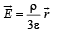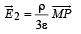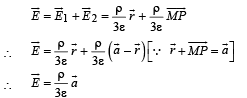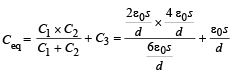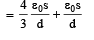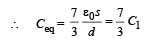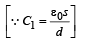Test: MCQs (One or More Correct Option): Electrostatics | JEE Advanced - ENGAA MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: MCQs (One or More Correct Option): Electrostatics | JEE Advanced
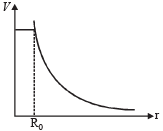
Two equal negative charges –q are fixed at points (0, – a) and (0, a) on y – axis. A positive charge Q is released from rest at the point (2a, 0) on the x - axis. The charge Q will
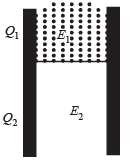
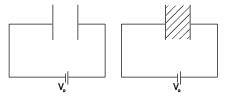
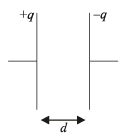
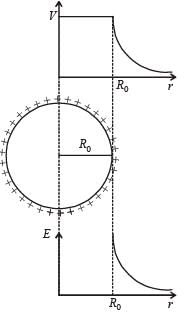
A parallel plate air capacitor is connected to a battery. The quantities charge, voltage, electric field and energy associated with this capacitor are given by Q0, V0, E0 and U0 respectively. A dielectric slab is now introduced to fill the space between the plates with battery still in connection.
The corresponding quantities now given by Q, V, E and U are related to th e previous one as
The corresponding quantities now given by Q, V, E and U are related to th e previous one as
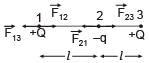
A charge q is placed at the centre of the line joining two equal charges Q. The system of the three charges will be in equilibrium if q is equal to :
A parallel plate capacitor is charged and the charging battery is then disconnected. If the plates of the capacitor are moved farther apart by means of insulating handles :
A solid conducting sphere having a charge Q is surrounded by an uncharged concentric conducting hollow spherical shell. Let the potential difference between the surface of the solid sphere and that of the outer surface of the hollow shell be V. If the shell is now given a charge of – 3Q, the new potential difference between the same two surfaces is :
Seven capacitors each of capacitan ce 2μF are to be connected in a configuration to obtain an effective capacitance of 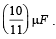 Which of the combination (s) shown in figure will achieve the desired result ?
Which of the combination (s) shown in figure will achieve the desired result ?
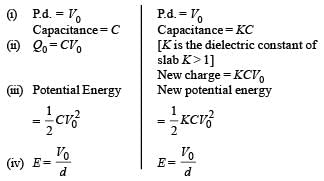
A parallel plate capacitor of plate area A and plate separation d is charged to potential difference V and then the battery is disconnected. A slab of dielectric constant K is then inserted between the plates of the capacitor so as to fill the space between the plates. If Q, E and W denote respectively, the magnitude of charge on each plate, the electric field between the plates (after the slab is inserted), and work done on the system, in question, in the process of inserting the slab, then
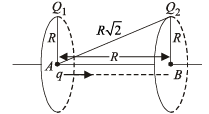
Two identical thin rings, each of radius R metres, are coaxially placed a distance R metres apart. If Q1 coulomb, and Q2 coulomb, are respectively the charges uniformly spread on the two rings, the work done in moving a charge q from the centre of one ring to that of the other is
The magnitude of electric field 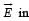 the annular region of a charged cylindrical capacitor.
the annular region of a charged cylindrical capacitor.
A metallic solid sphere is placed in a uniform electric fied. The lines of force follow the path(s) shown in Figure as
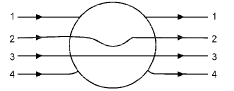
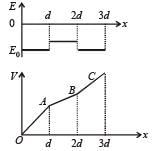
A dielectric slab of thickness d is inserted in a parallel plate capacitor whose negative plate is at x = 0 and positive plate is at x = 3d. The slab is equidistant from the plates. The capacitor is given some charge. As one goes from 0 to 3d,
A charge +q is fixed at each of the points x = x0, x = 3x0, x = 5x0,..... x = ∞ on the x axis, and a charge –q is fixed at each of the points x = 2x0, x = 4x0, x = 6x0,.... x = ∞. Here x0 is a positive constant. Take the electric potential at a point due to a charge Q at a distance r from it to be Q/(4πε0r).
Then, the potential at the origin due to the above system of charges is
A positively charged thin metal ring of radius R is fixed in the xy plane with its centre at the origin O. A negatively charged particle P is released from rest at the point (0, 0, z0) where z0 > 0. Then the motion of P is
A non-conducting solid sphere of radius R is uniformly charged. The magnitude of the electric field due to the sphere at a distance r from its centre
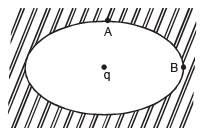
An ellipsoidal cavity is carved within a perfect conductor. A positive charge q is placed at the centre of the cavity. The points A and B are on the cavity surface as shown in the figure. Then
A spherical symmetric charge system is centered at origin. Given, Electric potential
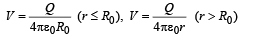
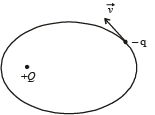
Under the influence of the Coulomb field of charge + Q, a charge –q is moving around it in an elliptical orbit. Find out the correct statement(s).
