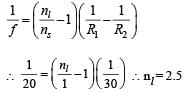Test: MCQs (One or More Correct Option): Ray & Wave Optics | JEE Advanced - ENGAA MCQ
25 Questions MCQ Test - Test: MCQs (One or More Correct Option): Ray & Wave Optics | JEE Advanced
In the Young’ s double slit experiment, the interference pattern is found to have an intensity ratio between the bright and dark fringes as 9. This implies that
A convex lens of focal length 40 cm is in contact with a concave lens of focal length 25 cm . The power of the combination is
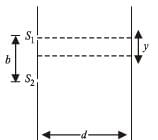
White light is used to illuminate the two slits in a Young’s double slit experiment. The separation between the slits is b and the screen is at a distance d (> b) from the slits. At a point on the screen directly in front of one of the slits, certain wavelengths are missing. Some of these missing wavelengths are
A converging lens is used to form an image on a screen. When the upper half of the lens is covered by an opaque screen
A short linear object of length b lies along the axis of a concave mirror of focal length f at a distanee u from the pole of the mirror. The size of the image is approximately equal to
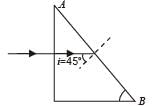
A beam of light consisting of red, green and blue colours is incident on a right angled prism, fig. The refractive indices of the material of the prism for the above red, green and blue wavelengths are 1.39, 1.44 and 1.47 respectively. The prism will
An astronomical telescope has an angular magnification of magnitude 5 for distant objects. The separation between the objective and the eyepiece is 36 cm and the final image is formed at infinity. The focal length f0 of the objective and the focal length f0 of the eyepiece are
A thin prism P1 with angle 4° and made from glass of refractive index 1.54 is combined with another thin prism P2 made from glass of refractive index 1.72 to produce dispersion without deviation. The angle of the prism P2 is
A planet is observed by an astronomical refracting telescope having an objective of focal length 16 m and an eyepiece of focal length 2 cm.
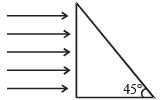
Two thin convex lenses of focal lengths f1 and f2 are separated by a horizontal distance d (where d <f1, d< f2) and their centres are displaced by a vertical separation Δ as shown in the fig.
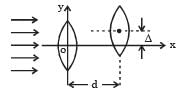
Taking the origin of coordinates O, at the centre of the first lens the x and y coordinates of the focal point of this lens system, for a parallel beam of rays coming from the left, are given by:
Which of the following form(s) a virtual and erect image for all positions of the object ?
A real image of a distant object is formed by a plano-convex lens on its principal axis. Spherical aberration
A ray of light travelling in a transparent medium falls on a surface separating the medium from air at an angle of incidence of 45°. The ray undergoes total internal reflection. If n is the refractive index of the medium with respect to air, select the possible value(s) of n from the following :
A parallel monochromatic beam of light is incident normally on a narrow slit. A diffraction pattern is formed on a screen placed perpendicular to the direction of the incident beam.
At the first minimum of the diffraction pattern, the phase difference between the rays coming from the two edges of the slit is
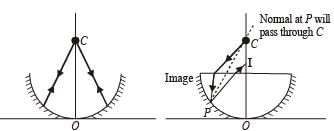
A concave mirror is placed on a horizontal table, with its axis directed vertically upwards. Let O be the pole of the mirror and C its centre of curvature. A point object is placed at C.
It has a real image, also located at C. If the mirror is now filled with water, the image will be.
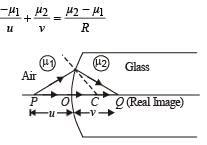
A spherical surface of radius of curvature R separates air (refractive index 1.0) from glass (refractive index 1.5). The centre of curvature is in the glass. A point object P placed in air is found to have a real image Q in the glass. The line PQ cuts the surface at a point O, and PO = OQ. The distance PO is equal to
In a Young’s double slit experiment, the separation between the two slits is d and the wavelength of the light is l. The intensity of light falling on slit 1 is four times the intensity of light falling on slit 2. Choose the correct choice(s).
A student performed the experiment of determination of focal length of a concave mirror by u-v method using an optical bench of length 1.5 meter. The focal length of the mirror used is 24 cm. The maximum error in the location of the image can be 0.2 cm. The 5 sets of (u, v) values recorded by the student (in cm) are :
(42, 56), (48, 48), (60, 40), (66, 33), (78, 39). The data set(s) that cannot come from experiment and is (are) incorrectly recorded, is (are)
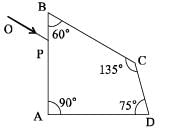
A ray OP of monochromatic light is incident on the face AB of prism ABCD near vertex B at an incident angle of 60° (see figure). If the refractive index of the material of the prism is √3, which of the following is (are) correct?
