Test: Synthetic Fibres & Plastics- 3 - Class 7 MCQ
20 Questions MCQ Test - Test: Synthetic Fibres & Plastics- 3
Which of the following statements is/are correct?


Pre-weighed pieces of cloth of nylon, cotton, silk and wool of equal measurements are taken and soaked in a beaker filled with water. After a few minutes, the cloth pieces were taken out of the beaker and weighed again. Which of the following options places them in the correct order of their final weights?
Why is it not advisable to wear clothes made up of synthetic fibres in hot and humid weather?
A brief information about three different plastics is given below :

Which of the following statements about plastics are true?

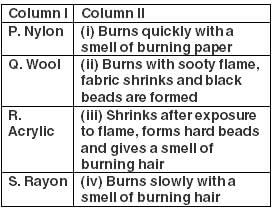
Match column I with column II and select the correct answer from the codes given below.
Which of the following materials is the best for making garments and jackets that can be used in wet or damp environment?
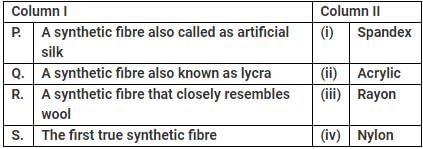
Match column I with column II and mark the correct option from the codes given below.
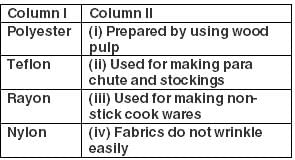
Choose the correct option for the given statements.

Read the given statements and mark the appropriate answer.
Statement 1: Polyester is synthesised from petrochemicals by linking ester units.
Statement 2: Polyester is a natural fibre
Which of the following is not a characteristic of plastics?
See the figure given below and select the correct statements regarding polymers.
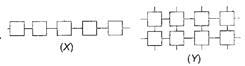
1. Figure (X) shows structure of a monomer while figure (Y) shows structure of a polymer.
2. Small boxes in the structure represent monomers which are joined to give a polymer.
3. Figure (X) shows structure of a linear polymer while (Y) shows structure of a cross-linked polymer.
Choose the option containing correct words word to replace P,Q,R and S:
Fibres are materials which are usually thin and have thread-like structure. They are generally classified as P and Q, on the basis of their origin. Natural fibres may be plant fibres like R or animal fibres like S.
Sneha has classified a few materials as shown in the table.
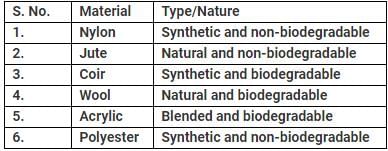
The materials which are classified incorrectly are
Anisha prepared a flowchart to show classification of fibres and plastics. She left few columns blank. Fill in the blanks by choosing the option with correct words.

A few polymers are grouped together on the basis of some common property as follows: Group I: Rayon, acrylic, nylon, jute Group II: PVC, melamine, teflon Group III: Polycot, terrywool, acrylic
Choose the odd one out in group I, II and III.
Read the given passage and fill in the blanks by choosing an appropriate option. Cellulose is a naturally occurring fibre. The walls of i are made of cellulose. It is used in making a synthetic fibre ii which resembles the most expensive natural fibre iii in appearance hence, it is also called iv .
Read the following statements carefully.
P. I am extensively used in the healthcare industry but my one disadvantage is that I am non-biodegradable.
Q. I am very familiar form of polyester and used for making bottles, utensils, films, wires, etc.
R. I am artificial silk and mixed with wool to make carpets. P, Q and R are respectively
Match column I with column II and choose the correct option from the codes given below.