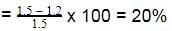Test: Thermochemistry - NEET MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Thermochemistry
How much heat will be required at constant pressure to form 1.28 kg of CaC2 from CaO(s) & C(s) ?
Given :
ΔfH°(CaO, s) = -152 kcal/mol
ΔfH°(CaC2, s) = -14 kcal/mol
ΔfH°(CO, g) = -26 kcal/mol
50.0 mL of 0.10 M HCl is mixed with 50.0 mL of 0.10 M NaOH. The solution temperature rises by 3.0°C Calculate the enthalpy of neutralization per mole of HCl. [take proper assumptions]
The enthalpy of neutralisation of a weak acid in 1 M solution with a strong base is -56.1 kJ mol-1. If the enthalpy of ionization of the acid is 1.5 kJ mol-1 and enthalpy of neutralization of the strong acid with a strong base is -57.3 kJ equiv-1, what is % ionization of the weak acid in molar solution (assume the acid to be monobasic) ?
For the allotropic change represented by the equation C (graphite) → C (diamond), ΔH = 1.9 kJ. If 6 g of diamond and 6 g of graphite are separately burnt to yield CO2, the heat liberated in first case is
If x1, x2 and x3 are enthalpies of H - H, O = O and O - H bonds respectively, and x4 is the enthalpy of vaporisation of water, estimate the standard enthalpy of combustion of hydrogen
NH3(g) + 3Cl2(g) NCl3(g) + 3HCl(g) ; -ΔH1
N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g) ; ΔH2
H2(g) + Cl2(g) 2HCl(g) ; ΔH3
The heat of formation of NCl3 (g) in the terms of ΔH1, ΔH2 and ΔH3 is
The enthalpy of neutralisation of HCl and NaOH is -57 kJ mol-1. The heat evolved at constant pressure (in kJ) when 0.5 mole of H2SO4 react with 0.75 mole of NaOH is equal to
Reaction involving gold have been of particular interest to a chemist. Consider the following reactions.
Au(OH)3 + 4 HCl → HAuCl4 + 3H2O, ΔH = -28 kcal
Au(OH)3 + 4 HBr → HAuBr4 + 3 H2O, ΔH = -36.8 kcal
In an experiment there was an absorption of 0.44 kcal when one mole of HAuBr4 was mixed with 4 moles of HCl. What is the percentage conversion of HAuBr4 into HAuCl4 ?
(i) Cis - 2 - butene → trans - 2 - butene, ΔH1
(ii) Cis - 2 - butene → 1 - butene, ΔH2
(iii) Trans - 2 - butene is more stable than cis - 2 - butene.
(iv) Enthalpy of combustion of 1 - butene, ΔH = -649.8 kcal/mol
(v) 9ΔH1 + 5 ΔH2 = 0
(vi) Enthalpy of combustion of trans 2 - butene, ΔH = -647.0 kcal/mol
Q. The value of ΔH1 & ΔH2 in Kcal/mole are
The reaction CH4(g) + Cl2(g) → CH3Cl(g) + HCl(g) has ΔH = -25 kCal.
From the given data, what is the bond energy of Cl - Cl bond
From the following data at 25°C
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct :
Statement(a) : ΔrH° for the reaction H2O(g) → 2H(g) + O(g) is 925 kJ/mol
Statement(b) : ΔrH° for the reaction OH(g) → H(g) + O(g) is 502 kJ/mol
Statement(c) : Enthalpy of formation of H(g) is-–218 kJ/mol
Statement(d) : Enthalpy of formation of OH(g) is 42 kJ/mol
The standard molar enthalpies for formation of cyclohexane (l) & benzene (l) at 25°C are -156 & + 49 kJ/mol respectively. The standard enthalpy of hydrogenation of cyclohexane (l) at 25° is -119 kJ mol-1. Use these data to estimate the magnitude of the resonance energy of benzene.
For hypothetical reaction -
A(g) + B (g) → C (g) + D (g)
Which of the following statements is correct -
ΔH for CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g) is 176 kJ mol-1 at 1240 K. The ΔU for the change is equal to :
When enthalpy of reactants is higher than product then reaction will be
In the combustion of 4g. of CH4, 2.5 K cal of heat is liberated. The heat of combustion of CH4 is -
Ammonium nitrate can decompose with explosion by the following reaction.
NH4NO3 (s) → N2O (g) + 2H2O ;
ΔH = -37.0 KJ/mol
Calculate the heat produced when 2.50g of NH4NO3 decomposes -
From the following data, the heat of formation of Ca(OH)2(s) at 18°C is ………..kcal:
HA + OH- → H2O + A- + q1 kJ
H+ + OH- → H2O + q2 kJ
The enthalpy of dissociation of HA is
The value of ΔHsol. of BaCl2(s) and BaCl2. 2H2O (s) are – a kJ and b kJ respectively. The value of ΔH Hydration of BaCl2 (s) is-
A solution of 500 ml of 0.2 M KOH and 500 ml of 0.2 M HCl is mixed and stirred; the rise in temperature is T1. The experiment is repeated using 250 ml of each solution, the temperature raised is T2. Which of the following is true -
The net heat change in a chemical reaction is same whether it is brought about in two or more different ways in one or several steps. It is known as -
According to Hess's Law the thermal effect of a reaction depends on -
How many kcal of heat is evolved by the complete neutralisation of one mole sulphuric acid with NaOH -