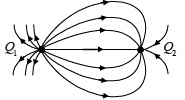
A few electric field lines for a system of two charges Q1 and Q2 fixed at two different points on the x-axis are shown in the figure. These lines suggest that
A spherical metal shell A of radius RA and a solid metal sphere B of radius RB(< RA) are kept far apart and each is given charge ‘+Q’. Now they are connected by a thin metal wire. Then
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
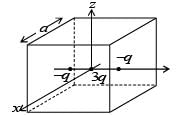
A cubical region of side a has its centre at the origin.
It encloses three fixed point charges, -q at (0, -a/4, 0), +3q at (0, 0, 0) and -q at (0, +a/4, 0). Choose the correct options(s)
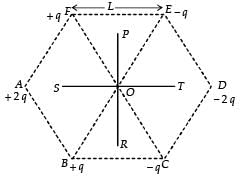
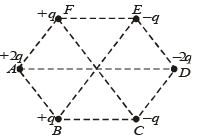
Six point charges are kept at the vertices of a regular hexagon of side L and centre O, as shown in the figure. Given that 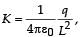 which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct?
which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct?
Two non-conducting solid spheres of radii R and 2R, having uniform volume charge densities ρ1 and ρ2 respectively, touch each other. The net electric field at a distance 2R from the centre of the smaller sphere, along the line joining the centres of the spheres, is zero. The ratio 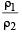
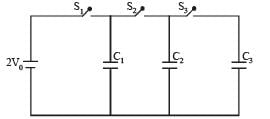
In the circuit shown in the figure, there are two parallel plate capacitors each of capacitance C. The switch S1 is pressed first to fully charge the capacitor C1 and then released. The switch S2 is then pressed to charge the capacitor C2. After some time, S2 is released and then S3 is pressed. After some time
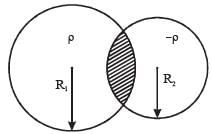
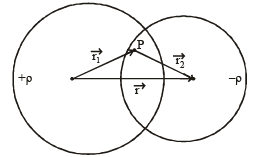
Two non-conducting spheres of radii R1 and R2 and carrying uniform volume charge densities +ρ and –ρ, respectively, are placed such that they partially overlap, as shown in the figure. At all points in the overlapping region
Let E1 (r), E2(r) and E3(r) be the respective electric field at a distance r from a point charge Q, an infinitely long wire with constant linear charge density λ, and an infinite plane with uniform surface charge density σ. If E1(r0) = E2(r0) = E3(r0) at a given distance r0, then
A parallel plate capacitor has a dielectric slab of dielectric constant K between its plates that covers 1/3 of the area of its plates, as shown in the figure. The total capacitance of the capacitor is C while that of the portion with dielectric in between is C1. When the capacitor is charged, the plate area covered by the dielectric gets charge Q1 and the rest of the area gets charge Q2. The electric field in the dielectric is E, and that in the other portion is E2. Choose the correct option/ options, ignoring edge effects.
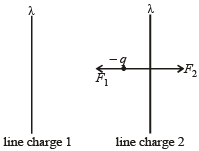
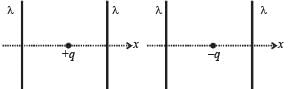
The figures below depict two situations in which two infinitely long static line charges of constant positive line charge density λ are kept parallel to each other. In their resulting electric field, point charges q and –q are kept in equilibrium between them. The point charges are confined to move in the x direction only. If they are given a small displacement about their equilibrium positions, then the correct statement(s) is(are)
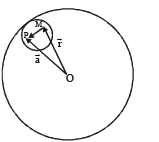
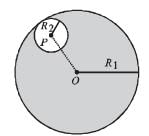
Consider a uniform spherical charge distribution of radius R1 centred at the origin O. In this distribution, a spherical cavity of radius R2, centred at P with distance OP = a = R1 – R2 (see figure) is made. If the electric field inside the cavity at position  then the correct statement(s) is (are)
then the correct statement(s) is (are)
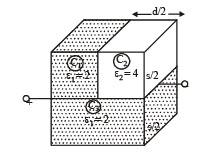
