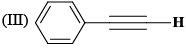Test: Spectroscopy Level - 1 - Chemistry MCQ
30 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Spectroscopy Level - 1
A molecule, AX, has a vibrational energy of 1000 cm–1 and rotational energy of 10 cm–1. Another molecule, BX, has a vibrational energy of 400 cm–1 and rotational energy of 40 cm–1. Which one of the following statements about the coupling of vibrational and rotational motion is true:
The order of carbonyl stretching frequency in the IR spectra of ketone, amide and anhydride is:
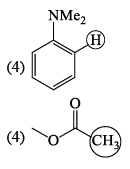
In the IR spectrum, carbonyl absorption band for the following compound appears at:

In the IR spectrum of p-nitrophenyl acetate, the carbonyl absorption band appears at:
A triatomic molecule of the type AB2 shows two IR absorption lines and one IR-Raman line. The structure of the molecule is:
In the IR spectrum, the absorption band due to carbonyl group in phenyl acetate appears at:
In the IR spectrum of p-nitrophenyl, acetate, the carbonyl absorption band appears at:
A compound with molecule formula C4H6O2 shows band at 1170 cm–1 in IR spectrum and peaks at 178, 68, 28 and 22 ppm in 13C NMR spectrum. The correct structure of the compound is:
The compound that exhibits sharp bands at 3300 and 2150 cm–1 in the IR spectrum is:
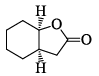
Correctly matched structure and carbonyl stretching frequency set is:
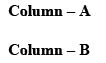
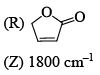
Among the following, the compound that displays an IR band at 2150 cm–1 is:
The compound which shows IR frequencies at both 3314 and 2126 cm–1 is:
For the molecule CBr4, the number of peaks which comprise the cluster for the molecular ion will be which of the following?
The IR stretching frequencies (cm–1) for the compound X are as follows: 3300-3500 (s, br); 3000 (m); 2225 (s); 1680(s). The correct assignment of the absorption bands is:
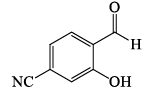
Among the compounds given in the option (a) to (d), the one that exhibits a sharp band at around 3300 cm–1 in the IR spectrum is:
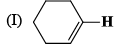
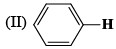
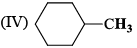
The correct order of IR stretching frequency of the C=C in the following olefins is:
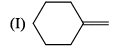
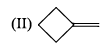
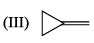
Arrange the chacacteristic timescales of the following set of dynamical spectroscopic techniques in decreasing order of time (longest to shortest); NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance), ESR (Electron Spin Resonance), Fluorescence, Raman and Absorption.
What are the limits of detection of the following common analytical methods used with capillary separations: fluorescence, mass spectrometry, UV-Vis absorbance, and NMR, respectively, in mol:
Of the molecules CH4, CO2, benzene and H2, the ones that will absorb infrared radiation are:
IR stretching frequencies of carbonyl groups in aldehydes and acid chlorides in cm–1 are:
The bond that gives the most intense band in the infrared spectrum for its stretching vibrations is:
An examinations of saturated hydrocarbons containing methyl group show asymmetrical (Vas) and symmetrical (Vs) stretching modes in the region of:
For each set of compounds below, choose the one in which the indicated hydrogen is farthest upfield in a proton NMR spectrum:
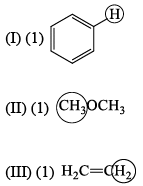
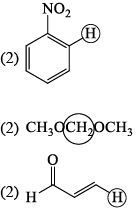
The molecule with the smallest rotational constant (in the microwave spectrum) among the following is:
Which of the following molecules has the lowest vibrational stretching frequency:
A radiation that has an energy of N 50 kJ mol–1 falls in the following region of the electromagnetic spectrum:
The rotational constant (B) of H35Cl, H37Cl and D35Cl follow the order:
The spectroscopic data for an organic compound with molecular formula C10H12O2 are given below. IR band around 1750 cm–1. 1H NMR d 7.3 (m, 5H), 5.85 (q, 1H, J = 7.2 Hz), 2.05 (s, 3H), 1.5 (d, 3H, J = 7.2 Hz) ppm. The compound is:
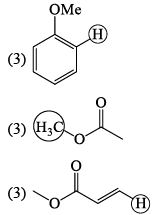
The correct order of the 1H NMR chemical shift values (β) for the indicated hydrogens (in bold) in the following compounds is: