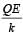JEE Advanced (Single Correct MCQs): Electrostatics - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - JEE Advanced (Single Correct MCQs): Electrostatics
A hollow metal sphere of radius 5 cms is charged such that the potential on its surface is 10 volts. The potential at the centre of the sphere is
Two point charges +q and –q are held fixed at (–d, o) and (d, o) respectively of a x-y coordinate system. Then
A parallel plate capacitor of capacitance C is connected to a battery and is charged to a potential difference V. Another capacitor of capacitance 2C is similarly charged to a potential difference 2V. The charging battery is now disconnected and the capacitors are connected in parallel to each other in such a way that the positive terminal of one is connected to the negative terminal of the other. The final energy of the configuration is
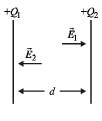
Two identical metal plates are given positive charges Q1 and Q2 (<Q1) respectively. If they are now brought close together to form a parallel plate capacitor with capacitance C, the potential difference between them is
For the circuit shown in Figure, which of the following statements is true?
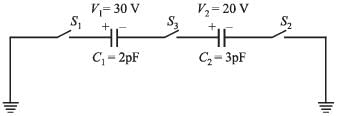
Three charges Q, +q and +q are placed at the vertices of a right-angled isosceles triangle as shown. The net electrostatic energy of the configuration is zero if Q is equal to
A parallel plate capacitor of area A, plate separation d and capacitance C is filled with three different dielectric materials having dielectric constants k1, k2 and k3 as shown. If a single dielectric material is to be used to have the same capacitance C in this capacitor, then its dielectric constant k is given by

Three positive charges of equal value q are placed at the vertices of an equilateral triangle. The resulting lines of force should be sketched as in
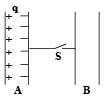
Consider the situation shown in the figure. The capacitor A has a charge q on it whereas B is uncharged. The charge appearing on the capacitor B a long time after the switch is closed is
A uniform electric field pointing in positive x-direction exists in a region. Let A be the origin, B be the point on the x-axis at x = +1 cm and C be the point on the y-axis at y = +1 cm. Then the potentials at the points A, B and C satisfy:
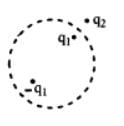
Two equal point charges are fixed at x = – a and x = + a on the x-axis. Another point charge Q is placed at the origin.
The change in the electrical potential energy of Q, when it is displaced by a small distance x along the x-axis, is approximately proportional to
Two identical capacitors, have the same capacitance C. One of them is charged to potential V1 and the other V2. The negative ends of the capacitors are connected together.
When the positive ends are also connected, the decrease in energy of the combined system is
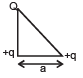
A metallic shell has a point charge ‘q’ kept inside its cavity. Which one of the following diagrams correctly represents the electric lines of forces?
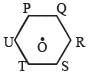
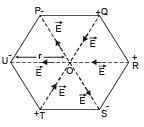
Six charges of equal magnitude, 3 positive and 3 negative are to be placed on PQRSTU corners of a regular hexagon, such that field at the centre is double that of what it would have been if only one +ve charge is placed at R. Which of the following arrangement of charge is possible for P, Q, R, S, T and U respectively.
A Gaussian surface in the figur e is shown by dotted line. The electric field on the surface will be
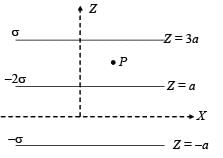
Three infinitely long charge sheets are placed as shown in figure. The electric field at point P is
A long, hollow conducting cylinder is kept coaxially inside another long, hollow conducting cylinder of larger radius.
Both the cylinders are initially electrically neutral.
Consider a neutral conducting sphere. A positive point charge is placed outside the sphere. The net charge on the sphere is then
A spherical portion has been removed from a solid sphere having a charge distributed uniformly in its volume as shown in the figure. The electric field inside the emptied space is
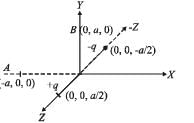
Positive and negative point charges of equal magnitude are kept at 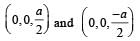 respectively. The work done by the electric field when another positive point charge is moved from (–a, 0, 0) to (0, a, 0) is
respectively. The work done by the electric field when another positive point charge is moved from (–a, 0, 0) to (0, a, 0) is
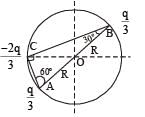
Consider a system of three charges q/3, q/3 and –2q/3 placed at points A, B and C, respectively, as shown in the figure.
Take O to be the centre of the circle of radius R and angle CAB = 60°
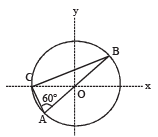
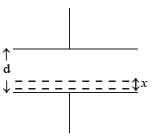
A parallel plate capacitor C with plates of unit area and separation d is filled with a liquid of dielectric constant K = 2. The level of liquid is d/3 initially. Suppose the liquid level decreases at a constant speed v, the time constant as a function of time t is –
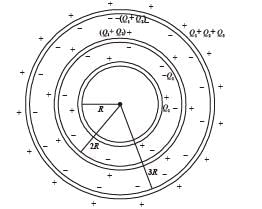
Three concentric metallic spherical shells of radii R, 2R, 3R, are given charges Q1, Q2, Q3, respectively. It is found that the surface charge densities on the outer surfaces of the shells are equal. Then, the ratio of the charges given to the shells, Q1 : Q2 : Q3, is
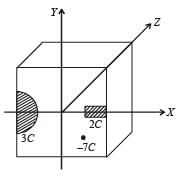
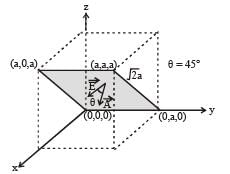
A disc of radius a / 4 having a uniformly distributed charge 6C is placed in the x - y plane with its centre at (–a / 2, 0, 0).
