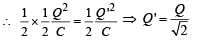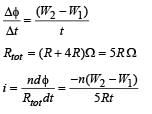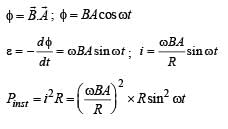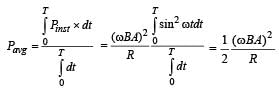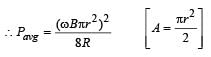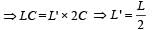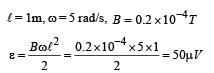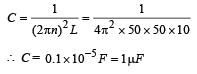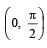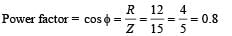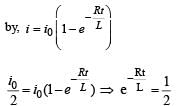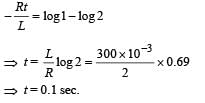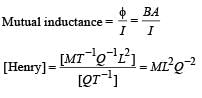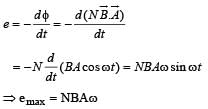Test: JEE Main 35 Year PYQs- Electromagnetic Induction & Alternating Current - JEE MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: JEE Main 35 Year PYQs- Electromagnetic Induction & Alternating Current
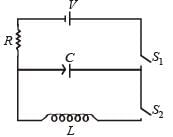
In the given circuit the capacitor (C) may be charged through resistance R by a battery V by closing switch S1. Also when S1 is opened and S2 is closed the capacitor is connected in series with inductor (L).
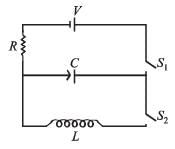
Q. At the start, the capacitor was uncharged. When switch S1 is closed and S2 is kept open, the time constant of this circuit is τ. Which of the following is correct

In the given circuit the capacitor (C) may be charged through resistance R by a battery V by closing switch S1. Also when S1 is opened and S2 is closed the capacitor is connected in series with inductor (L).

Q. When the capacitor gets charged completely, S1 is opened and S2 is closed. Then,

In the given circuit the capacitor (C) may be charged through resistance R by a battery V by closing switch S1. Also when S1 is opened and S2 is closed the capacitor is connected in series with inductor (L).

