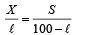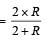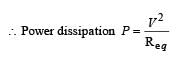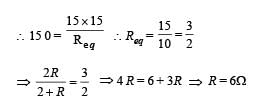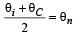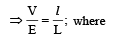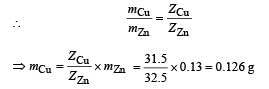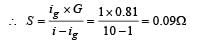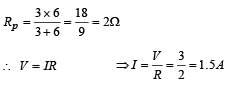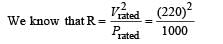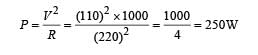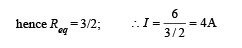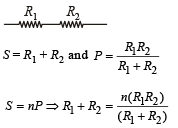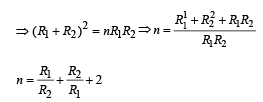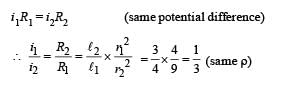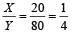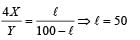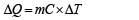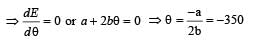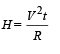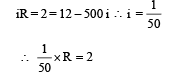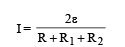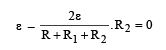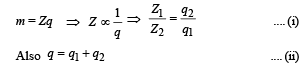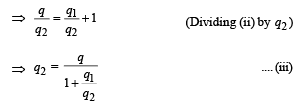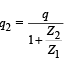Test: JEE Main 35 Year PYQs- Current Electricity - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: JEE Main 35 Year PYQs- Current Electricity
Electrical resistance of certain materials, known as superconductors, changes abruptly from a nonzero value to zero as their temperature is lowered below a critical temperature TC(0). An interesting property of superconductors is that their critical temperature becomes smaller than TC (0) if they are placed in a magnetic field, i.e., the critical temperature TC (B) is a function of the magnetic field strength B. The dependence of TC (B) on B is shown in the figure.

Q.1. In the graphs below, the resistance R of a superconductor is shown as a function of its temperature T for two different magnetic fields B1 (solid line) and B2 (dashed line). If B2 is larger than B1 which of the following graphs shows the correct variation of R with T in these fields?

Electrical resistance of certain materials, known as superconductors, changes abruptly from a nonzero value to zero as their temperature is lowered below a critical temperature TC(0). An interesting property of superconductors is that their critical temperature becomes smaller than TC (0) if they are placed in a magnetic field, i.e., the critical temperature TC (B) is a function of the magnetic field strength B. The dependence of TC (B) on B is shown in the figure.

Q.2.A superconductor has TC (0) = 100 K. When a magnetic field of 7.5 Tesla is applied, its TC decreases to 75 K. For this material one can definitely say that when