A rod of length a carrying a uniformly distributed charge 8C is placed on the x - axis from x = a /4 to x = 5a / 4. Two point charges – 7 C and 3 C are placed at (a / 4, – a /4, 0) and (– 3a /4, 3a / 4, 0), respectively. Consider a cubical surface formed by six surfaces x = ± a / 2, y = ± a / 2, z = ± a / 2. The electric flux through this cubical surface is
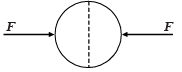
A uniformly charged thin spherical shell of radius R carries uniform surface charge density of σ per unit area. It is made of two hemispherical shells, held together by pressing them with force F (see figure). F is proportional to
A tiny spherical oil drop carrying a net charge q is balanced in still air with a vertical uniform electric field of strength 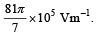 When the field is switched off, the drop is observed to fall with terminal velocity 2 ×10–3 ms –1. Given g = 9.8 m s–2, viscosity of the air = 1.8 × 10–5 Ns m–2 and the density of oil = 900 kg m–3, the magnitude of q is
When the field is switched off, the drop is observed to fall with terminal velocity 2 ×10–3 ms –1. Given g = 9.8 m s–2, viscosity of the air = 1.8 × 10–5 Ns m–2 and the density of oil = 900 kg m–3, the magnitude of q is
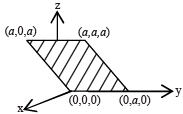
Consider an electric field 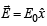 where E0 is a constant.
where E0 is a constant.
The flux through the shaded area (as shown in the figure) due to this field is
A 2 μF capacitor is charged as shown in the figure. The percentage of its stored energy dissipated after the switch S is turned to position 2 is
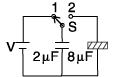
Which of the field patterns given below is valid for electric field as well as for magnetic field?
A wooden block performs SHM on a frictionless surface with frequency, v0. The block carries a charge +Q on its surface. If now a uniform electric field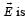 switched-on as shown, then the SHM of the block will be
switched-on as shown, then the SHM of the block will be





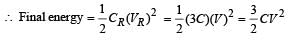
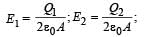
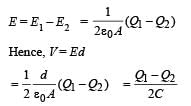
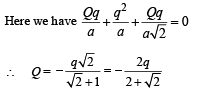
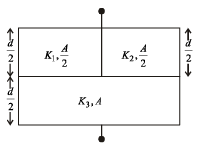
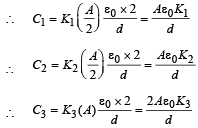
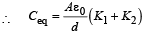
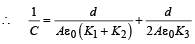
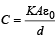 for single equivalent capacitor
for single equivalent capacitor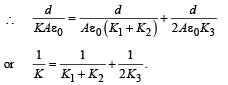
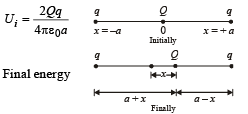
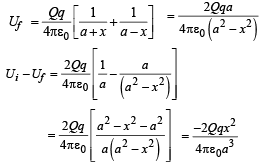
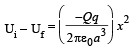
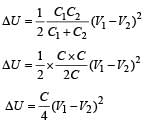
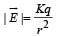
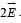
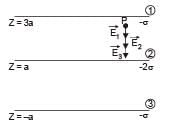
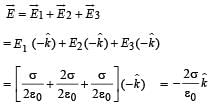
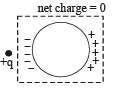
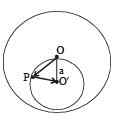
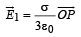
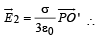 The total electric field
The total electric field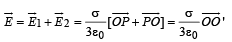
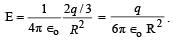
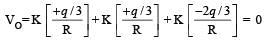
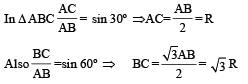
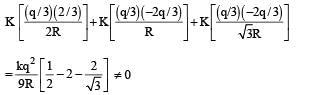
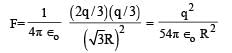
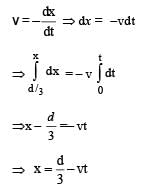
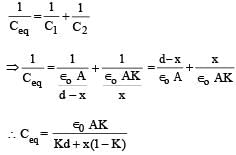
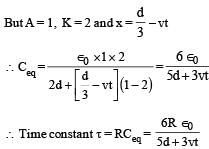
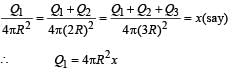
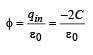
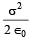
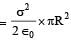
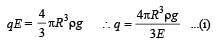
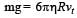
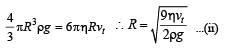
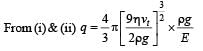
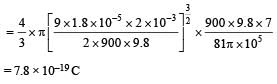
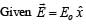
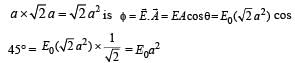
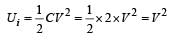
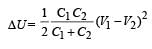
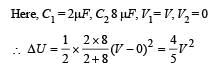
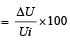
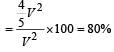
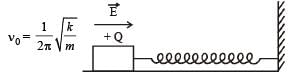 when electric field is switched on, the value of k and m is not affected and therefore the frequency of SHM remains the same. But as an external force QE starts acting on the block towards right, the mean position of SHM shifts towards right by
when electric field is switched on, the value of k and m is not affected and therefore the frequency of SHM remains the same. But as an external force QE starts acting on the block towards right, the mean position of SHM shifts towards right by