Q. Given that the total charge stored in the LC circuit is Q0, for t > 0, the charge on the capacitor is

A thermal power plant produces electric power of 600 kW at 4000 V, which is to be transported to a place 20 km away from the power plant for consumers' usage. It can be transported either directly with a cable of large current carrying capacity or by using a combination of step-up and step-down transformers at the two ends. The drawback of the direct transmission is the large energy dissipation. In the method using transformers, the dissipation is much smaller. In this method , a step-up transformer is used at the plant side so that the current is reduced to a smaller value. At the consumers' end, a step-down transformer is used to supply power to the consumers at the specified lower voltage. It is reasonable to assume that the power cable is purely resistive and the transformers are ideal with power factor unity. All the currents and voltages mentioned are rms values.
Q. If the direct transmission method with a cable of resistance 0.4 Ω km–1 is used, the power dissipation| (in %) during transmission is
A thermal power plant produces electric power of 600 kW at 4000 V, which is to be transported to a place 20 km away from the power plant for consumers' usage. It can be transported either directly with a cable of large current carrying capacity or by using a combination of step-up and step-down transformers at the two ends. The drawback of the direct transmission is the large energy dissipation. In the method using transformers, the dissipation is much smaller. In this method , a step-up transformer is used at the plant side so that the current is reduced to a smaller value. At the consumers' end, a step-down transformer is used to supply power to the consumers at the specified lower voltage. It is reasonable to assume that the power cable is purely resistive and the transformers are ideal with power factor unity. All the currents and voltages mentioned are rms values.
Q. In the method using the transformers, assume that the ratio of the number of turns in the primary to that in the secondary in the step-up transformer is 1 : 10. If the power to the consumers has to be supplied at 200 V, the ratio of the number of turns in the primary to that in the secondary in the stepdown transformer is
A point charge Q is moving in a circular orbit of radius R in the x-y plane with an angular velocity w. This can be considered as equivalent to a loop carrying a steady current 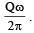 A uniform magnetic field along the positive z-axis is now switched on, which increases at a constant rate from 0 to B in one second. Assume that the radius of the orbit remains constant. The application of the magnetic field induces an emf in the orbit. The induced emf is defined as the work done by an induced electric field in moving a unit positive charge around a closed loop. It is known that, for an orbiting charge, the magnetic dipole moment is proportional to the angular momentum with a proportionality constant γ.
A uniform magnetic field along the positive z-axis is now switched on, which increases at a constant rate from 0 to B in one second. Assume that the radius of the orbit remains constant. The application of the magnetic field induces an emf in the orbit. The induced emf is defined as the work done by an induced electric field in moving a unit positive charge around a closed loop. It is known that, for an orbiting charge, the magnetic dipole moment is proportional to the angular momentum with a proportionality constant γ.
Q. The magnitude of the induced electric field in the orbit at any instant of time during the time interval of the magnetic field change is
A point charge Q is moving in a circular orbit of radius R in the x-y plane with an angular velocity w. This can be considered as equivalent to a loop carrying a steady current 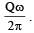 A uniform magnetic field along the positive z-axis is now switched on, which increases at a constant rate from 0 to B in one second. Assume that the radius of the orbit remains constant. The application of the magnetic field induces an emf in the orbit. The induced emf is defined as the work done by an induced electric field in moving a unit positive charge around a closed loop. It is known that, for an orbiting charge, the magnetic dipole moment is proportional to the angular momentum with a proportionality constant γ.
A uniform magnetic field along the positive z-axis is now switched on, which increases at a constant rate from 0 to B in one second. Assume that the radius of the orbit remains constant. The application of the magnetic field induces an emf in the orbit. The induced emf is defined as the work done by an induced electric field in moving a unit positive charge around a closed loop. It is known that, for an orbiting charge, the magnetic dipole moment is proportional to the angular momentum with a proportionality constant γ.
Q. The change in the magnetic dipole moment associated with the orbit, at the end of the time interval of the magnetic field change, is
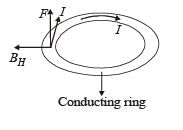
Statement-1 : A vertical iron rod has coil of wire wound over it at the bottom end. An alternating current flows in the coil. The rod goes through a conducting ring as shown in the figure. The ring can float at a certain height above the coil.
Statement-2 : In the above situation, a current is induced in the ring which interacts with the horizontal component of the magnetic field to produce an average force in the upward direction.
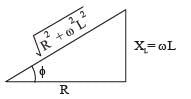
The power factor of an AC circuit having resistance (R) and inductance (L) connected in series and an angular velocity ω is
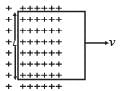
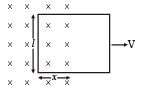
A conducting square loop of side L and resistance R moves in its plane with a uniform velocity v perpendicular to one of its sides. A magnetic induction B constant in time and space, pointing perpendicular and into the plane at the loop exists everywhere with half the loop outside the field, as shown in figure. The induced emf is
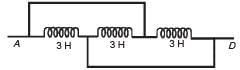
The inductance between A and D is
In a transformer, number of turns in the primary coil are 140 and that in the secondary coil are 280. If current in primary coil is 4 A, then that in the secondary coil is
Two coils are placed close to each other. The mutual inductance of the pair of coils depends upon
When the current changes from +2 A to -2A in 0.05 second, an e.m.f. of 8 V is induced in a coil. The coefficient of self -induction of the coil is
In an oscillating LC circuit the maximum charge on the capacitor is Q. The charge on the capacitor when the energy is stored equally between the electric and magnetic field is
The core of any transformer is laminated so as to
Alternating current can not be measured by D.C. ammeter because
In an LCR series a.c. circuit, the voltage across each of the components, L, C and R is 50V. The voltage across the LC combination will be
A coil having n turns and resistance RΩ is connected with a galvanometer of resistance 4RΩ. This combination is moved in time t seconds from a magnetic field W1 weber to W2 weber. The induced current in the circuit is
In a uniform magnetic field of induction B a wire in the form of a semicircle of radius r rotates about the diameter of the circle with an angular frequency ω. The axis of rotation is perpendicular to the field. If the total resistance of the circuit is R, the mean power generated per period of rotation is
In a LCR circuit capacitance is changed from C to 2 C. For the resonant frequency to remain unchanged, the inductance should be changed from L to
A metal conductor of length 1 m rotates vertically about one of its ends at angular velocity 5 radians per second. If the horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field is 0.2×10–4T, then the e.m.f. developed between the two ends of the conductor is
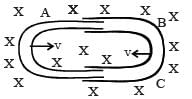
One conducting U tube can slide inside another as shown in figure, maintaining electrical contacts between the tubes.
The magnetic field B is perpendicular to the plane of the figure . If each tube moves towards the other at a constant speed v, then the emf induced in the circuit in terms of B, l and v where l is the width of each tube, will be
The self inductance of the motor of an electric fan is 10 H. In order to impart maximum power at 50 Hz, it should be connected to a capacitance of
The phase difference between the alternating current and emf is π/2. Which of the following cannot be the constituent of the circuit?
A circuit has a resistance of 12 ohm and an impedance of 15 ohm. The power factor of the circuit will be
A coil of inductance 300 mH and resistance 2 W is connected to a source of voltage 2 Ω The current reaches half of its steady state value in
Which of the following units denotes the dimension 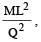 where Q denotes the electric charge?
where Q denotes the electric charge?
In a series resonant LCR circuit, the voltage across R is 100 volts and R = 1 kΩ with C = 2μF. The resonant frequency w is 200 rad/s. At resonance the voltage across L is
In an AC generator, a coil with N turns, all of the same area A and total resistance R, rotates with frequency ω in a magnetic field B. The maximum value of emf generated in the coil is


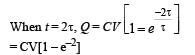
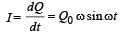
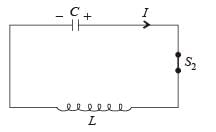
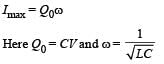
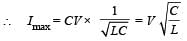

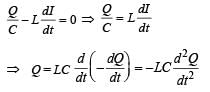
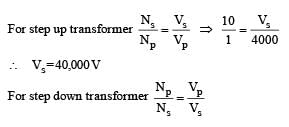
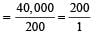
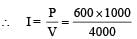
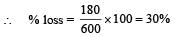
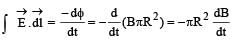 = -πR2B
= -πR2B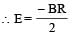
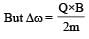 ...(2)
...(2)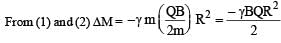

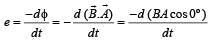
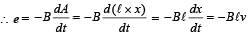
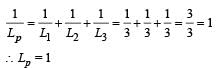
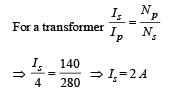
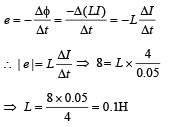
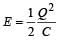
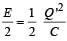 where Q ' is the charge on one plate of the capacitor
where Q ' is the charge on one plate of the capacitor