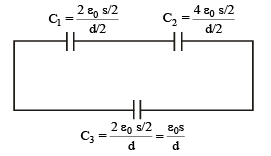
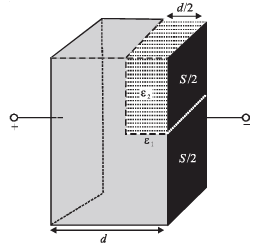
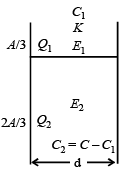
A parallel plate capacitor having plates of area S and plate separation d, has capacitance C1 in air. When two dielectrics of different relative primitivities (ε1 = 2 and ε2 = 4) are introduced between the two plates as shown in the figure, the capacitance becomes C2. The ratio 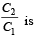


 On resolving these two forces we find that F sin θ cancels out. The resultant force is
On resolving these two forces we find that F sin θ cancels out. The resultant force is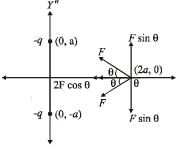
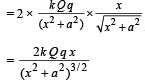

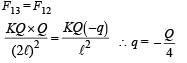
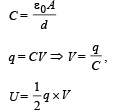
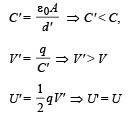
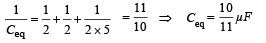
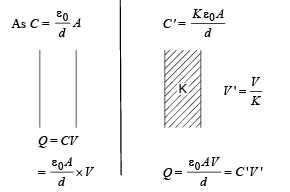
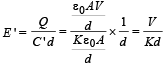
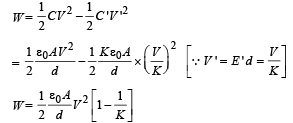
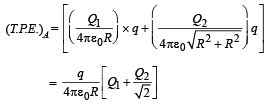
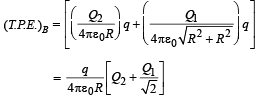
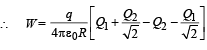
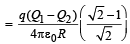
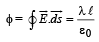
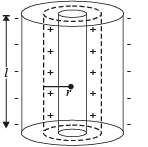
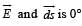 (for curved surface)
(for curved surface)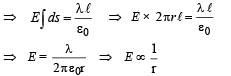
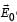 directedfrom positive to negative. In region II, due to orientation of dipoles, there is an electric field
directedfrom positive to negative. In region II, due to orientation of dipoles, there is an electric field 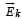 present in opposite
present in opposite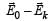 in the direction of
in the direction of 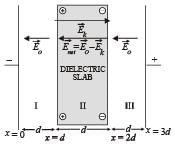
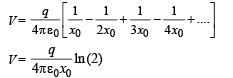
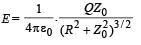
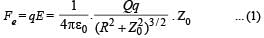
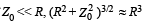
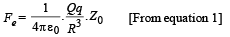
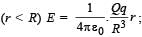 outside the sphere
outside the sphere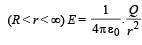
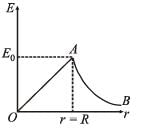
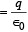
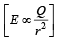
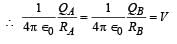
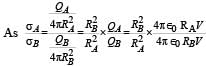
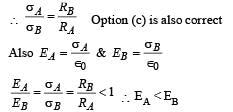
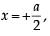
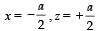 is same due to symmetry.
is same due to symmetry.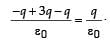
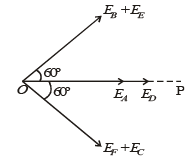
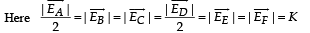
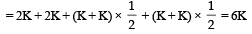
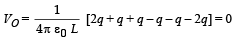
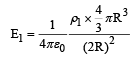
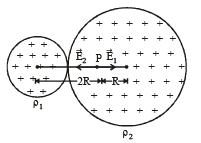
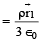
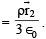 The total electric field,
The total electric field,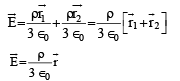
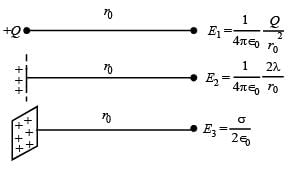
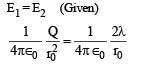
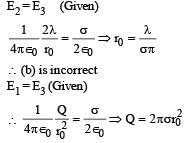
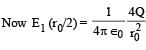
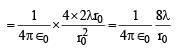
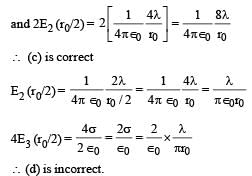
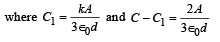
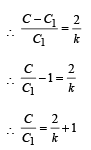
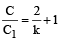
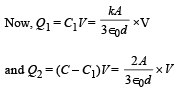
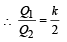 ∴ (c) is incorrect
∴ (c) is incorrect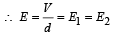 ∴ (a) is a correct option
∴ (a) is a correct option
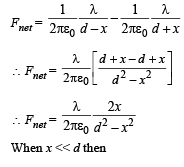
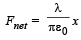 and is directed towards the mean position therefore the charge +q will execute SHM.
and is directed towards the mean position therefore the charge +q will execute SHM.