A transparent thin film of uniform thickness and refractive index n1 = 1.4 is coated on the convex spherical surface of radius R at one end of a long solid glass cylinder of refractive index n2 = 1.5, as shown in the figure. Rays of light parallel to the axis of the cylinder traversing through the film from air to glass get focused at distance f1 from the film, while rays of light traversing from glass to air get focused at distance f2 from the film, Then
A light source, which emits two wavelength λ1 = 400 nm and λ2 = 600 nm, is used in a Young’s double slit experiment. If recorded fringe widths for λ1 and λ2 are β1 and β2 and the number of fringes for them within a distance y on one side of the central maximum are m1 and m2 respectively, then
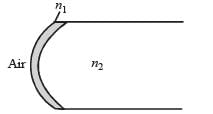
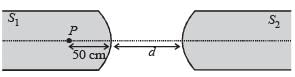
Two identical glass rods S1 and S2 (refractive index = 1.5) have one convex end of radius of curvature 10 cm. They are placed with the curved surfaces at a distance d as shown in the figure, with their axes (shown by the dashed line) aligned.
When a point source of light P is placed inside rod S1 on its axis at a distance of 50 cm from the curved face, the light rays emanating from it are found to be parallel to the axis inside S2. The distance d is
A plano–convex lens is made of a material of refractive index n. When a small object is placed 30 cm away in front of the curved surface of the lens, an image of double the size of the object is produced. Due to reflection from the convex surface of the lens, another faint image is observed at a distance of 10 cm away from the lens. Which of the following statement(s) is(are) true?
A transparent slab of thickness d has a refractive index n(z) that increases with z. Here z is the vertical distance inside the slab, measured from the top. The slab is placed between two media with uniform refractive indices n1 and n2 (> n1), as shown in the figure. A ray of light is incident with angle θi, from medium 1 and emerges in medium 2 with refraction angle θt with a lateral displacement l.
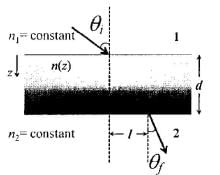
Which of the following statement(s) is(are) true?
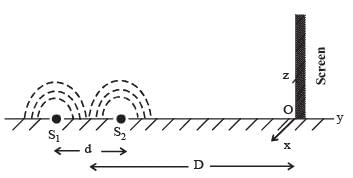
While conducting the Young’s double slit exper iment, a student replaced the two slits with a large opaque plate in the x-y plane containing two small holes that act as two coherent point sources (S1, S2) emitting light of wavelength 600 nm. The student mistakenly placed the screen parallel to the x-z plane (for z > 0) at a distance D = 3 m from the midpoint of S1S2, as shown schematically in the figure. The distance between the sources d = 0.6003 mm. The origin O is at the intersection of the screen and the line joining S1S2.
Which of the following is(are) true of the intensity pattern on the screen?


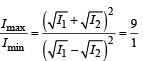
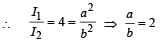
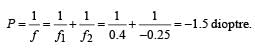

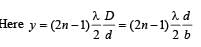
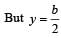
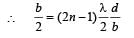
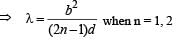
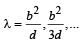
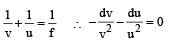
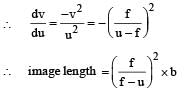
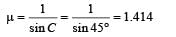
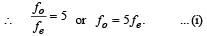
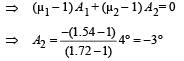
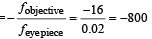
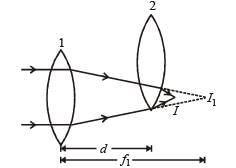 Applying lens formula for lens 2
Applying lens formula for lens 2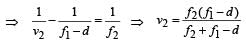 ∴ The horizontal distance of the image I from O is
∴ The horizontal distance of the image I from O is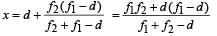
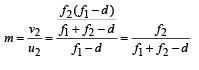
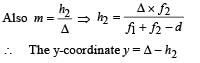
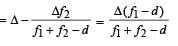
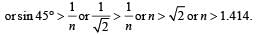
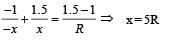
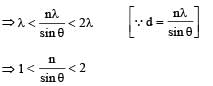
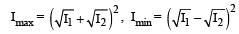
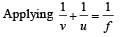
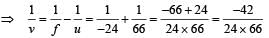
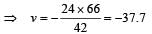
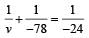
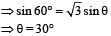
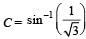 which is less than 45°.
which is less than 45°.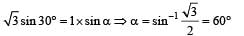
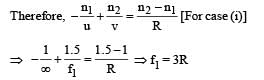 ∴ (a) is a correct option
∴ (a) is a correct option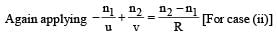
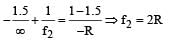
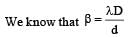
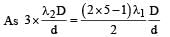
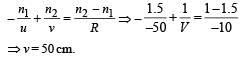
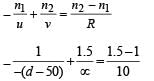
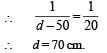
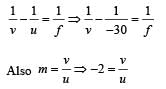
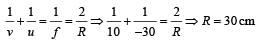 The image formed by convex side is faint erect and virtual.
The image formed by convex side is faint erect and virtual.