and 700 K are 1 × 10–10 and 1× 10–5 respectively. The given reaction is[1996]
2A at 500 K and 700 K are 1 × 10–10 and 1× 10–5 respectively. The given reaction is[1996]
The solubility products of CuS, Ag2S and HgS are 10–31, 10–44, 10–54 respectively. The solubilities of these sulphides are in the order
A physician wishes to prepare a buffer solution of pH = 3.58 that efficiently resists a change in pH yet contains only small concentrations of the buffering agents. Which one of the following weak acids together with its sodium salt would be the best to use ? [1997]
In a two-step exothermic reaction
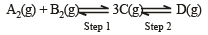
Steps 1 and 2 are favoured respectively by [1997]
If K1 and K2 are the respective equilibrium constants for the two reactions
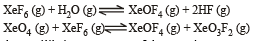
the equilibrium constant of the reaction
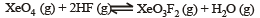
will be[1998]
Among boron trifluoride, stannic chloride and stannous chloride, Lewis acid is represented by
What is the H+ ion concentration of a solution prepared by dissolving 4 g of NaOH (Atomic weight of Na = 23 amu) in 1000 ml? [1999]
The solubility product of a sparingly soluble salt BA2 is 4 × 10–12. The solubility of BA2 is[1999]
A base when dissolved in water yields a solution with a hydroxyl ion concentration of 0.05 mol litre–1.The solution is [2000]
Value of KP in the reaction 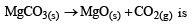
Conjugate acid of NH-2 is : [2000]
For dibasic acid correct order is [2000]
Which of the following statements about pH and H+ ion concentration is incorrect? [2000]
Solubility of a M2S salt is 3.5 × 10–6, then its solubility product will be [2001]
Ionisation constant of CH3COOH is 1.7 × 10–5 if concentration of H+ ions is 3.4 × 10–4M, then find out initial concentration of CH3COOH molecules [2001]
In HS–, I–, RNH2 and NH3, order of proton accepting tendency will be [2001]
For the reaction
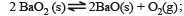
ΔH = +ve. In equilibrium condition, pressure of O2 is dependent on [2002]


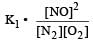
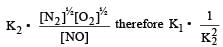



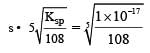
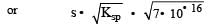
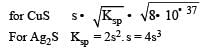

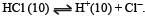
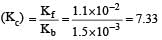
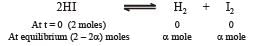
 Equilibrium constant is given by
Equilibrium constant is given by
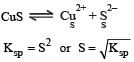
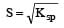
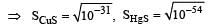
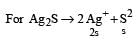
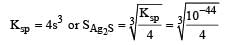
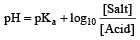
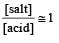
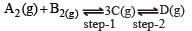
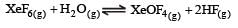
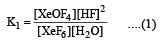
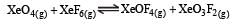
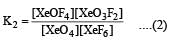
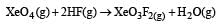
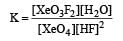
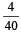 = 0.1
= 0.1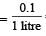 = 0.1Mole /L
= 0.1Mole /L