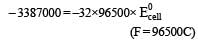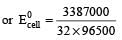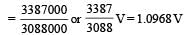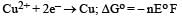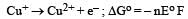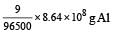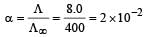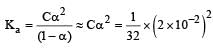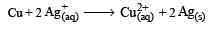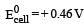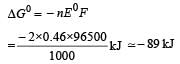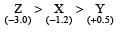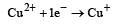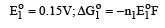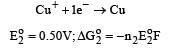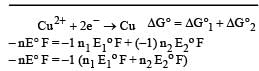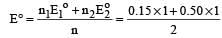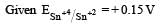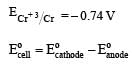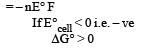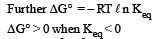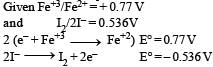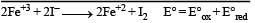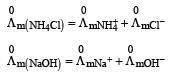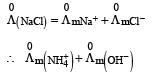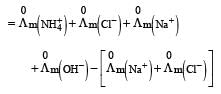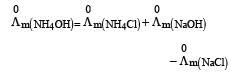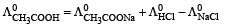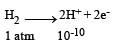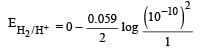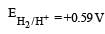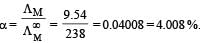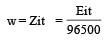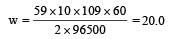31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Electrochemistry - 1 - NEET MCQ
23 Questions MCQ Test - 31 Year NEET Previous Year Questions: Electrochemistry - 1
The equilibrium constant of the reaction:
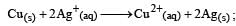
E° = 0.46 V at 298 K is [2007]
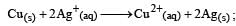
On the basis of the following E° values, the strongest oxidizing agent is : [2008]
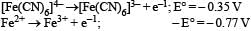
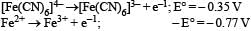
Kohlrausch’s law states that at : [2008]
Standard free energies of formation (in kJ/mol) at 298 K are – 237.2, – 394.4 and – 8.2 for H2O(l), CO2(g) and pentane (g), respectively. The value E°cell for the pentane-oxygen fuel cell is : [2008]
Given: [2009]
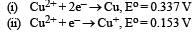
Electrode potential, Eo for the reaction, 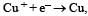 will be :
will be :
Al 2O3 is reduced by electrolysisat low potentials and high currents. If 4.0 × 104 amperes of current is passed through molten Al2O3 for 6 hours, what mass of aluminium is produced? (Assume 100% current efficiency. At. mass of Al = 27 g mol–1) [2009]
The equivalent conductance of 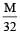 solution ofa weak monobasic acid is 8.0 mhos cm2 and at infinite dilution is 400 mhos cm2. The dissociation constant of this acid is: [2009]
solution ofa weak monobasic acid is 8.0 mhos cm2 and at infinite dilution is 400 mhos cm2. The dissociation constant of this acid is: [2009]
For the reduction of silver ions with copper metal, the standard cell potential was found to be + 0.46 V at 25°C. The value of standard Gibbs energy, ΔG0 will be (F = 96500 C mol –1)
An increase in equivalent conductance of a strong electrolyte with dilution is mainly due to: [2010]
Which of the following expressions correctly represents the equivalent conductance at infinite dilution of Al2 (SO4)3, Given that 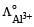 and
and 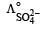 are the equivalent conductances at infinite dilution of the respective ions? [2010]
are the equivalent conductances at infinite dilution of the respective ions? [2010]
Consider the following relations for emf of a electrochemical cell: [2010]
(i) emf of cell = (Oxidation potential of anode) – (Reduction potential of cathode)
(ii) emf of cell = (Oxidation potential of anode) + (Reduction potential of cathode)
(iii) emf of cell = (Reduction potential of anode) + (Reduction potential of cathode)
(iv) emf of cell = (Oxidation potential of anode) – (Oxidation potential of cathode)
Which of the above relations are correct?
Standard electrode potential of three metals X, Y and Z are – 1.2 V, + 0.5 V and – 3.0 V, respectively. The reducing power of these metals will be : [2011]
The electrode potentials for [2011]
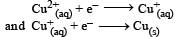
are + 0.15 V and + 0.50, respectively. The value of E° Cu 2+ / Cu will be :
Standard electrode potential for Sn4+ / Sn2+ couple is + 0.15 V and that for the Cr3+ / Cr couple is – 0.74 V. These two couples in their standard state are connected to make a cell. The cell potential will be : [2011]
If the E°cell for a given reaction has a negative value, then which of the following gives the correct relationships for the values of ΔG° and Keq ?[2011]
A solution contains Fe2+, Fe3+ and I– ions. This solution was treated with iodine at 35°C. E° for Fe3+ / Fe2+ is + 0.77 V and E° for I2/2I– = 0.536 V.The favourable redox reaction is : [2011 M]
Limiting molar conductivity of NH4OH
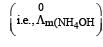 is equal to : [2012]
is equal to : [2012]
Molar conductivities 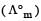 at infinite dilution of NaCl, HCl and CH3COONa are 126.4, 425.9 and 91.0 S cm2 mol–1 respectively.
at infinite dilution of NaCl, HCl and CH3COONa are 126.4, 425.9 and 91.0 S cm2 mol–1 respectively. 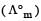 for CH3COOH will be : [2012 M]
for CH3COOH will be : [2012 M]
A hydrogen gas electrode is made by dipping platinum wire in a solution of HCl of pH = 10 and by passing hydrogen gas around the platinum wire at one atm pressure. The oxidation potential of electrode would be ? [NEET 2013]
At 25°C molar conductance of 0.1 molar aqueous solution of ammonium hydroxide is 9.54 ohm-1 cm2mol-1 and at infinite dilution its molar conductance is 238 ohm-1 cm2 mol-1. The degree or ionisation of ammonium hydroxide at the same concentration and temperature is :[NEET 2013]
A button cell used in watches function s as following
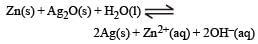
If half cell potentials are :
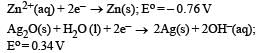
The cell potential will be : [NEET 2013]
How many grams of cobalt metal will be deposited when a solution of cobalt (II) chloride is electrolyzed with a current of 10 amperes for 109 minutes (1 Faraday = 96,500 C; Atomic mass of Co = 59 u) [NEET Kar. 2013]
Consider the half-cell reduction reaction :
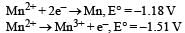
The E° for the reaction 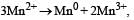 and possibility of the forward reaction are, respectively [NEET Kar. 2013]
and possibility of the forward reaction are, respectively [NEET Kar. 2013]


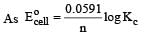
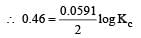
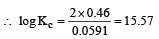

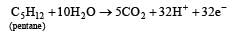
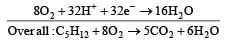
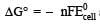 and substituting various values, we get
and substituting various values, we get