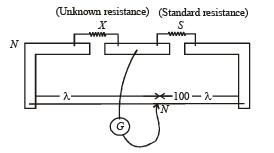
STATEMENT-1 : In a Meter Bridge experiment, null point for an unknown resistance is measured. Now, the unknown resistance is put inside an enclosure maintained at a higher temperature. The null point can be obtained at the same point as before by decreasing the value of the standard resistance.
STATEMENT-2 : Resistance of a metal increases with increase in temperature.
STATEMENT-2 : Resistance of a metal increases with increase in temperature.
If an ammeter is to be used in place of a voltmeter, then we must connect with the ammeter a
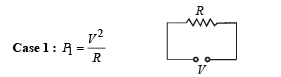
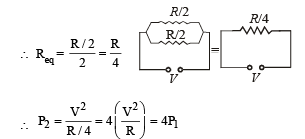
A wire when connected to 220 V mains supply has power dissipation P1. Now the wire is cut into two equal pieces which are connected in parallel to the same supply. Power dissipation in this case is P2. Then P2 : P1 is
If a current is passed through a spring then the spring will
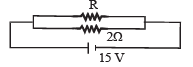
If in the circuit, power dissipation is 150 W, then R is
The mass of product liberated on anode in an electrochemical cell depends on (where t is the time period for which the current is passed).
If θi , is the inversion temperature, θn is the neutral temperature, θc is the temperature of the cold junction, then
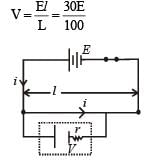
The length of a wire of a potentiometer is 100 cm, and the e. m.f. of its standard cell is E volt. It is employed to measure the e.m.f. of a battery whose internal resistance is 0.5Ω. If the balance point is obtained at l = 30 cm from the positive end, the e.m.f. of the battery is
where i is the current in the potentiometer wire.
The thermo e.m.f. of a thermo -couple is 25 μV / o C at room temperature. A galvanometer of 40 ohm resistance, capable of detecting current as low as 10 -5 A , is connected with the thermo couple. The smallest temperature difference that can be detected by this system is
The negative Zn pole of a Daniell cell, sending a constant current through a circuit, decreases in mass by 0.13g in 30 minutes. If the electeochemical equivalent of Zn and Cu are 32.5 and 31.5 respectively, the increase in the mass of the positive Cu pole in this time is
An ammeter reads upto 1 ampere. Its internal resistance is 0.81ohm. To increase the range to 10 A the value of the required shunt is
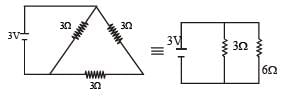
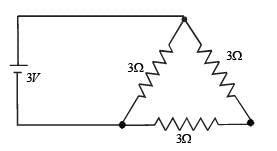
A 3 volt battery with negligible internal resistance is connected in a circuit as shown in the figure. The current I, in the circuit will be
A 220 volt, 1000 watt bulb is connected across a 110 volt mains supply . The power consumed will be
The total current supplied to the circuit by the battery is
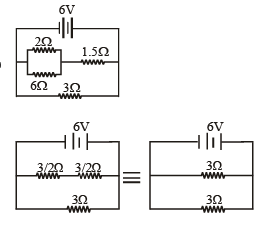
The resistance of the series combination of two resistances is S. when they are joined in parallel the total resistance is P.
If S = nP then the Minimum possible value of n is
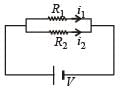
An electric current is passed through a circuit containing two wires of the same material, connected in parallel. If the lengths and radii arein the ratio of 4/3 and 2/3, then the ratio of the current passing through the wires will be
In a meter bridge experiment null point is obtained at 20 cm. from one end of the wire when resistance X is balanced against another resistance Y. If X < Y, then where will be the new position of the null point from the same end, if one decides to balance a resistance of 4 X against Y
The termistors are usually made of
Time taken by a 836 W heater to heat one litre of water from 10°C to 40°C is
The thermo emf of a thermocouple varies with the temperature q of the hot junction as E = aθ+bθ2 in volts where the ratio a/b is 700°C. If the cold junction is kept at 0°C, then the neutral temperature is
The electrochemical equivalent of a metal is 3.35109-7 kg per Coulomb. The mass of the metal liberated at the cathode when a 3A current is passed for 2 seconds will be
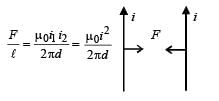
Two thin, long, parallel wires, separated by a distance ‘d’ carry a current of ‘i’ A in the same direction. They will
A heater coil is cut into two equal parts and only one part is now used in the heater. The heat generated will now be
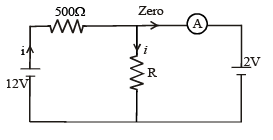
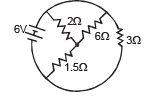
In the circuit , the galvanometer G shows zero deflection. If the batteries A and B have negligible internal resistance, the value of the resistor R will be -
A moving coil galvanometer has 150 equal divisions. Its current sensitivity is 10-divisions per milliampere and voltage sensitivity is 2 divisions per millivolt. In order that each division reads 1 volt, the resistance in ohms needed to be connected in series with the coil will be -
Two sources of equal emf are connected to an external resistance R. The internal resistance of the two sources are R1and R2 (R1 > R1). If the potential difference across the source having internal resistance R2 is zero, then
Two voltameters, one of copper and another of silver, are joined in parallel. When a total charge q flows through the voltameters, equal amount of metals are deposited. If the electrochemical equivalents of copper and silver are Z1 and Z2 respectively the charge which flows through the silver voltameter is
In a potentiometer experiment the balancing with a cell is at length 240 cm. On shunting the cell with a resistance of 2W, the balancing length becomes 120 cm. The internal resistance of the cell is